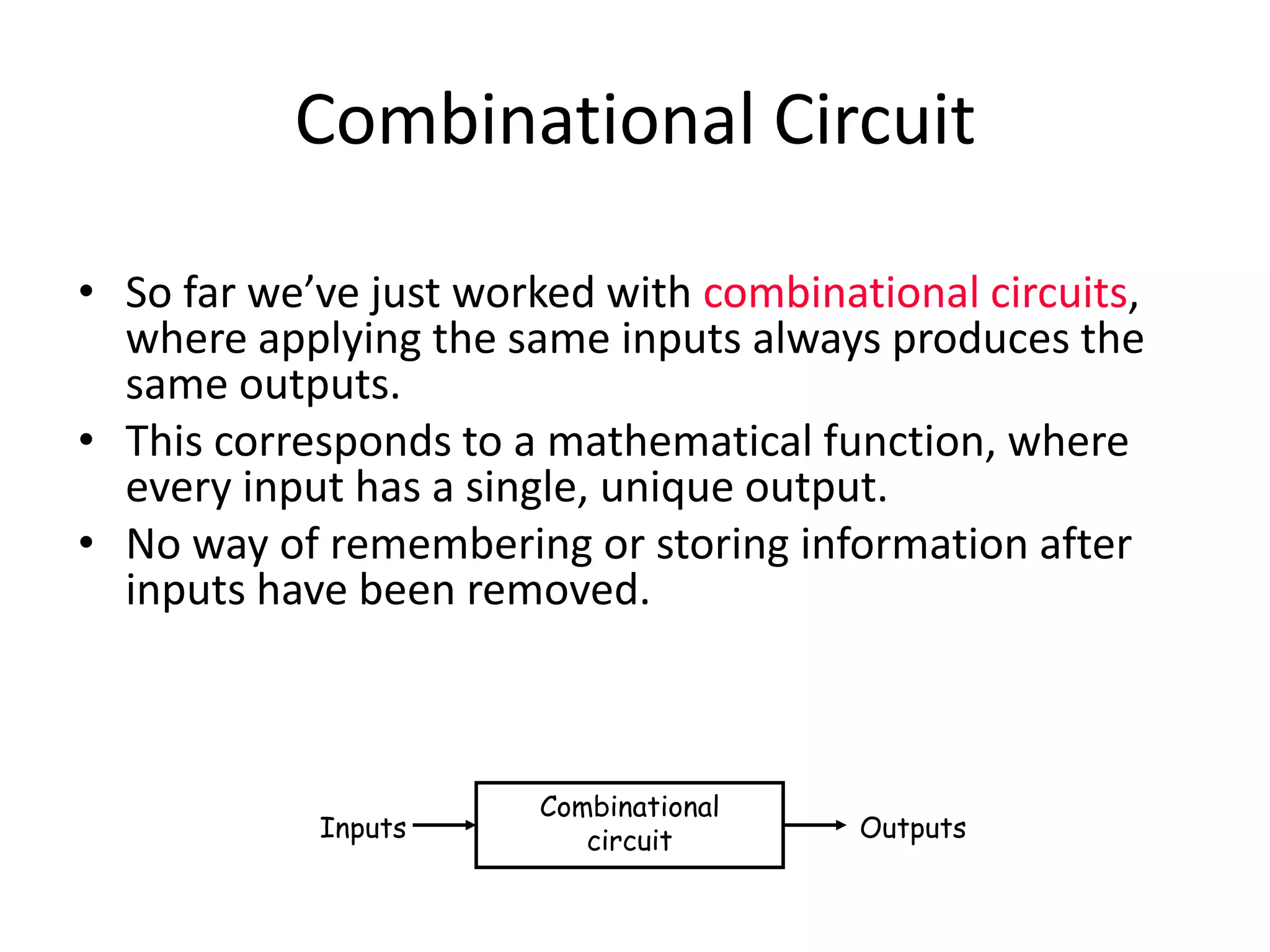
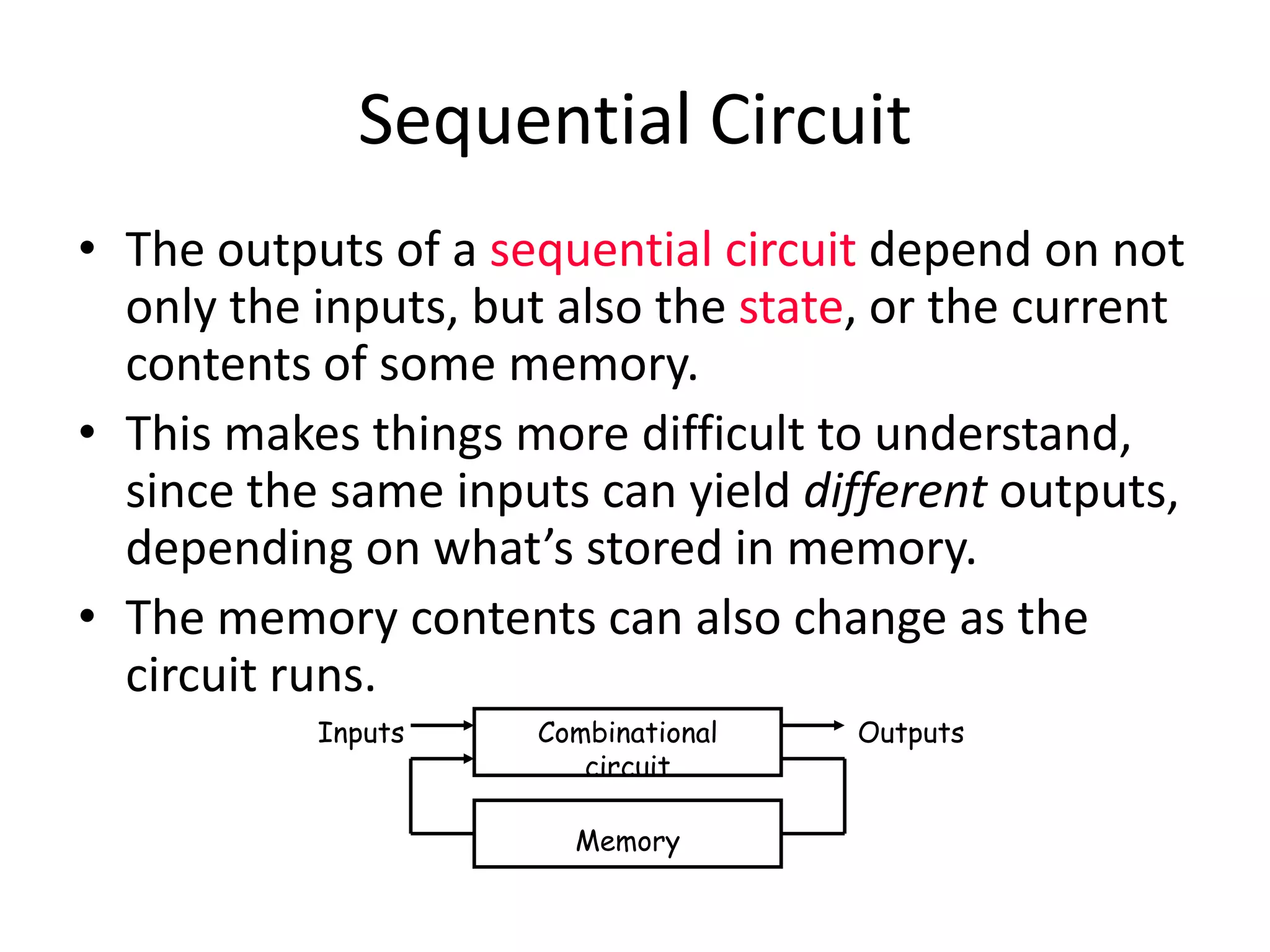
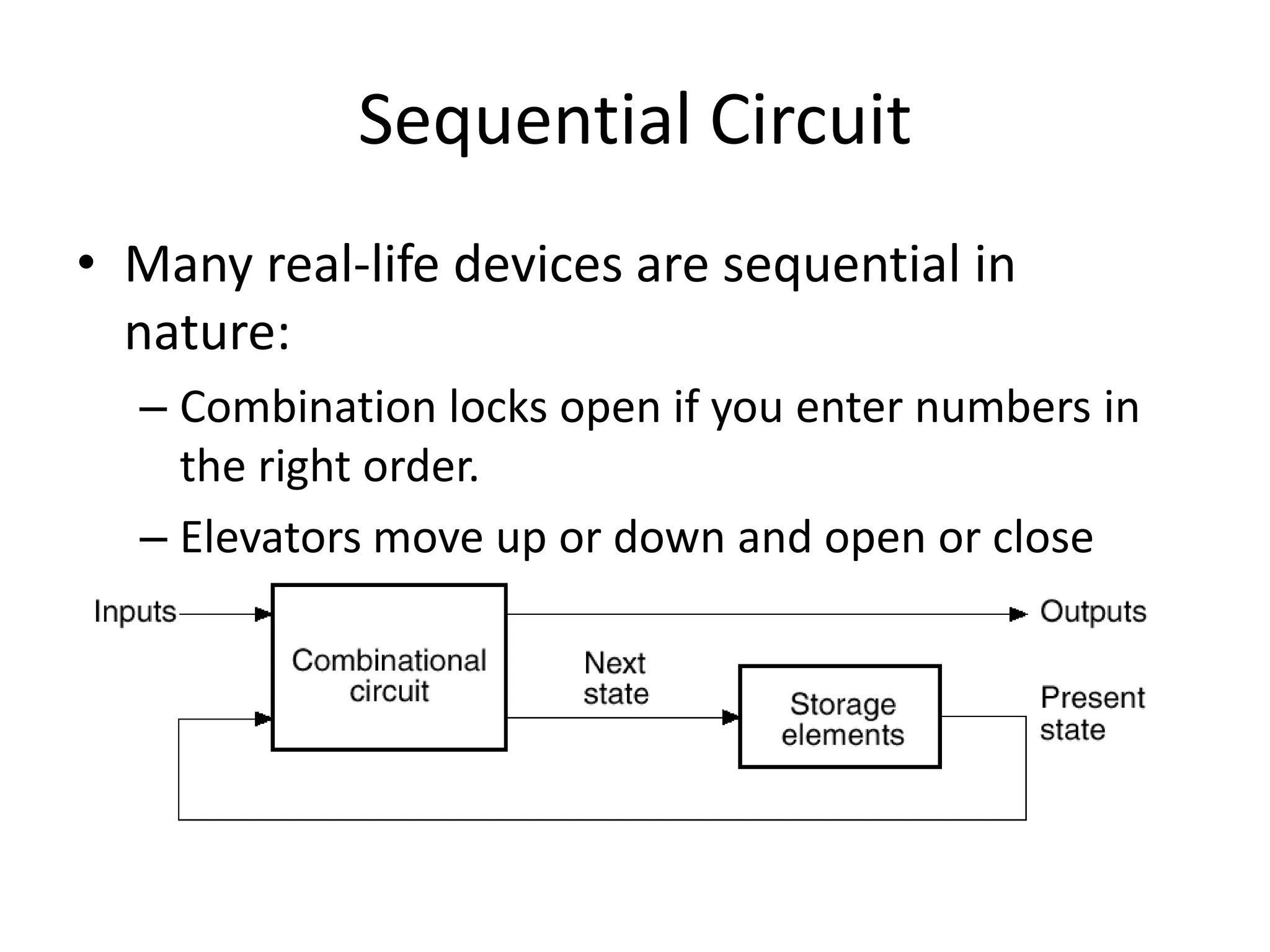
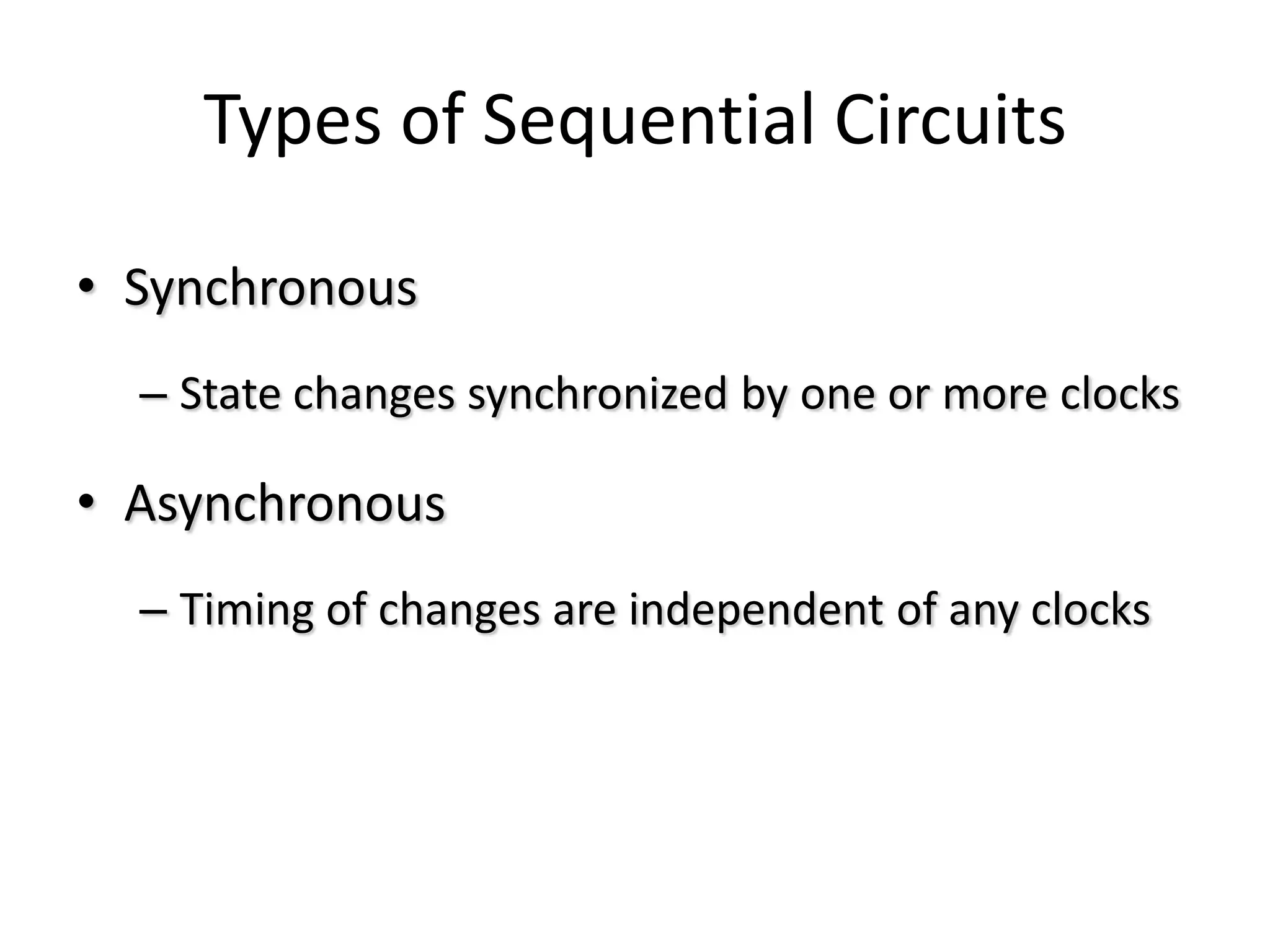
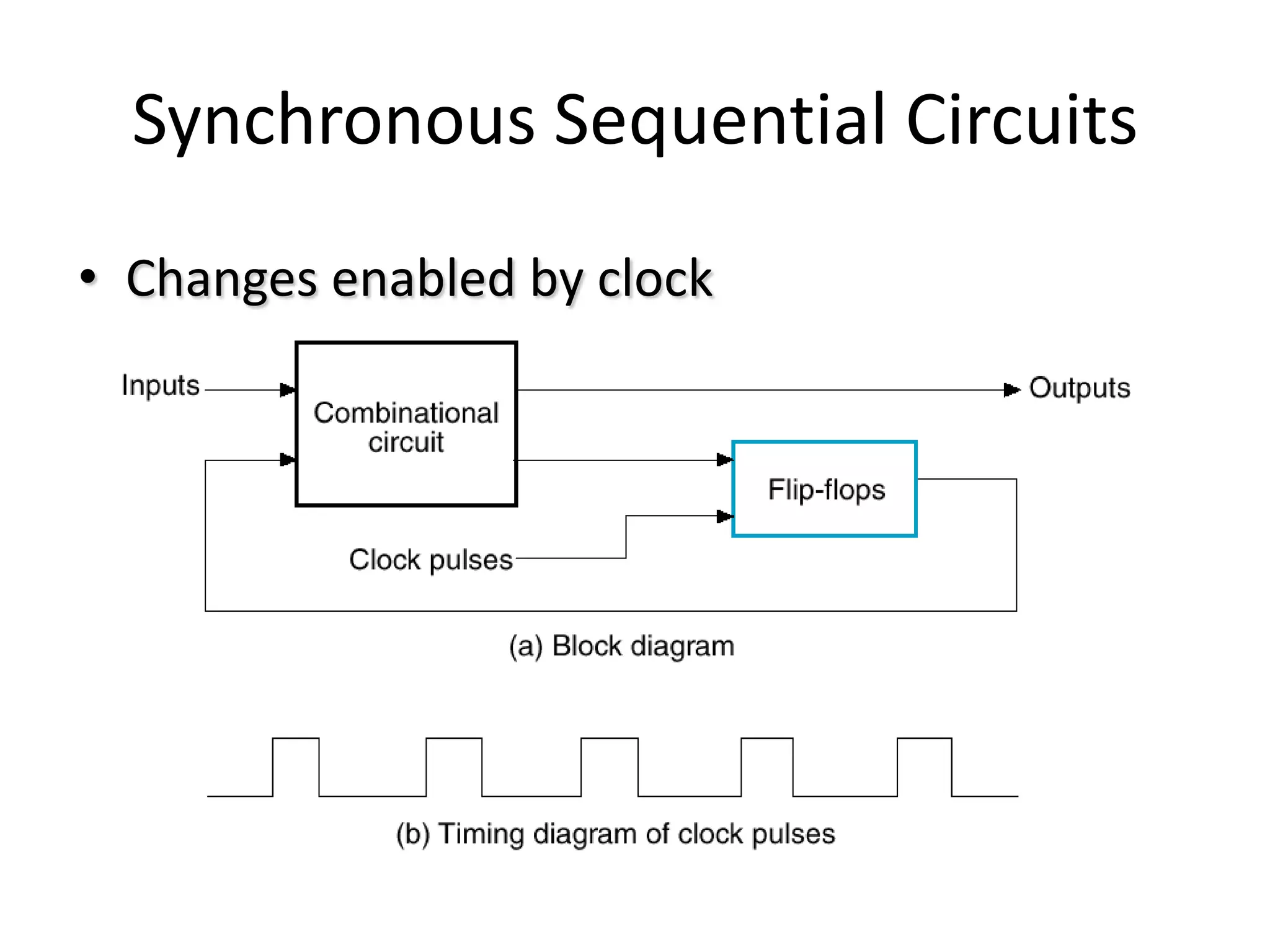
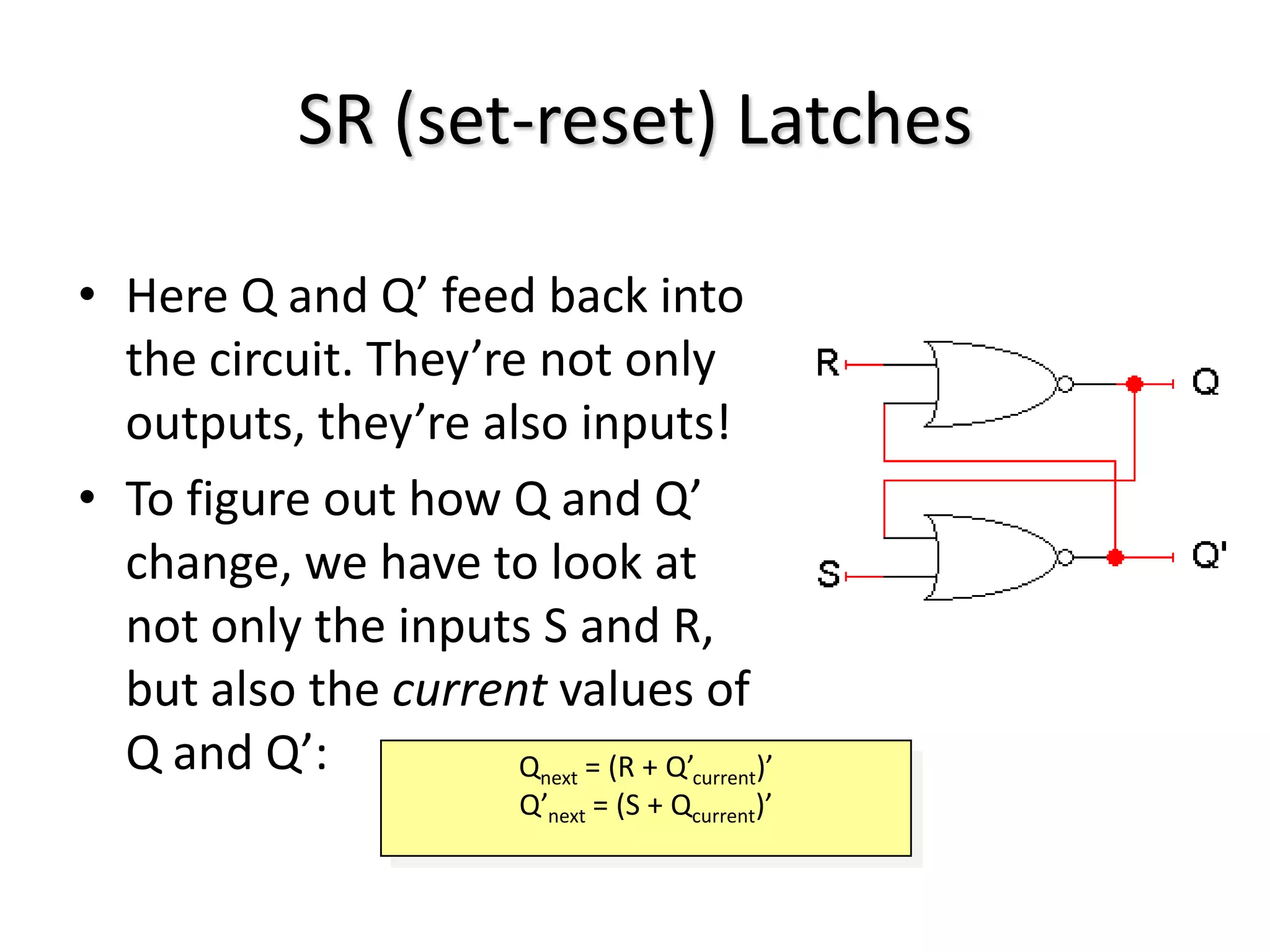
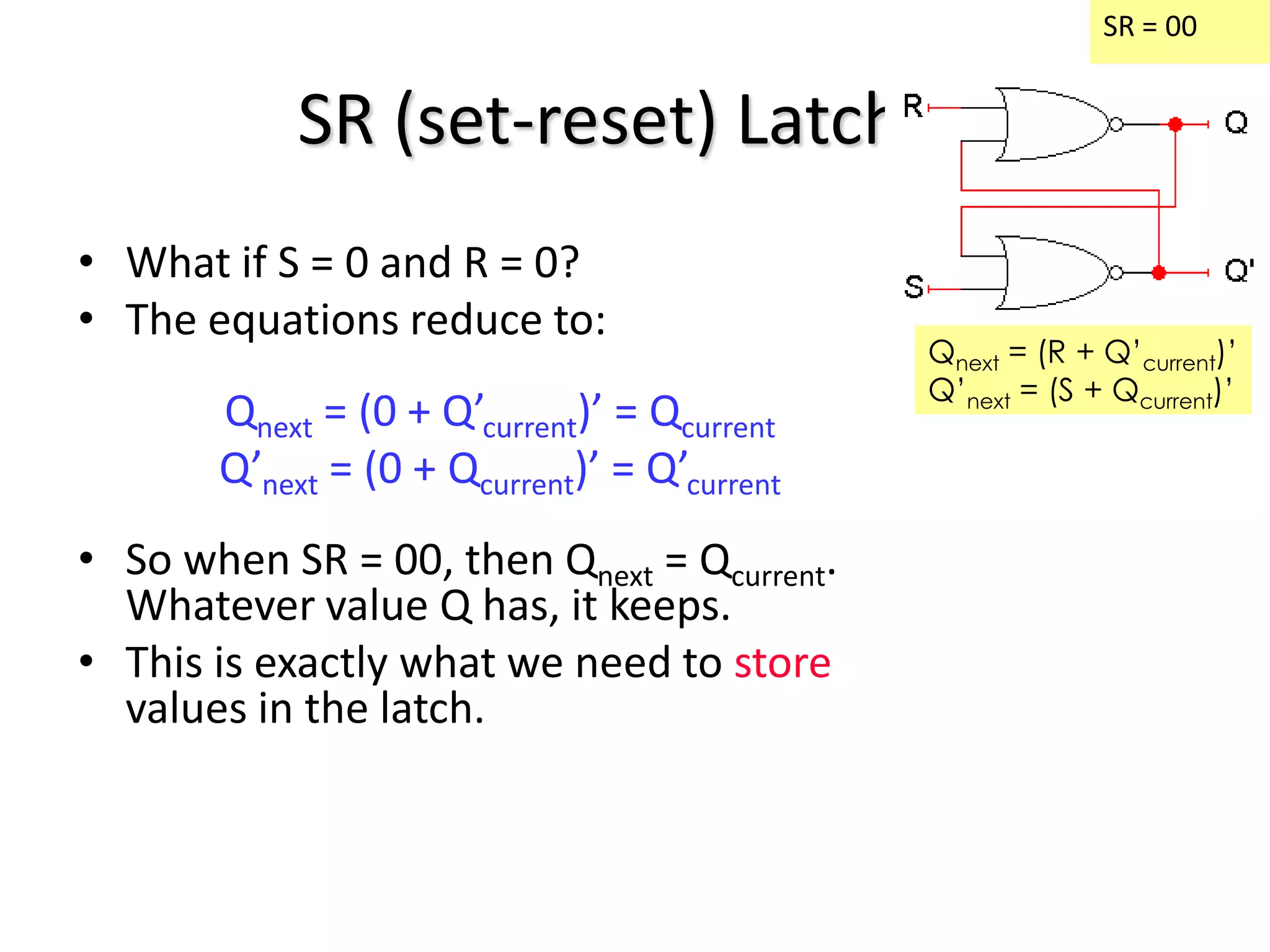
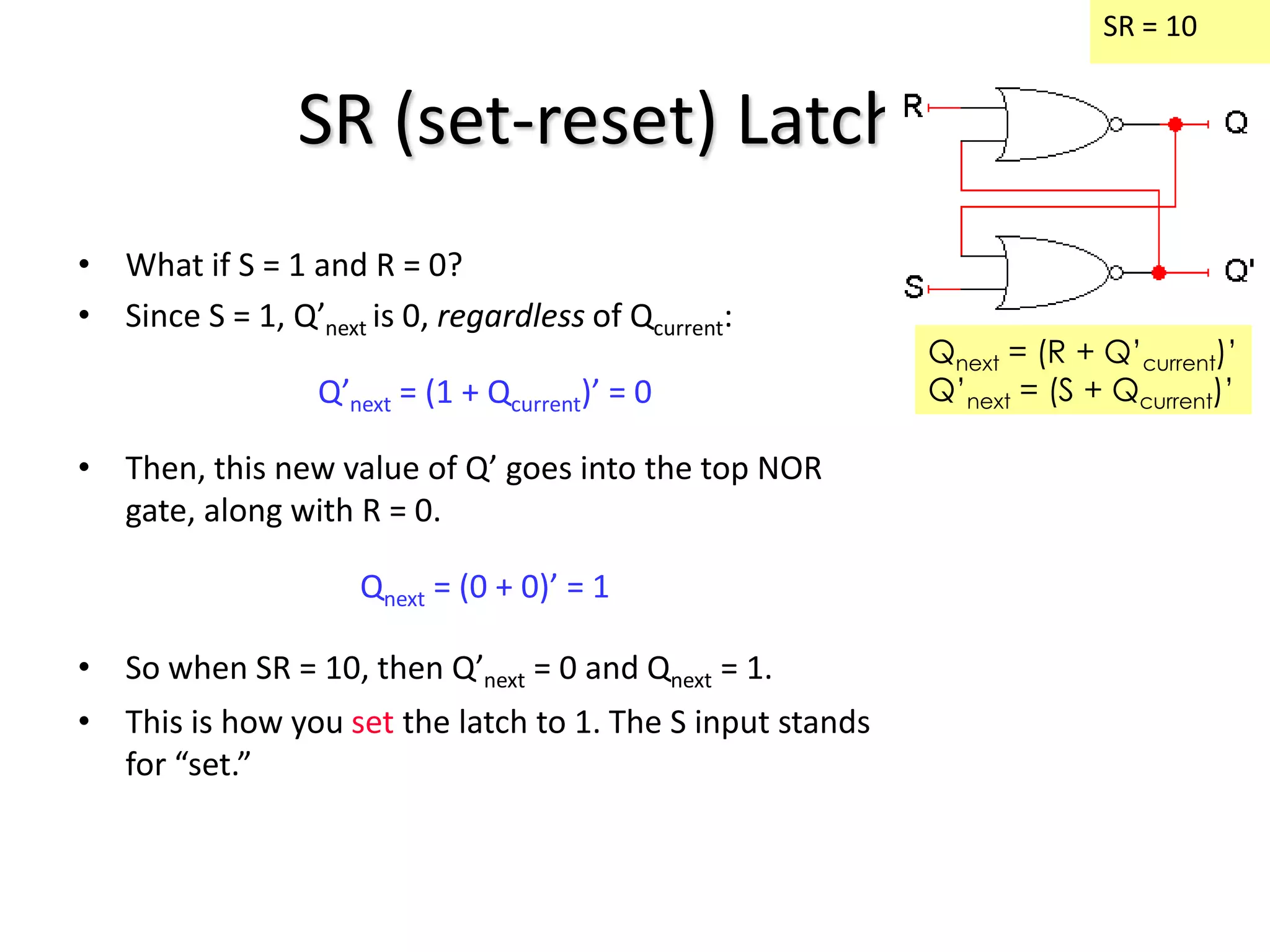
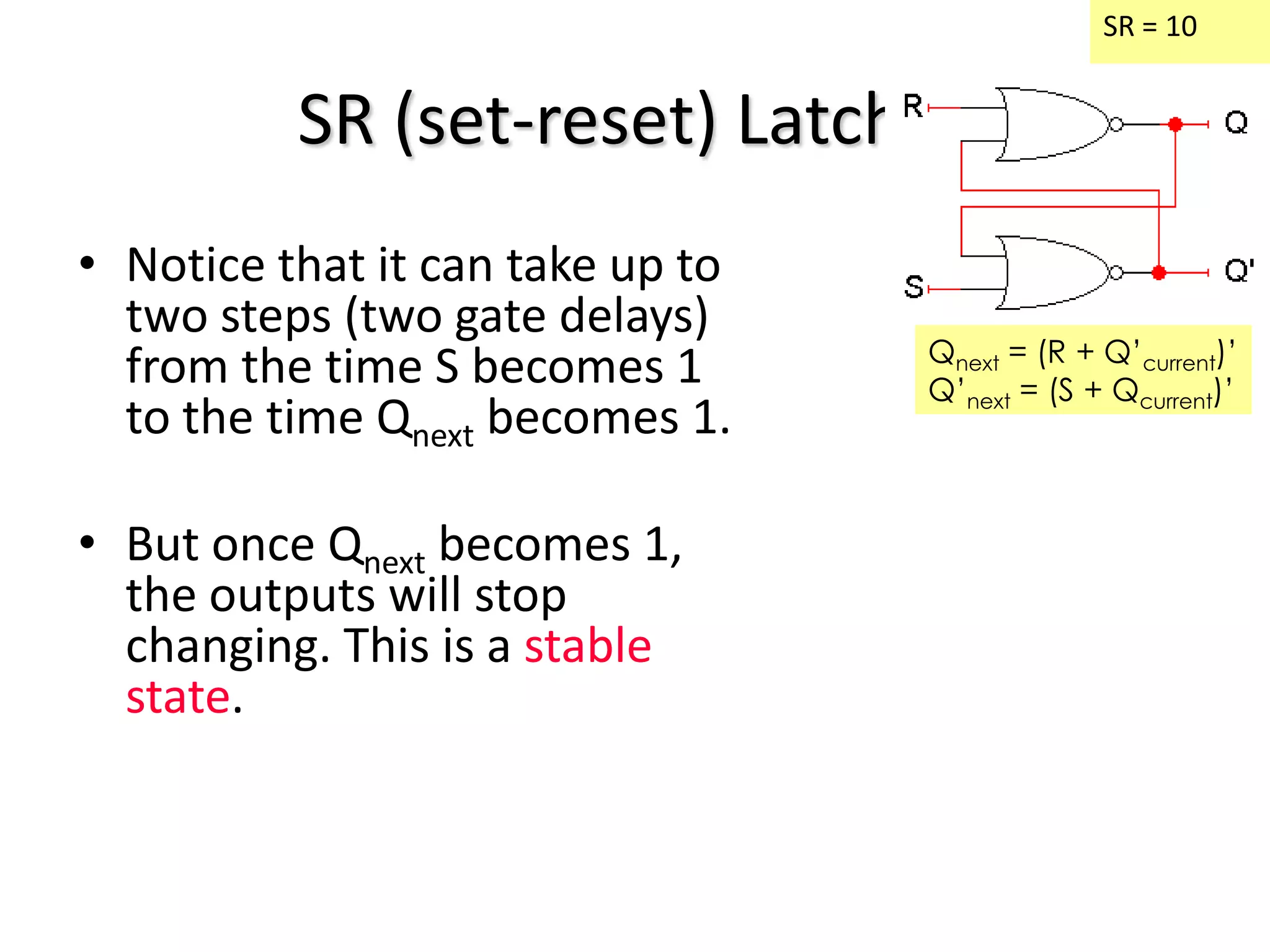
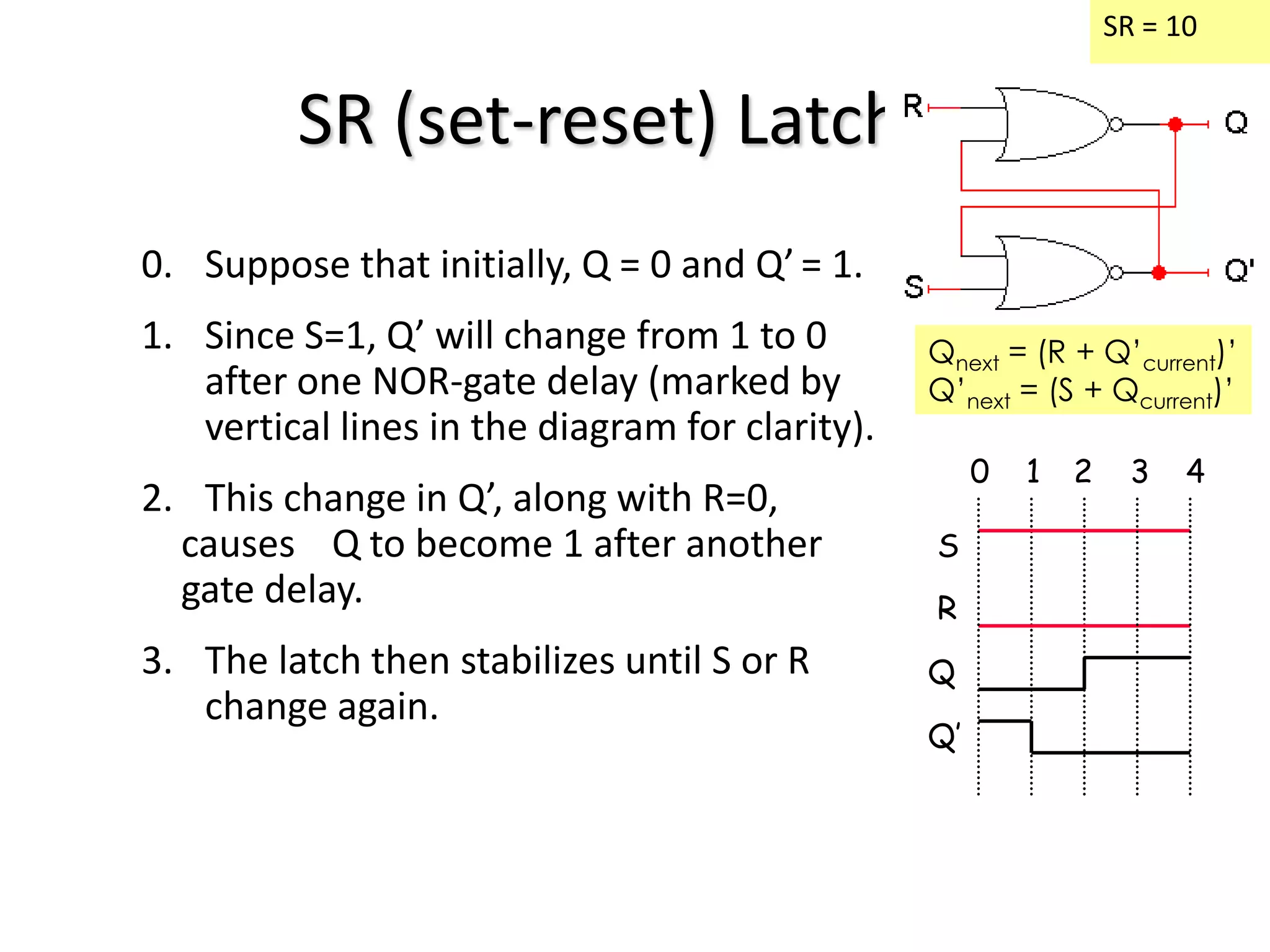
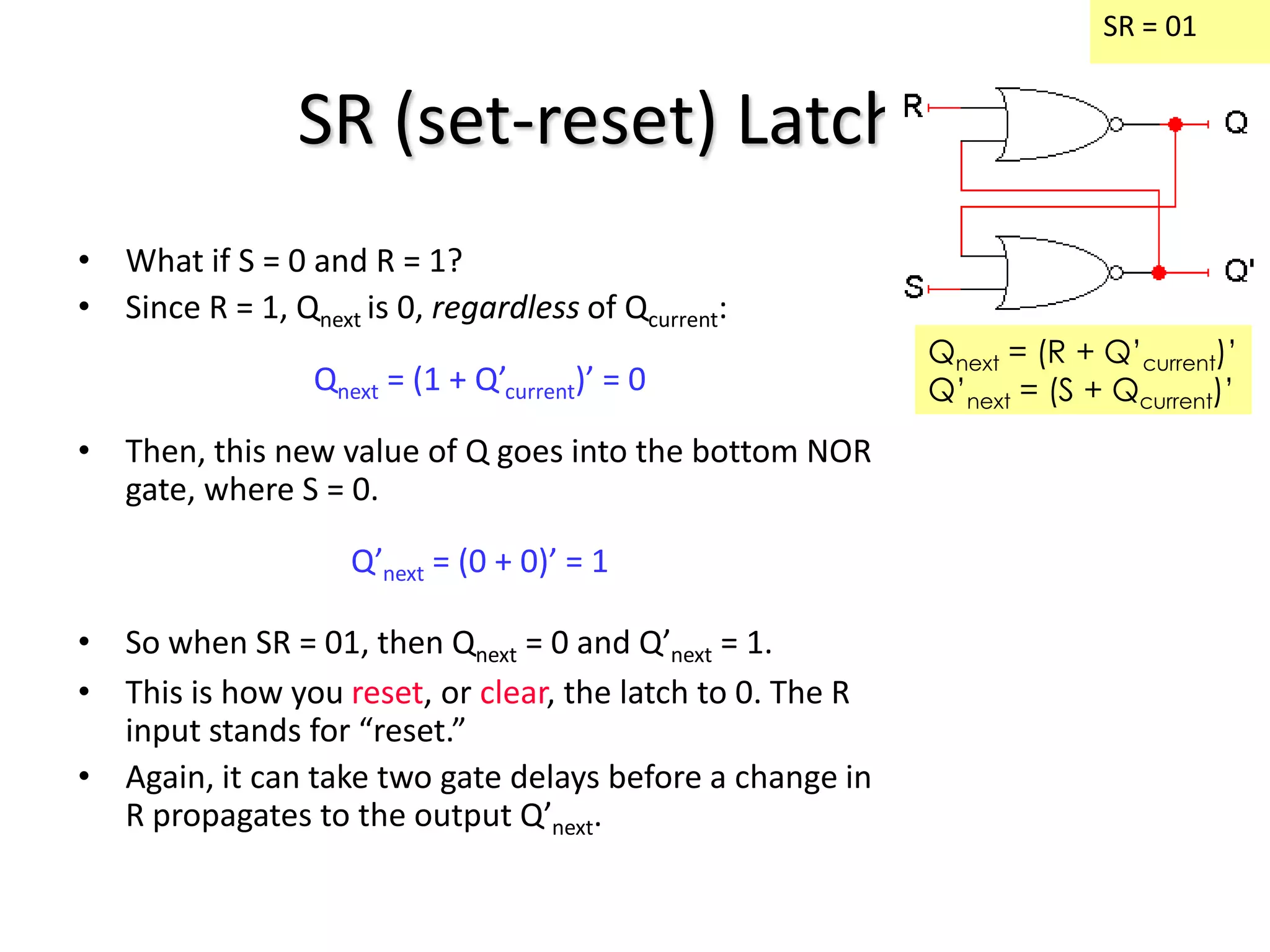
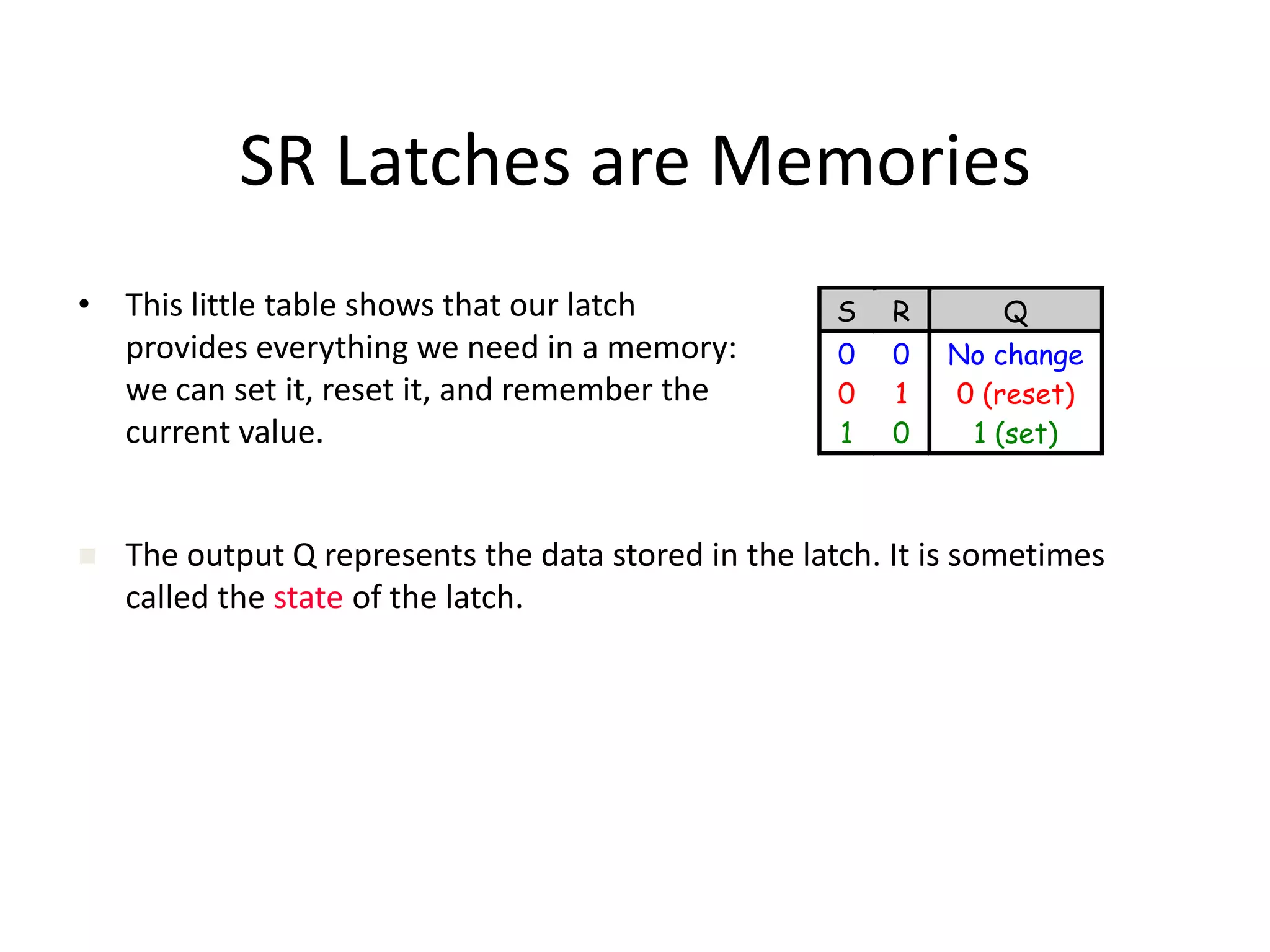
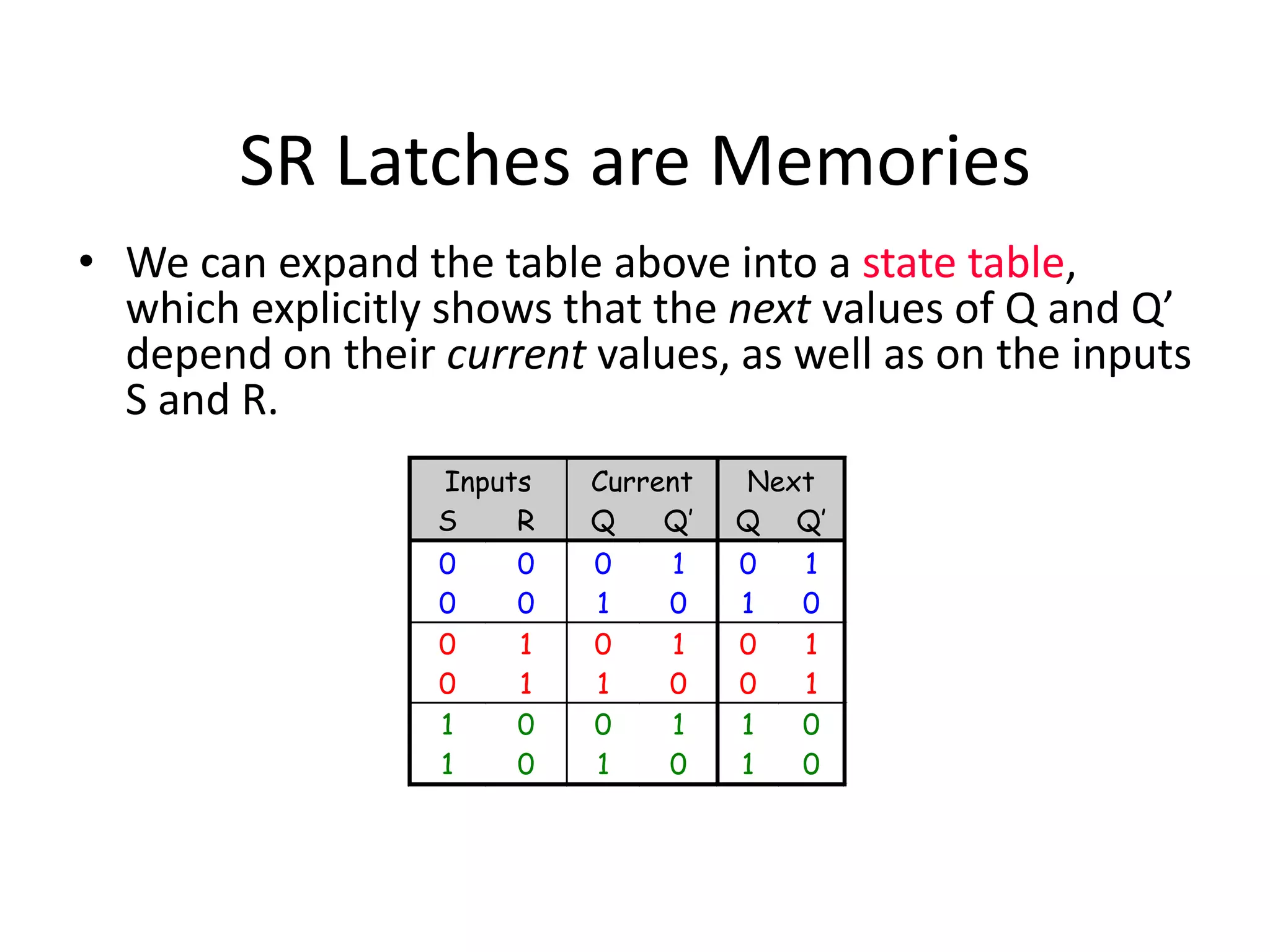
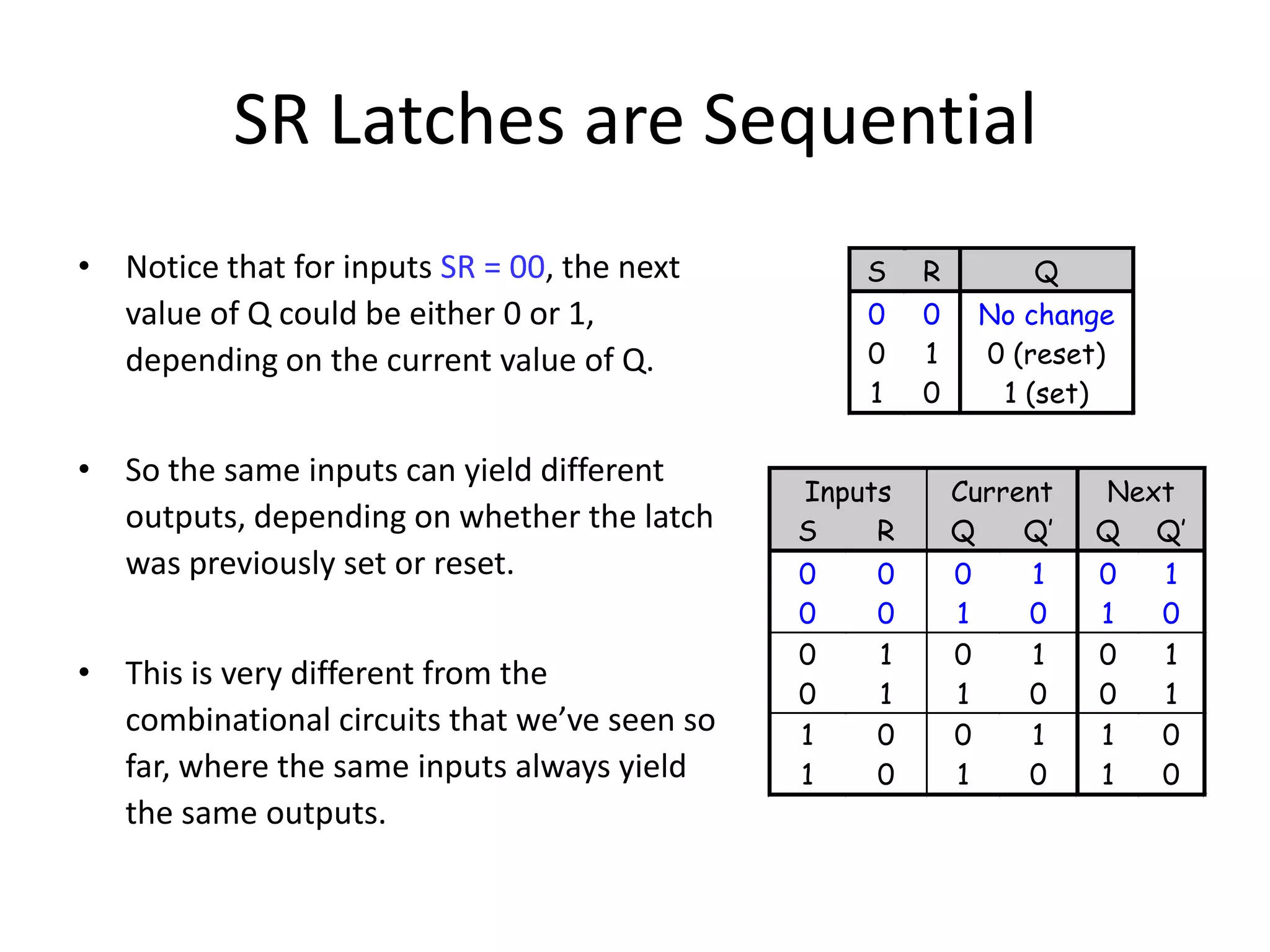
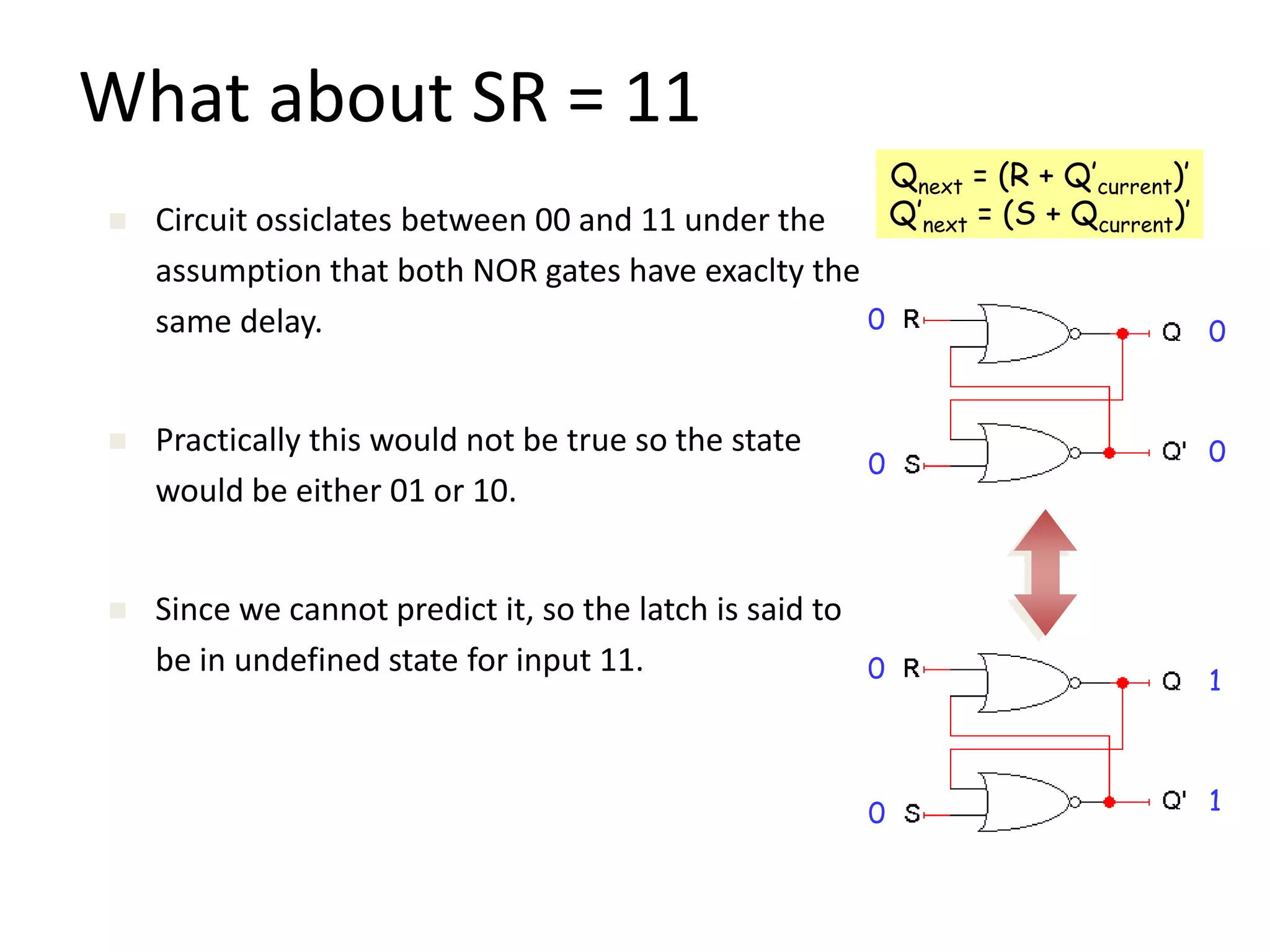
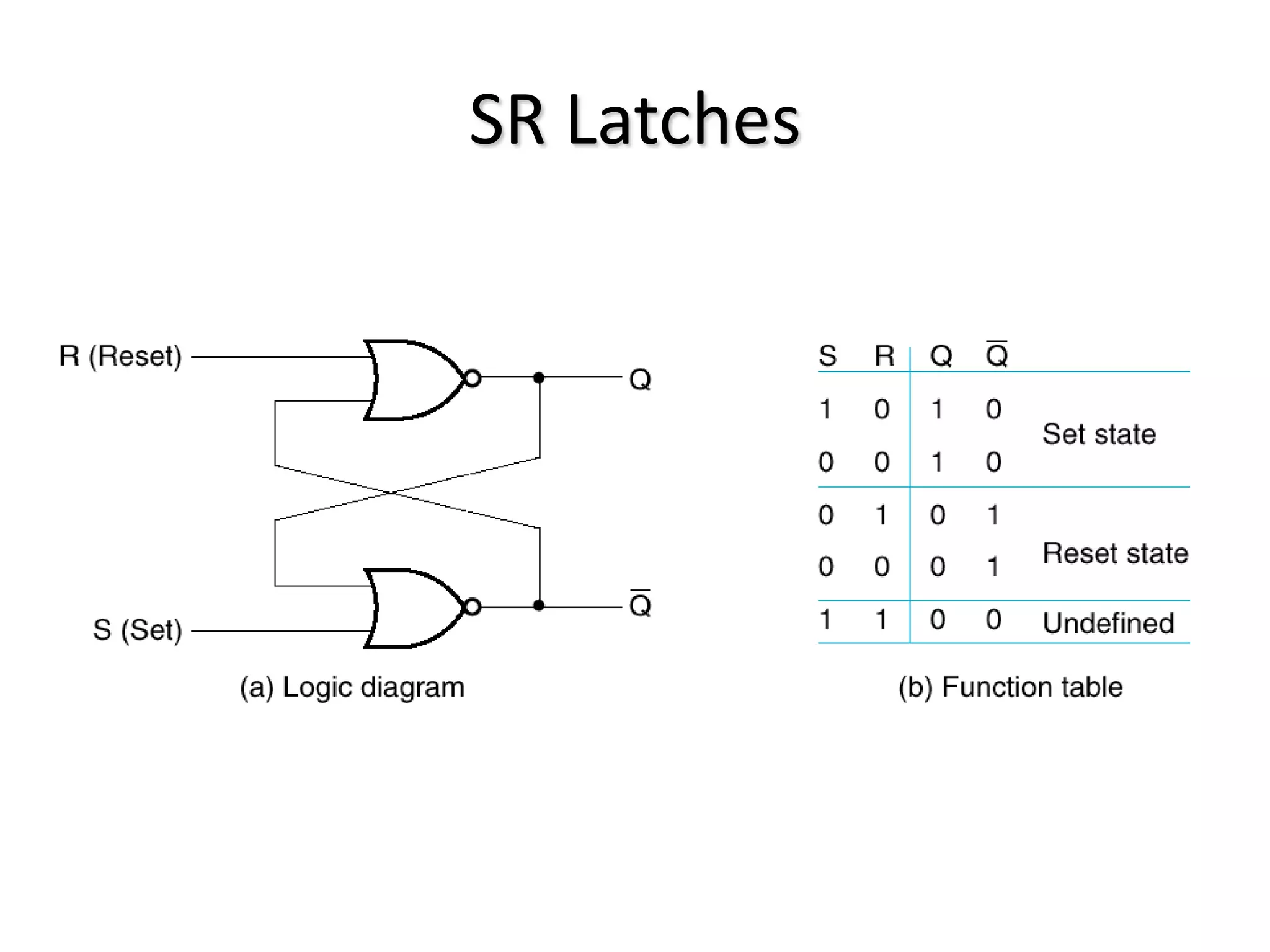
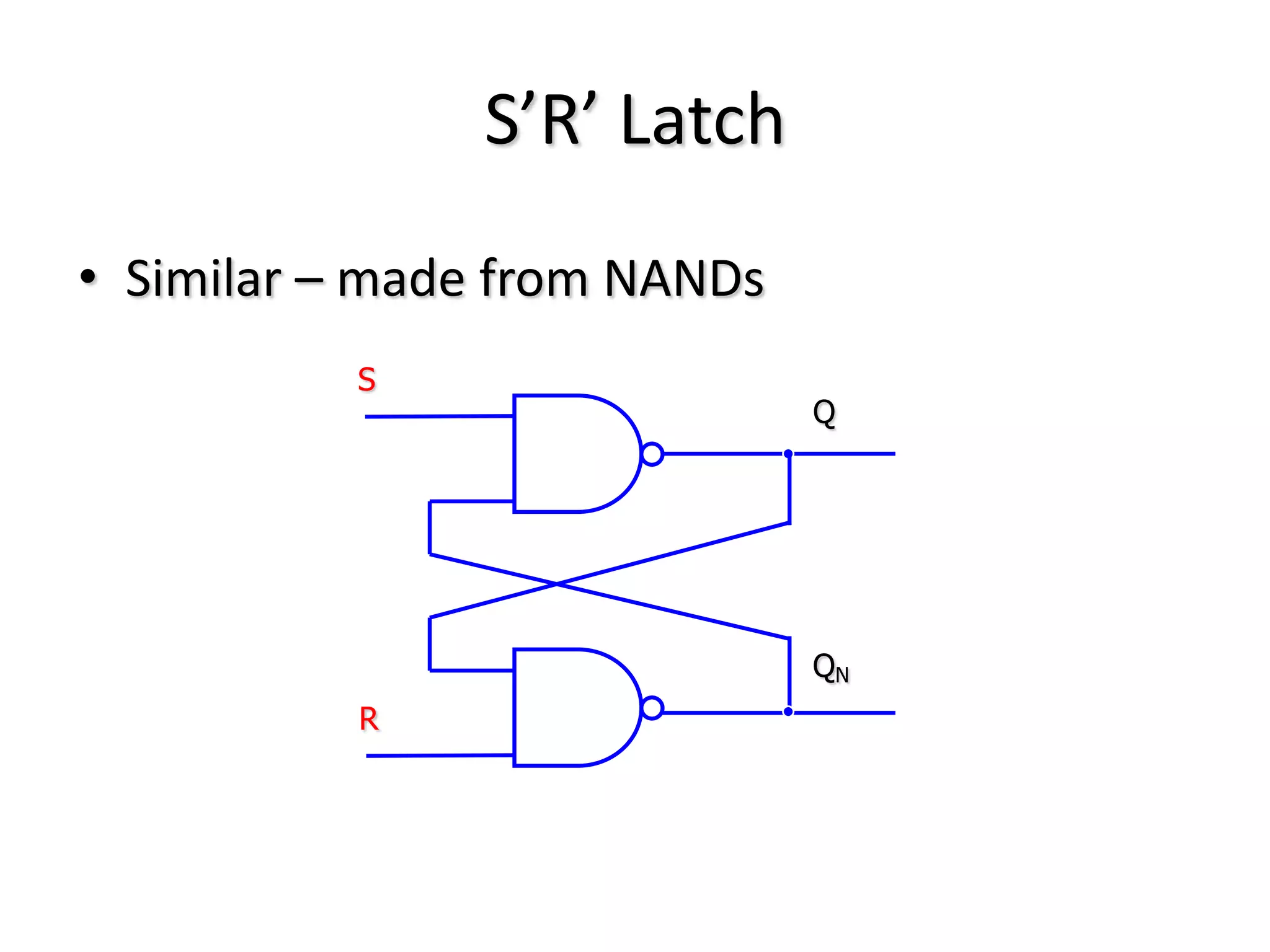
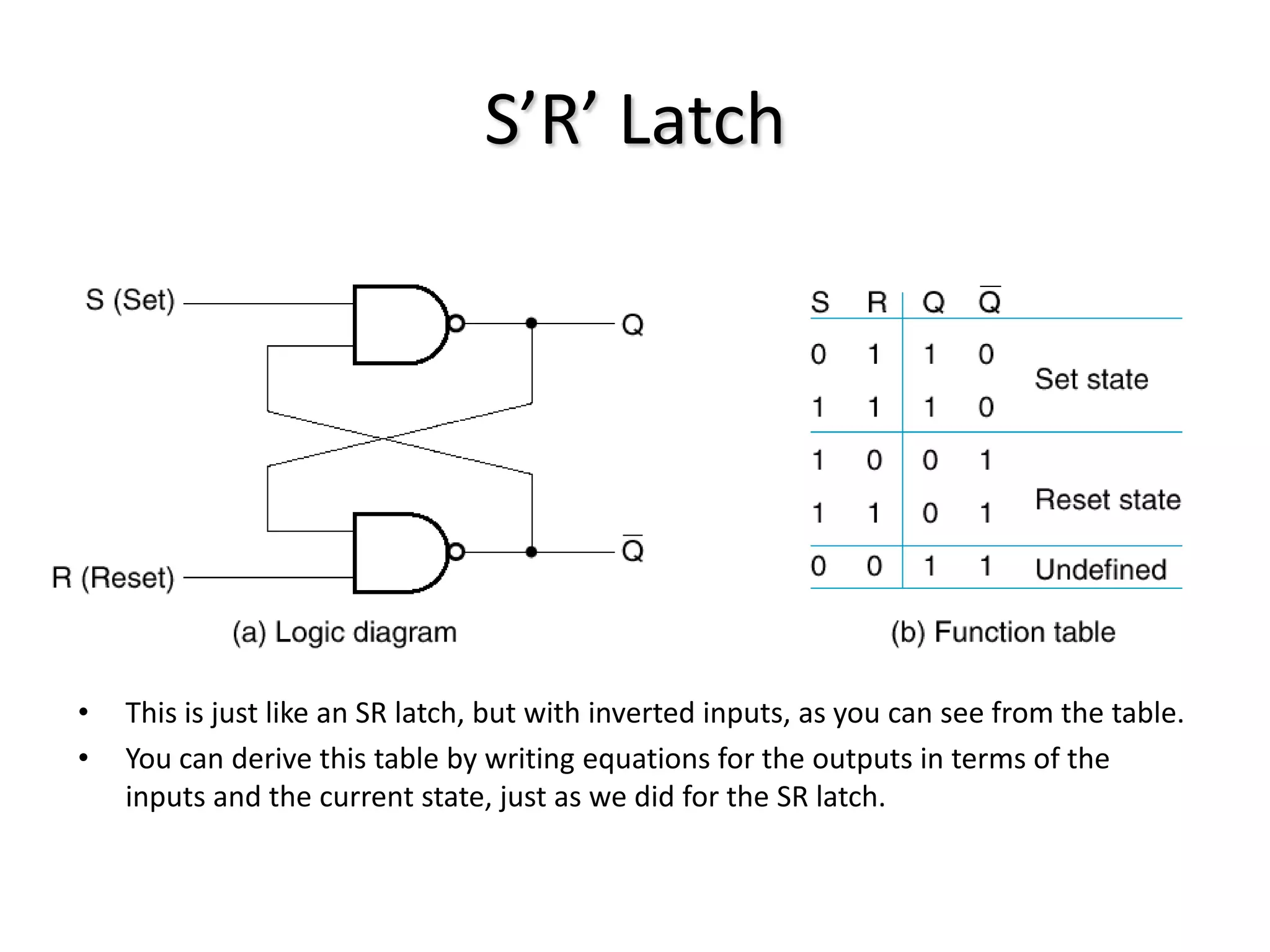
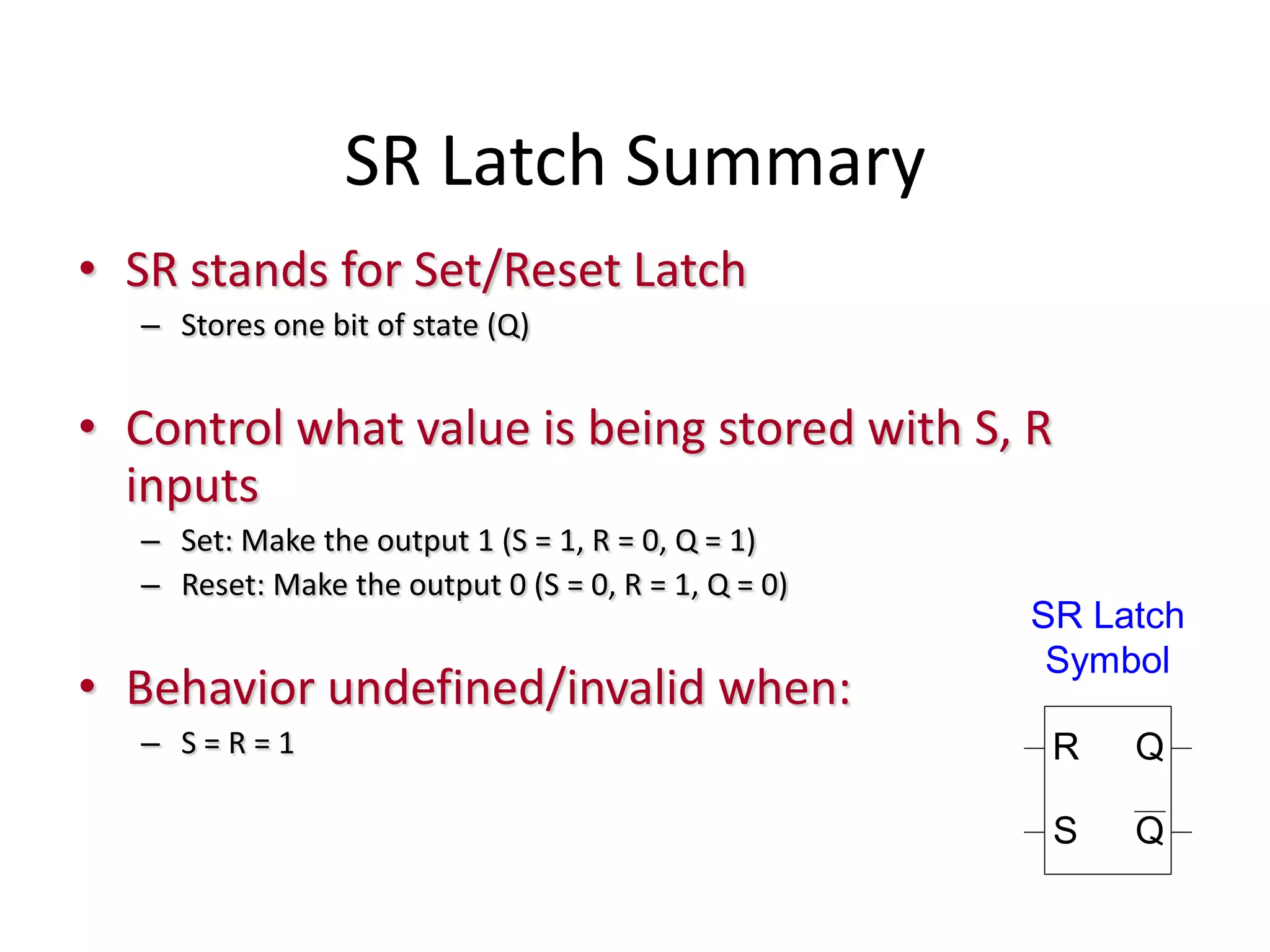
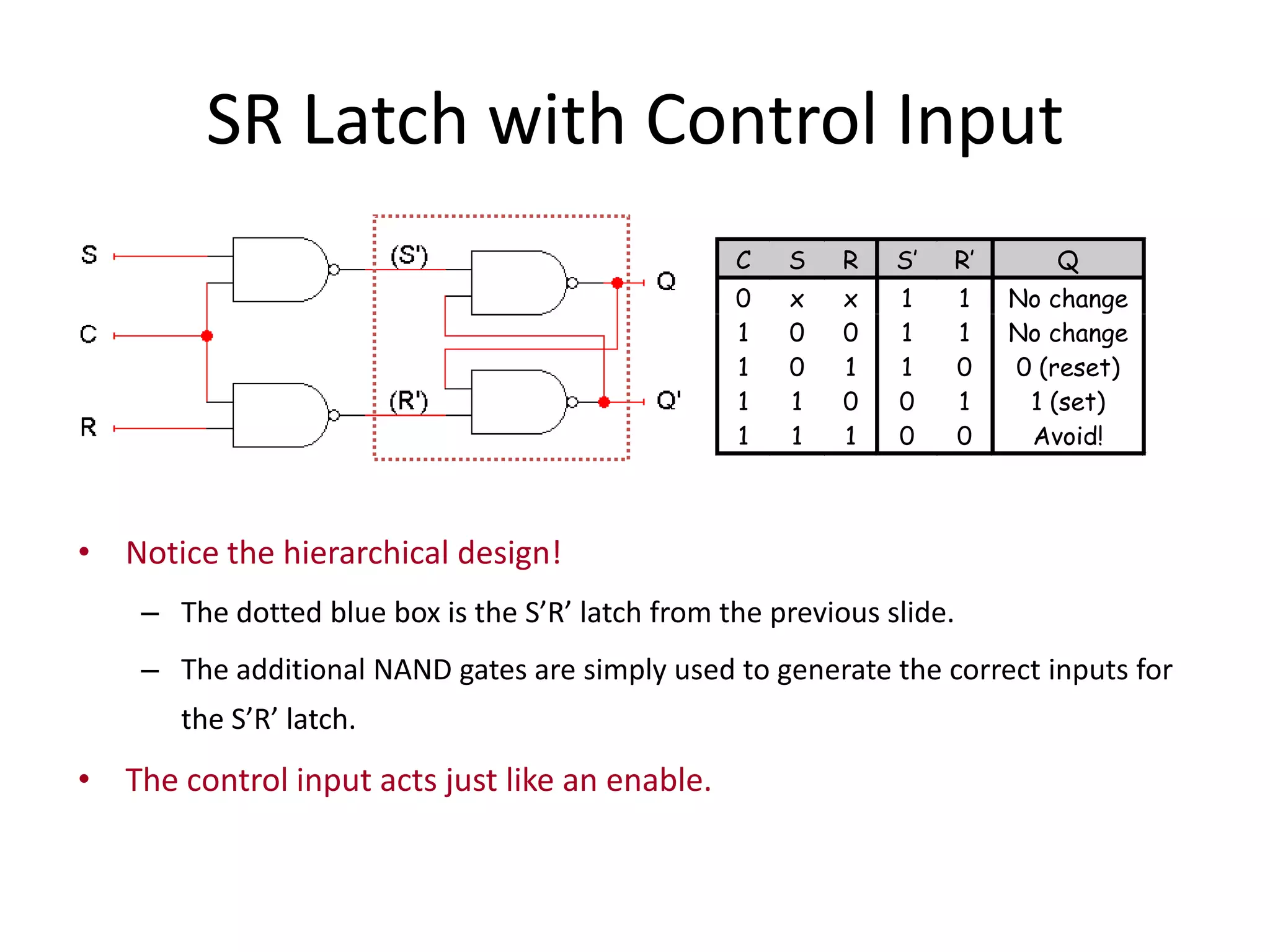
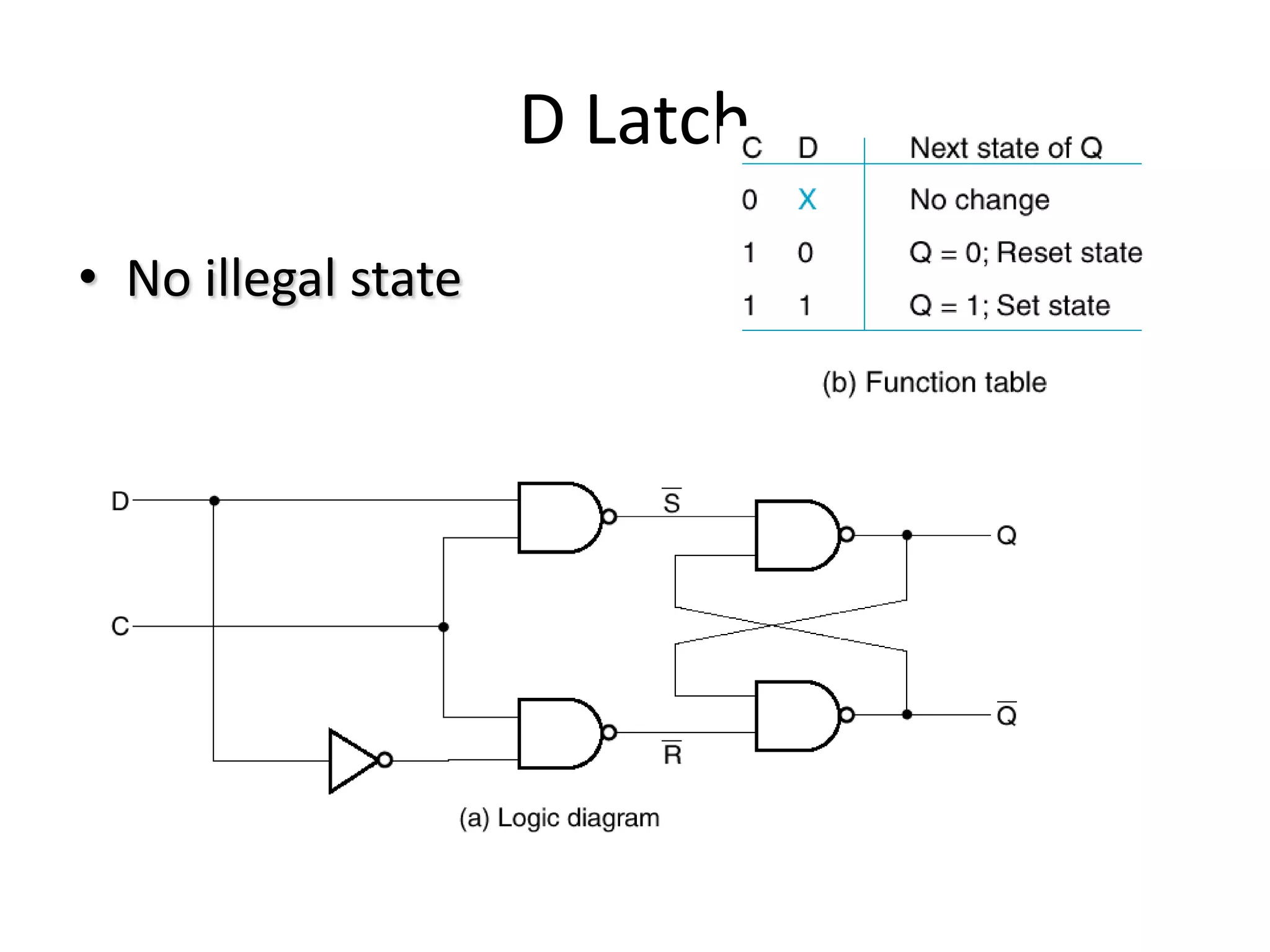
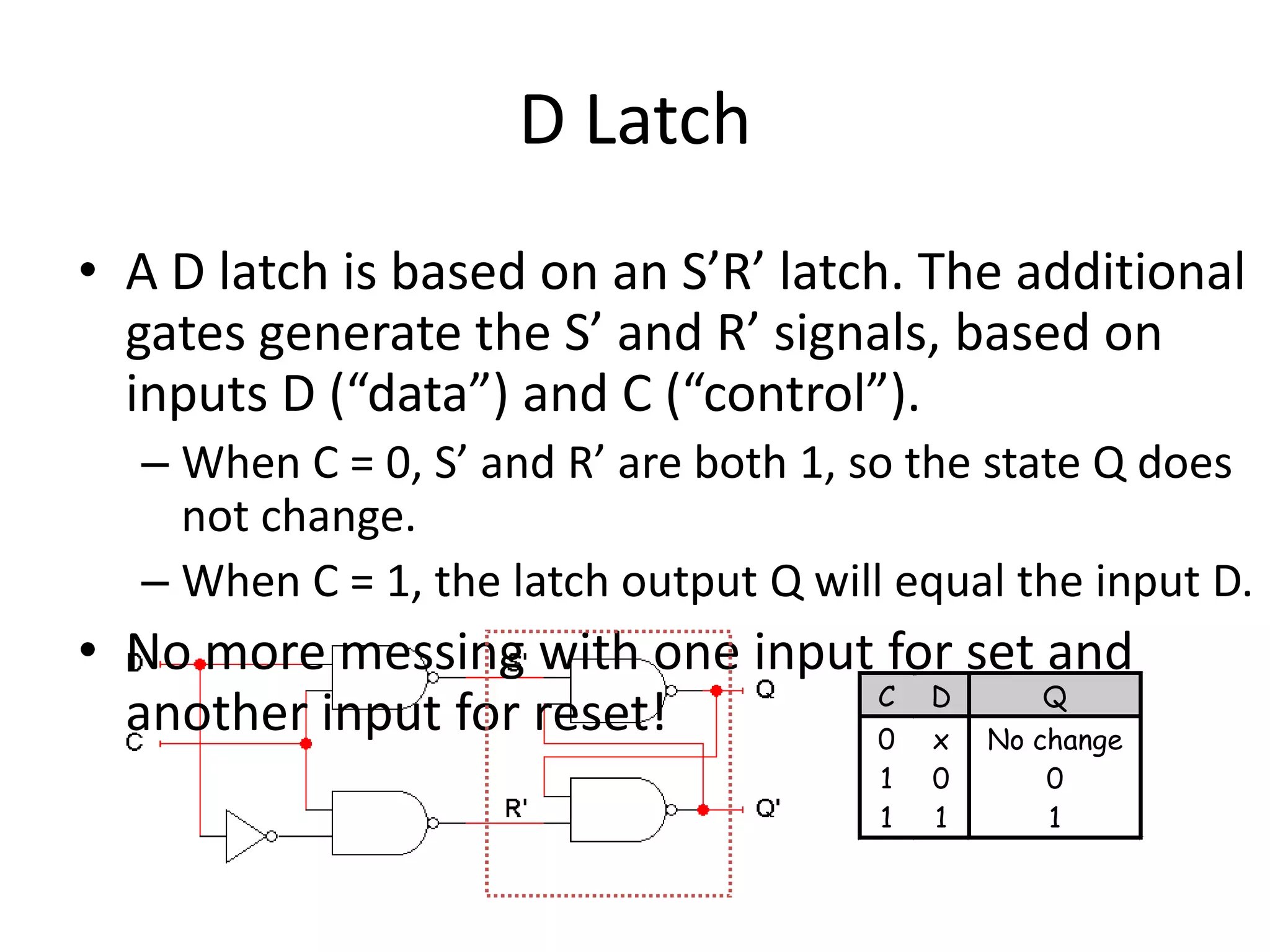
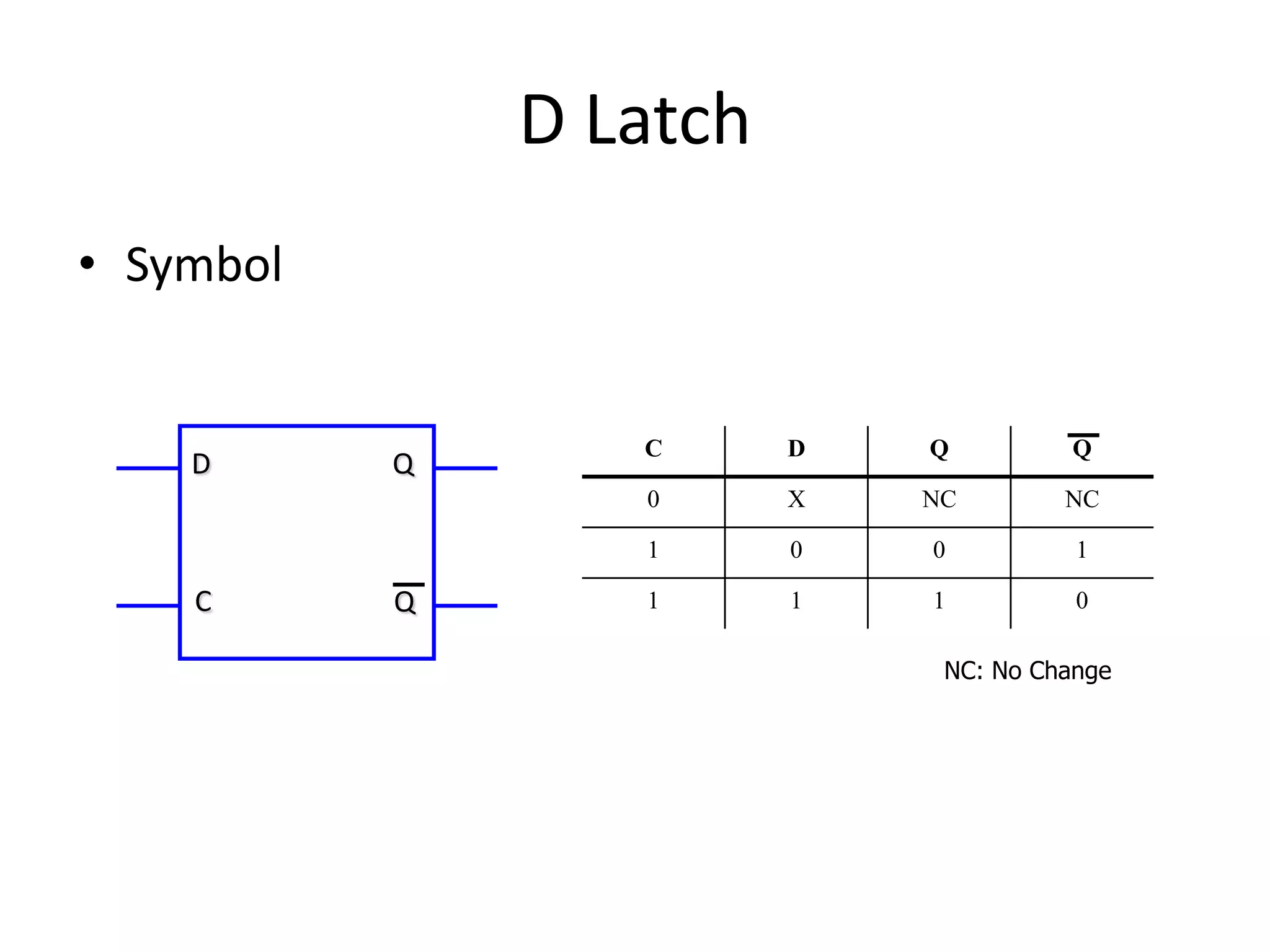
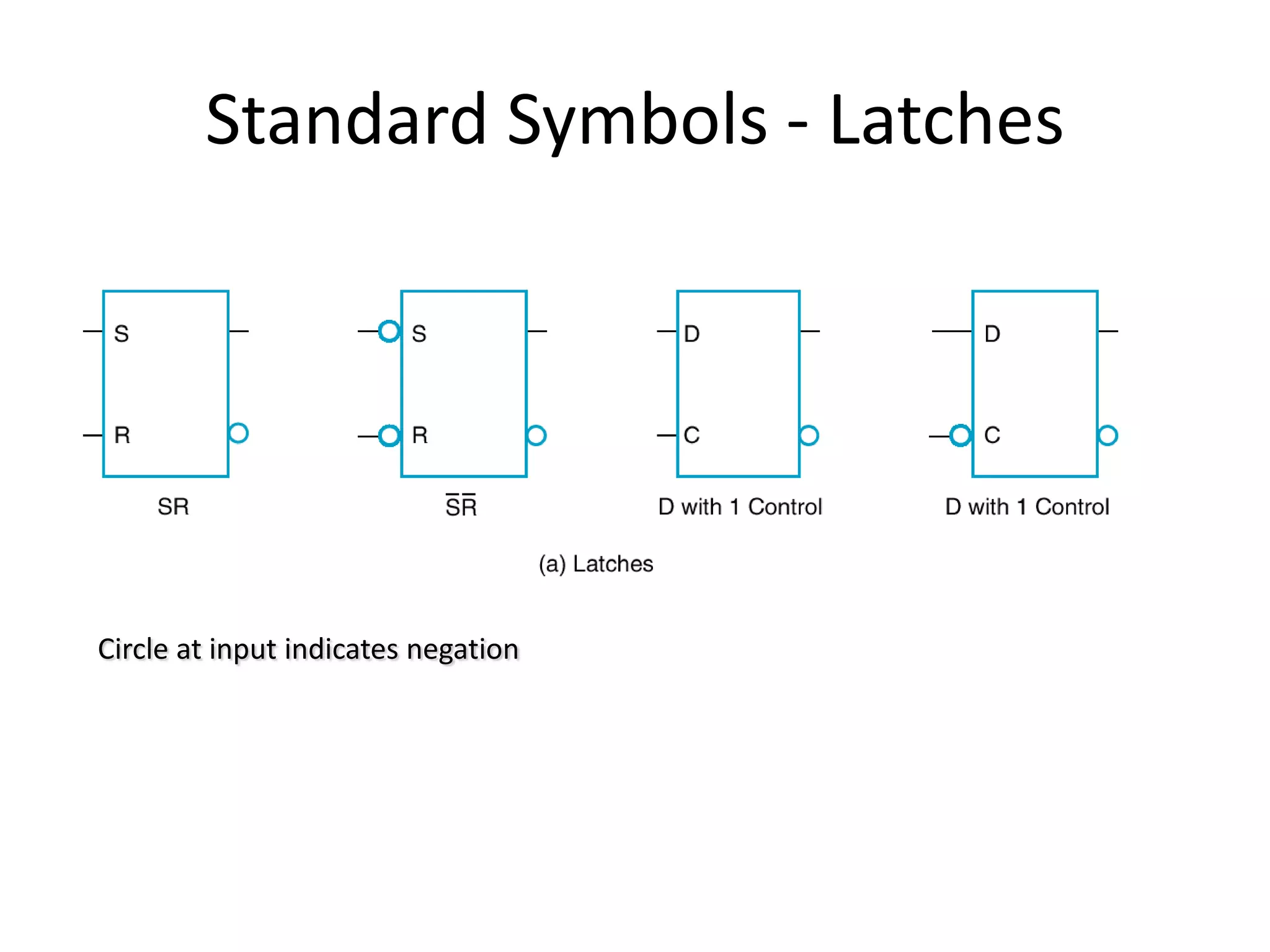
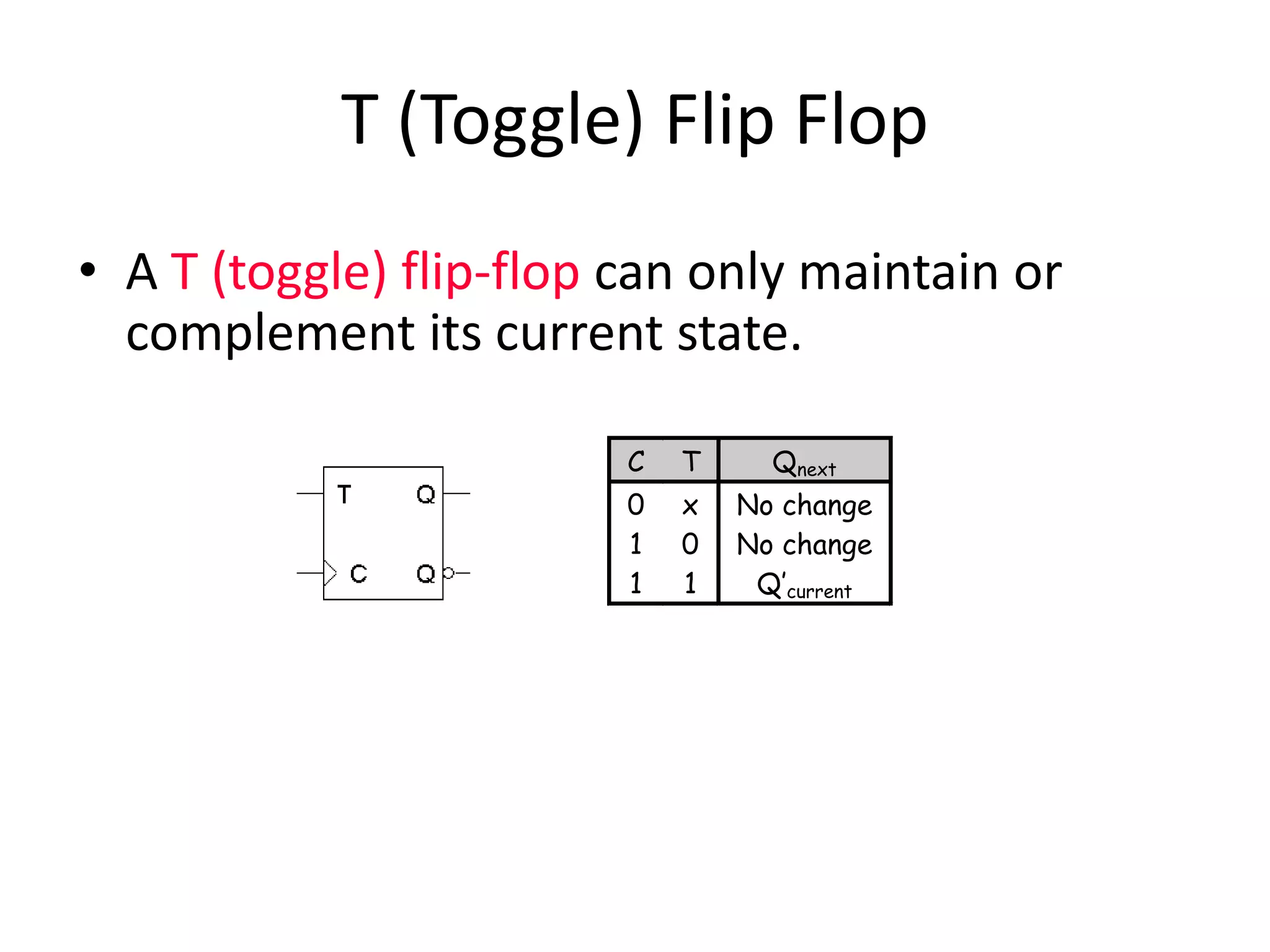
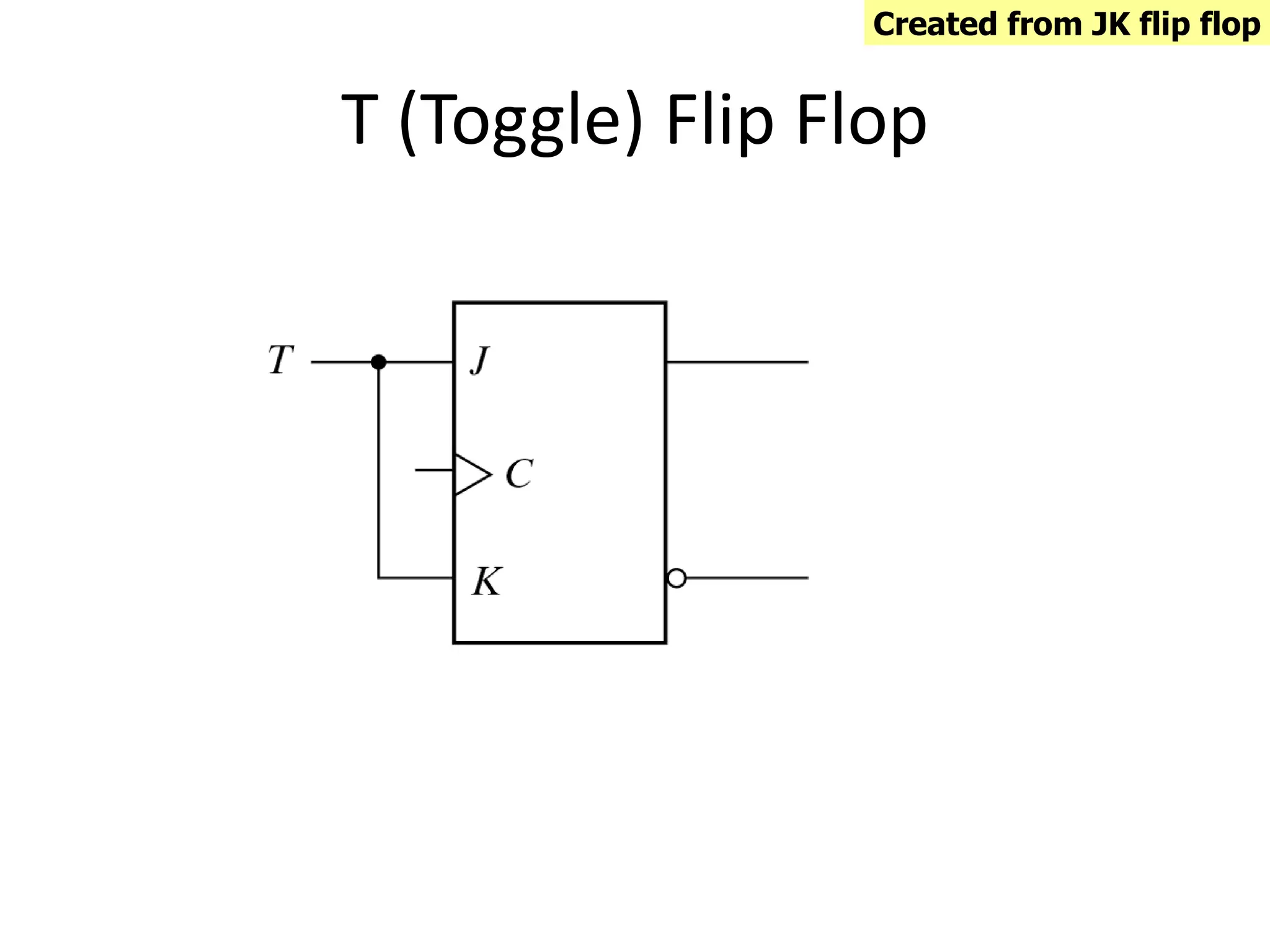
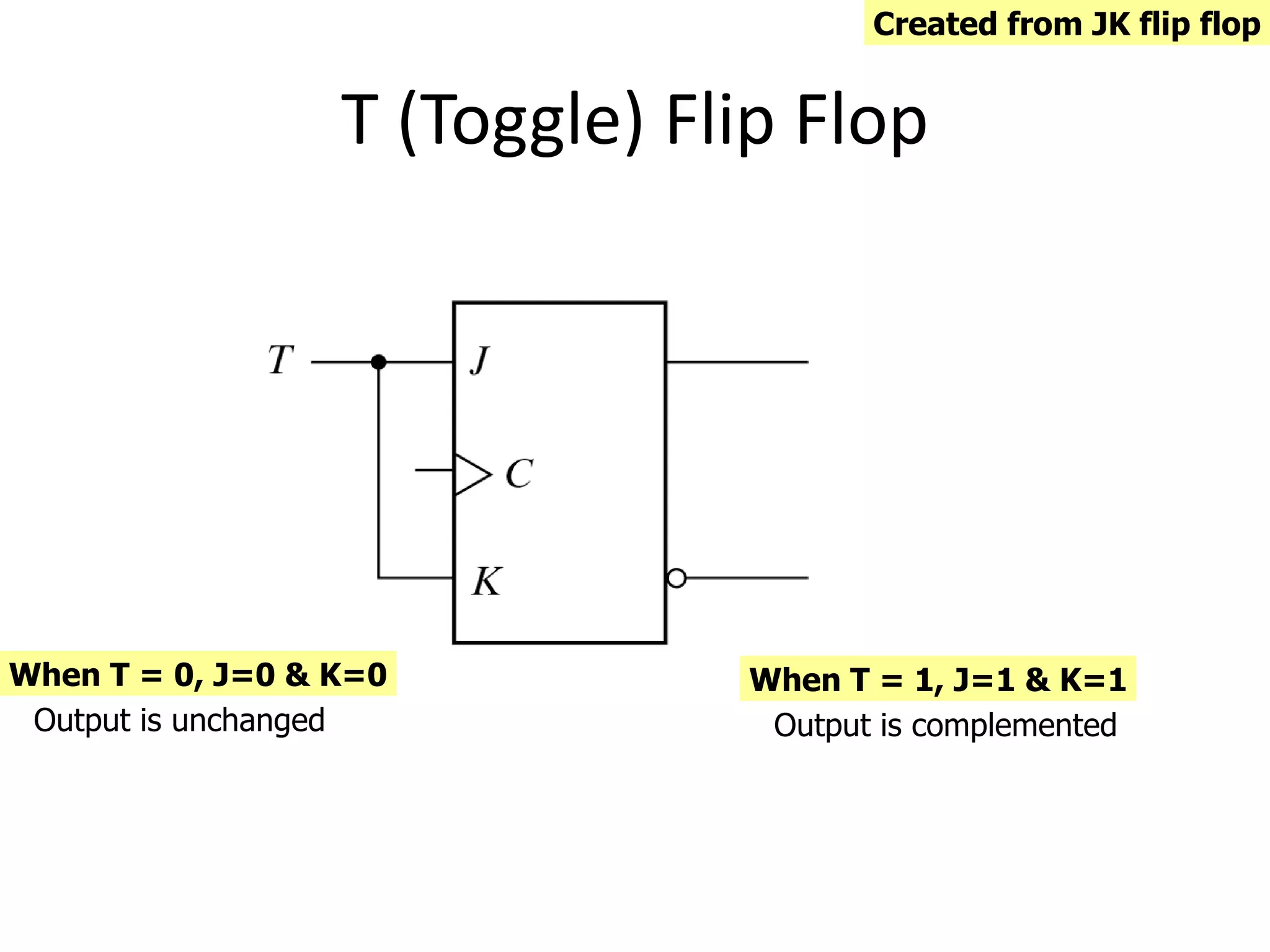
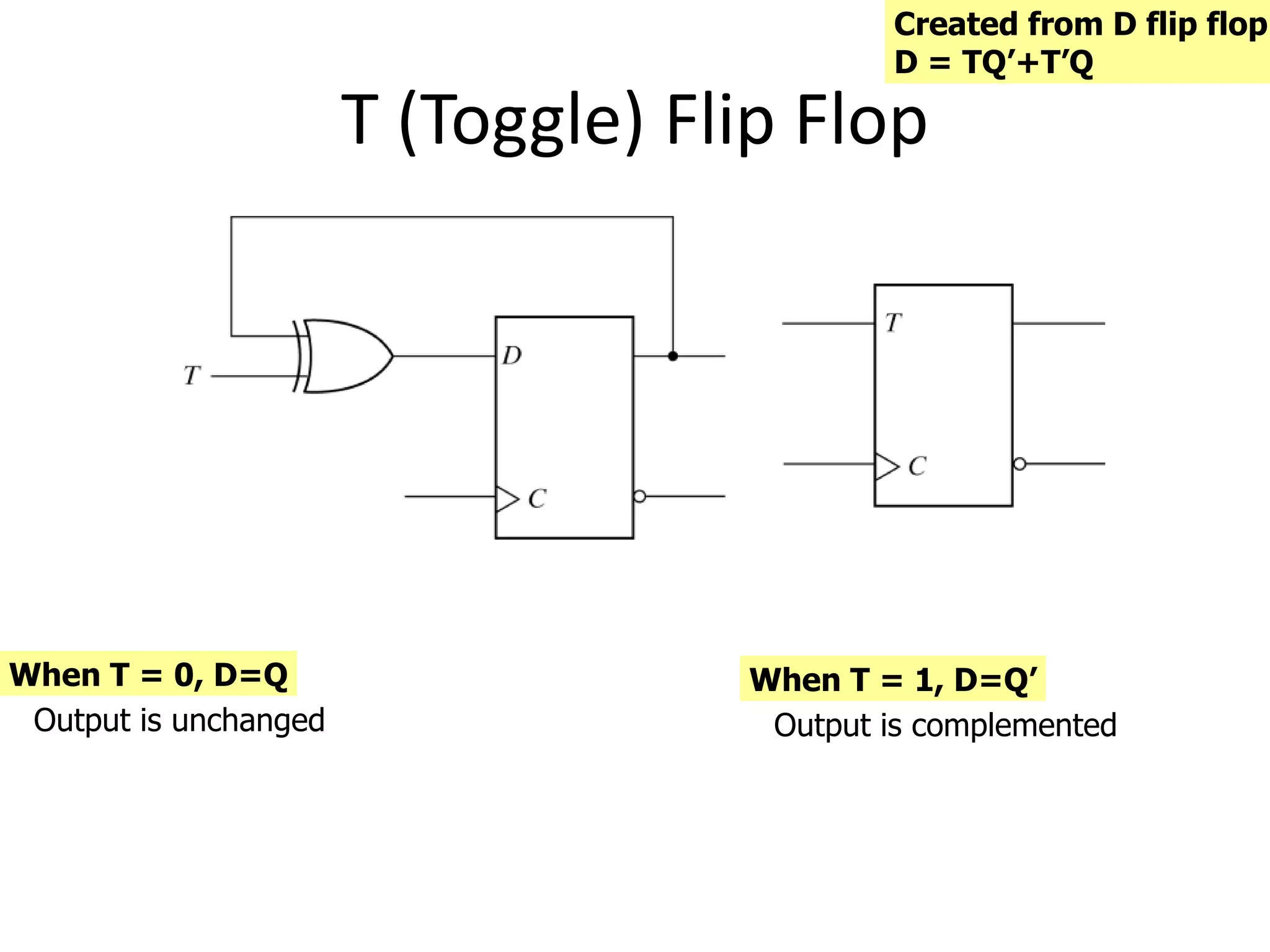
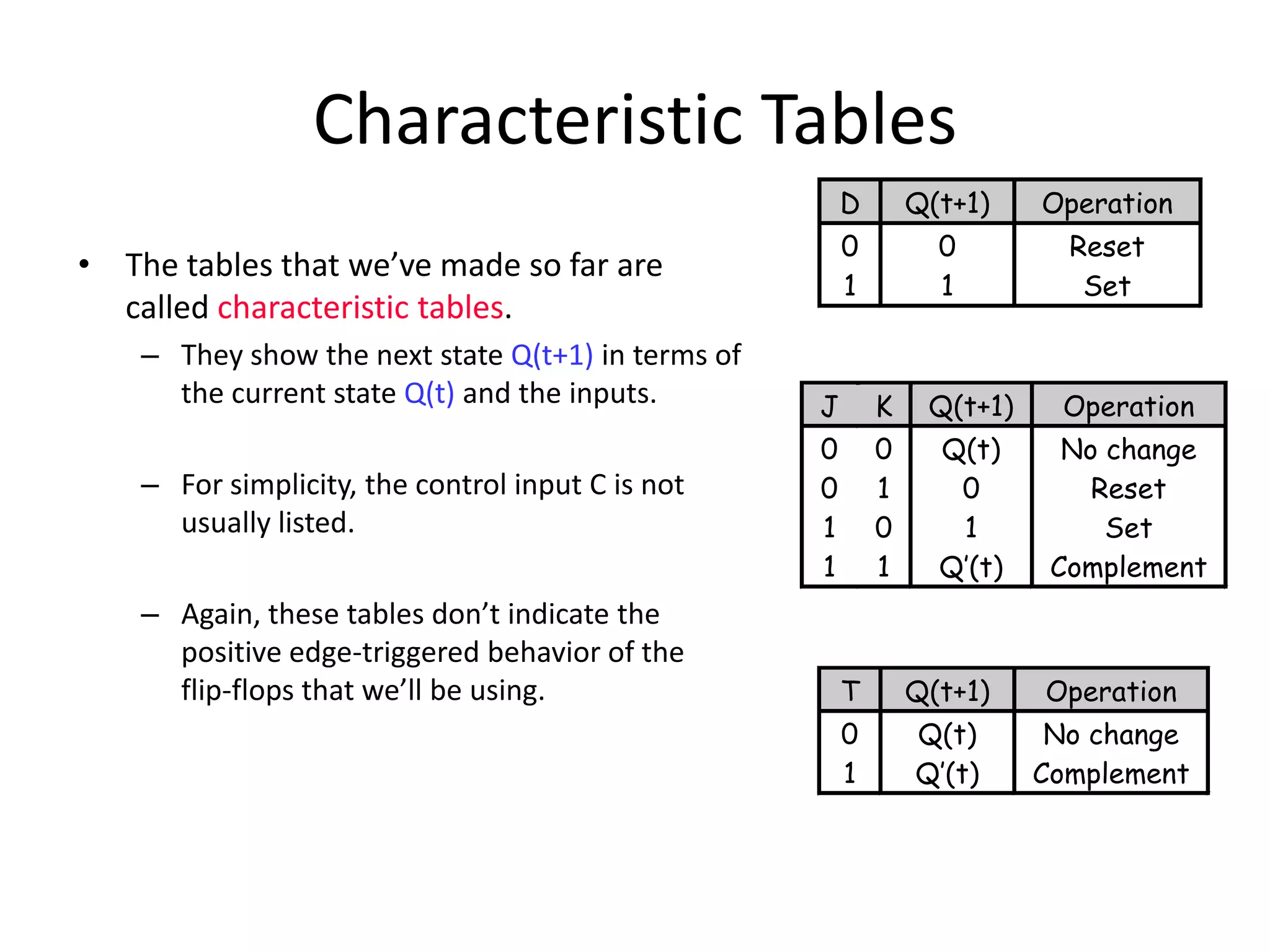
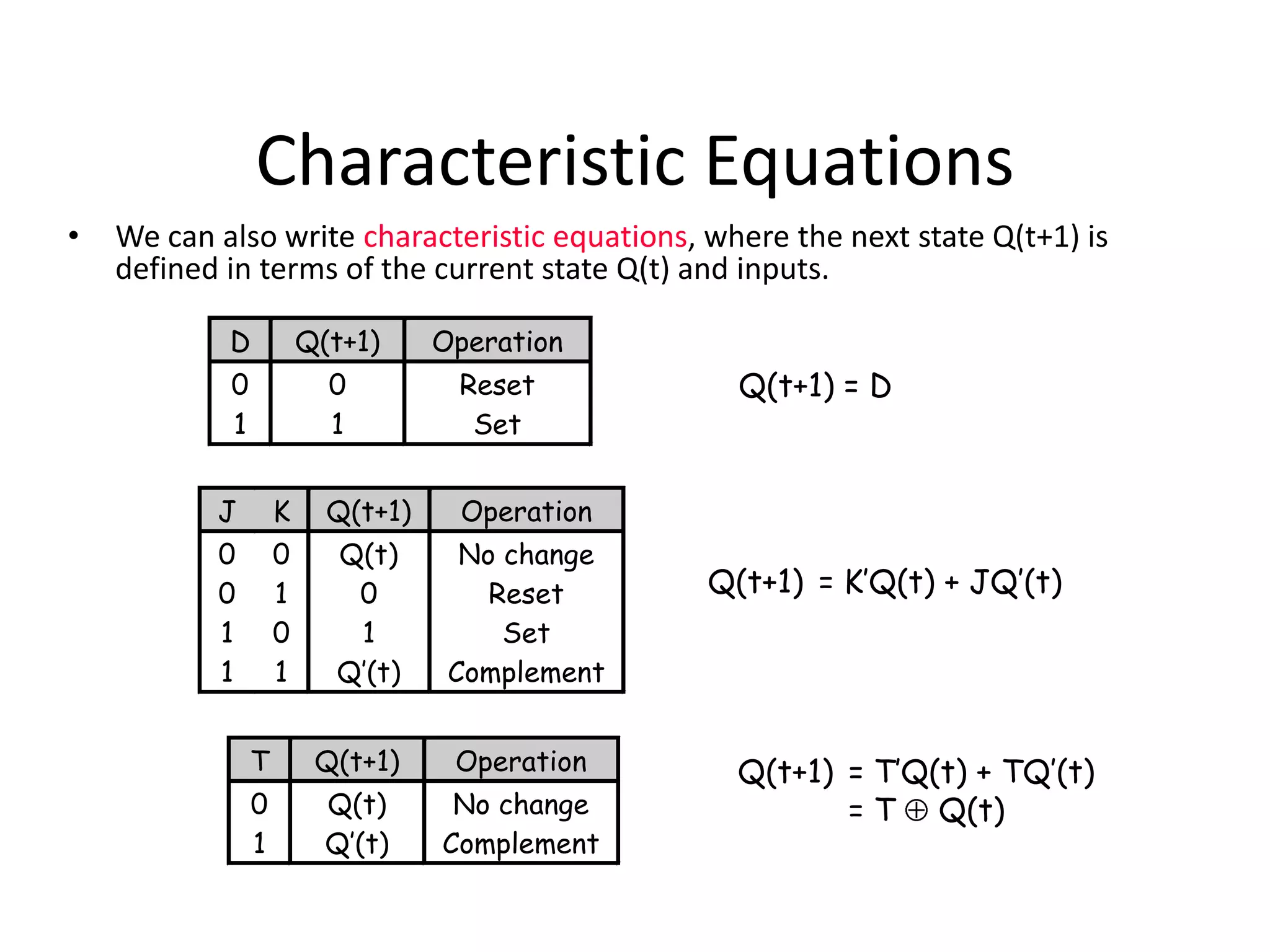
1) Sequential circuits have memory and their outputs depend not only on current inputs but also on the state of the circuit.
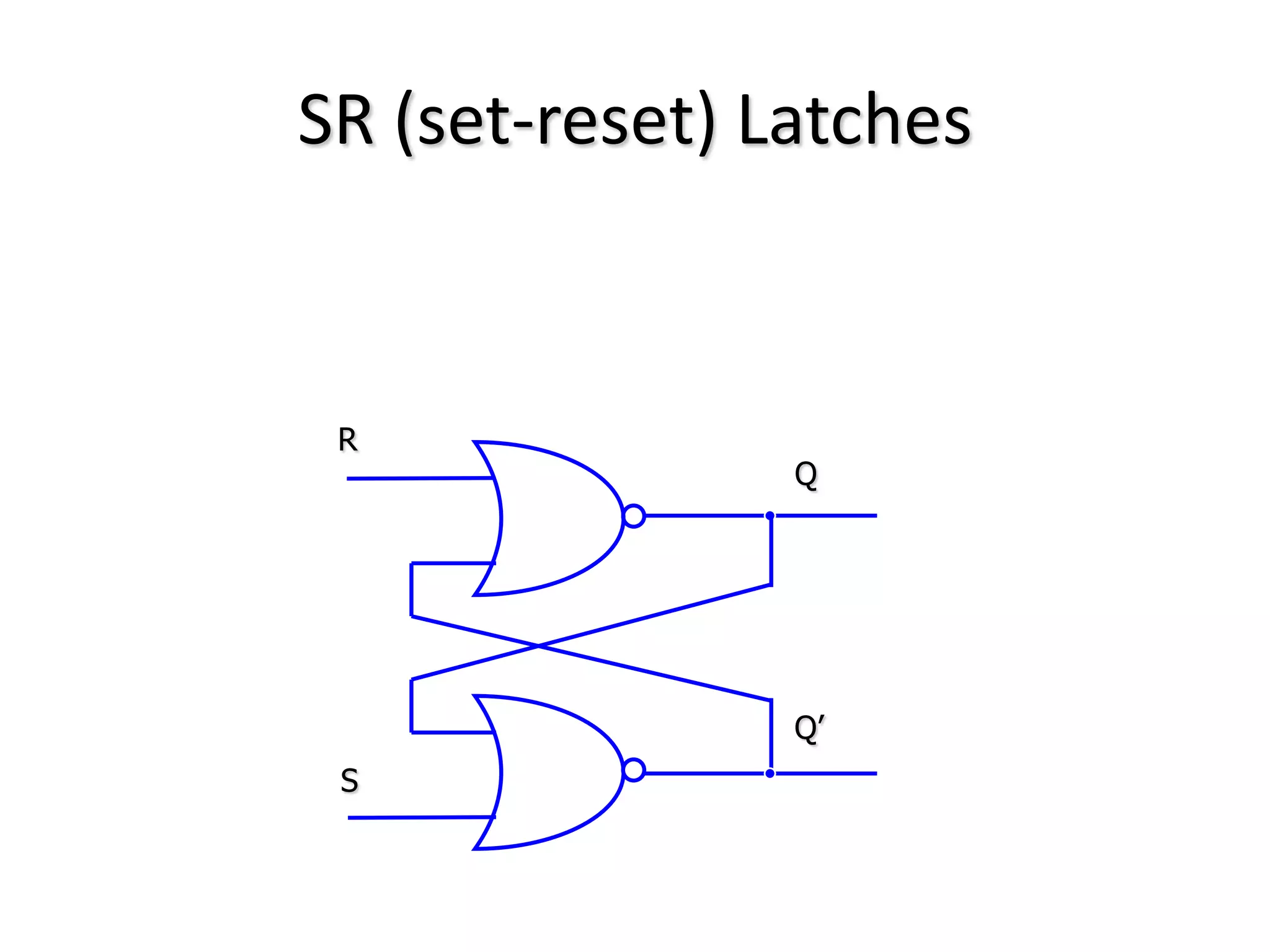
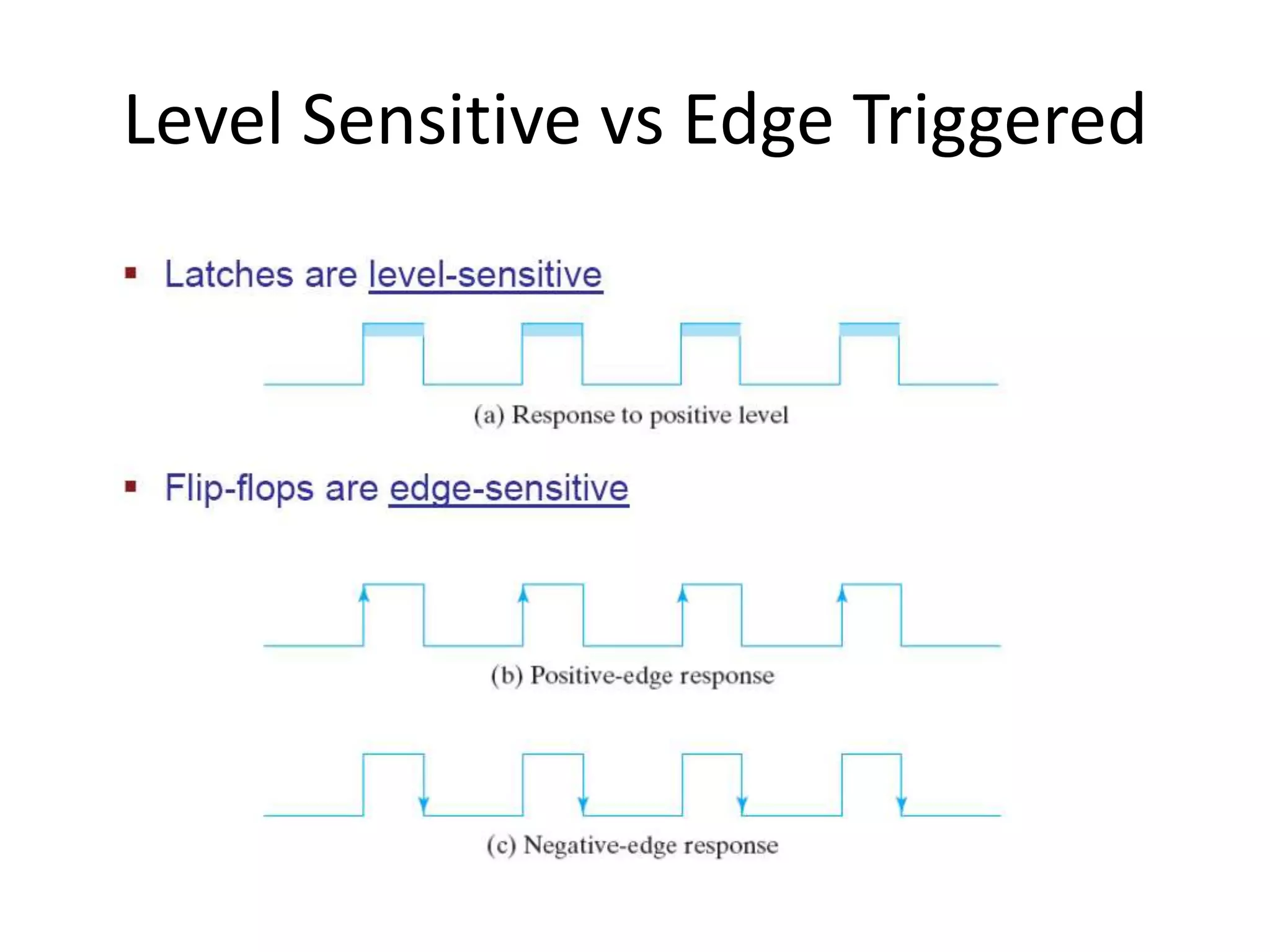
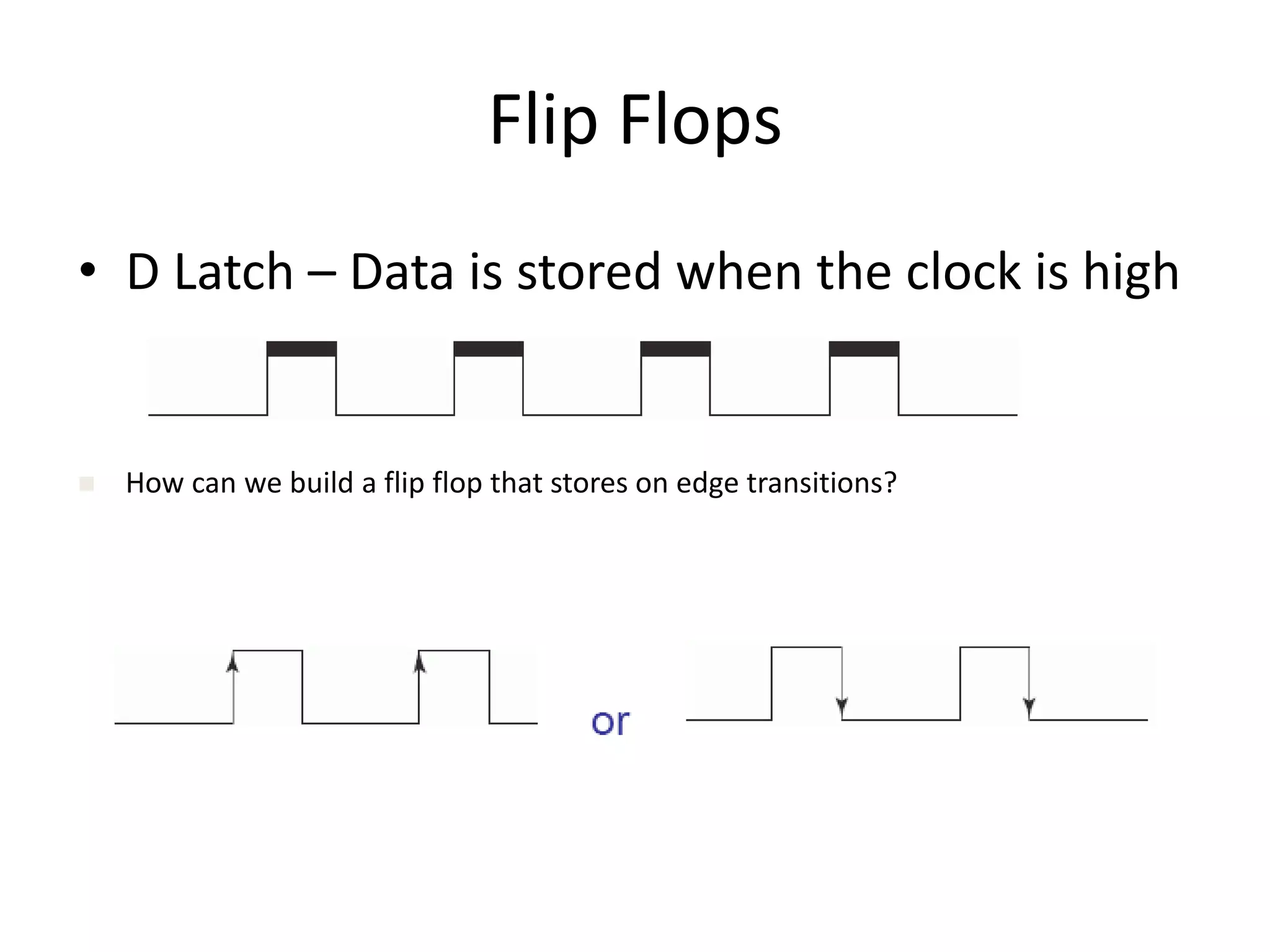
2) Latches are the simplest memory elements that can store a single bit and have two stable states, set and reset.
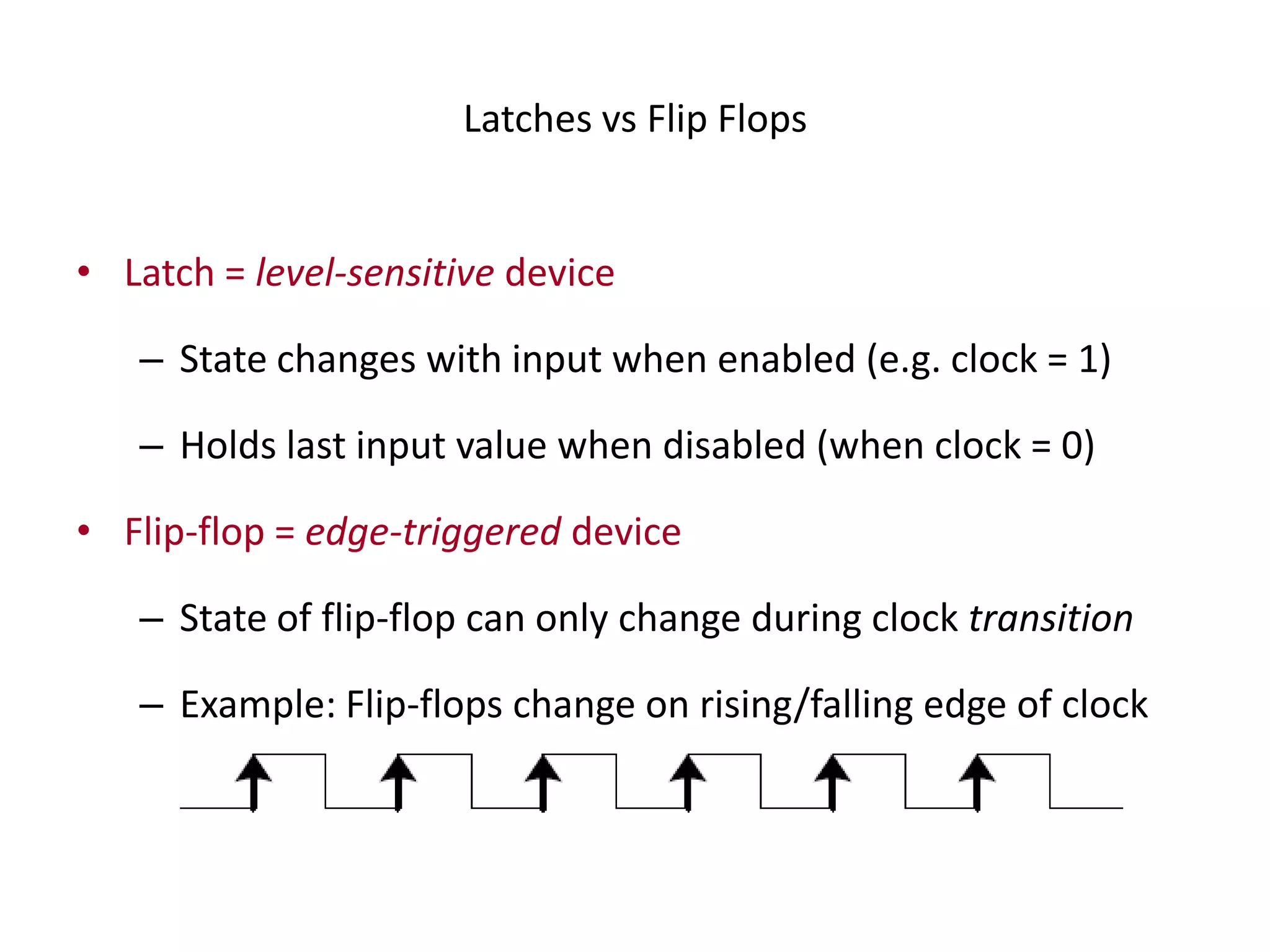
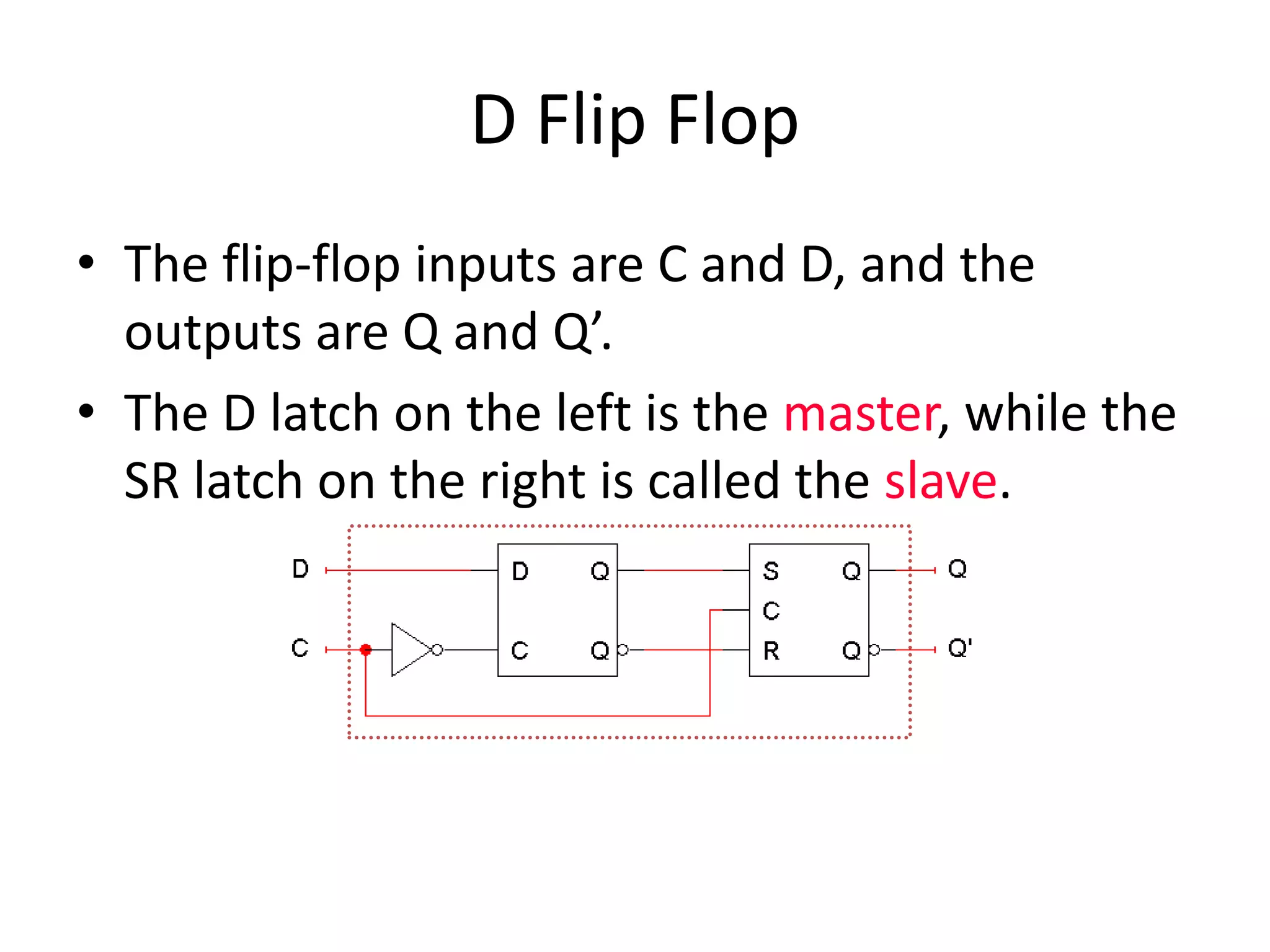
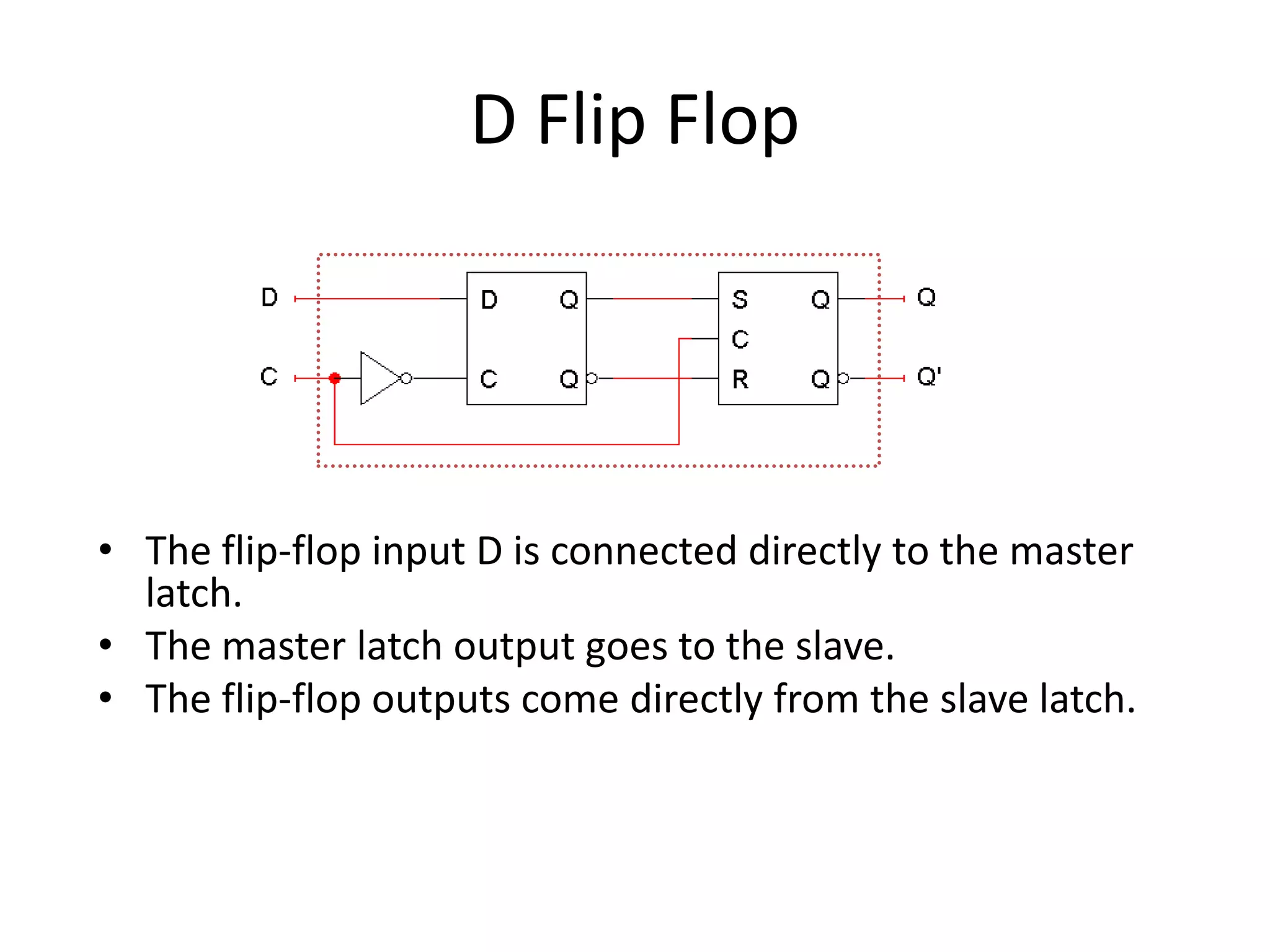
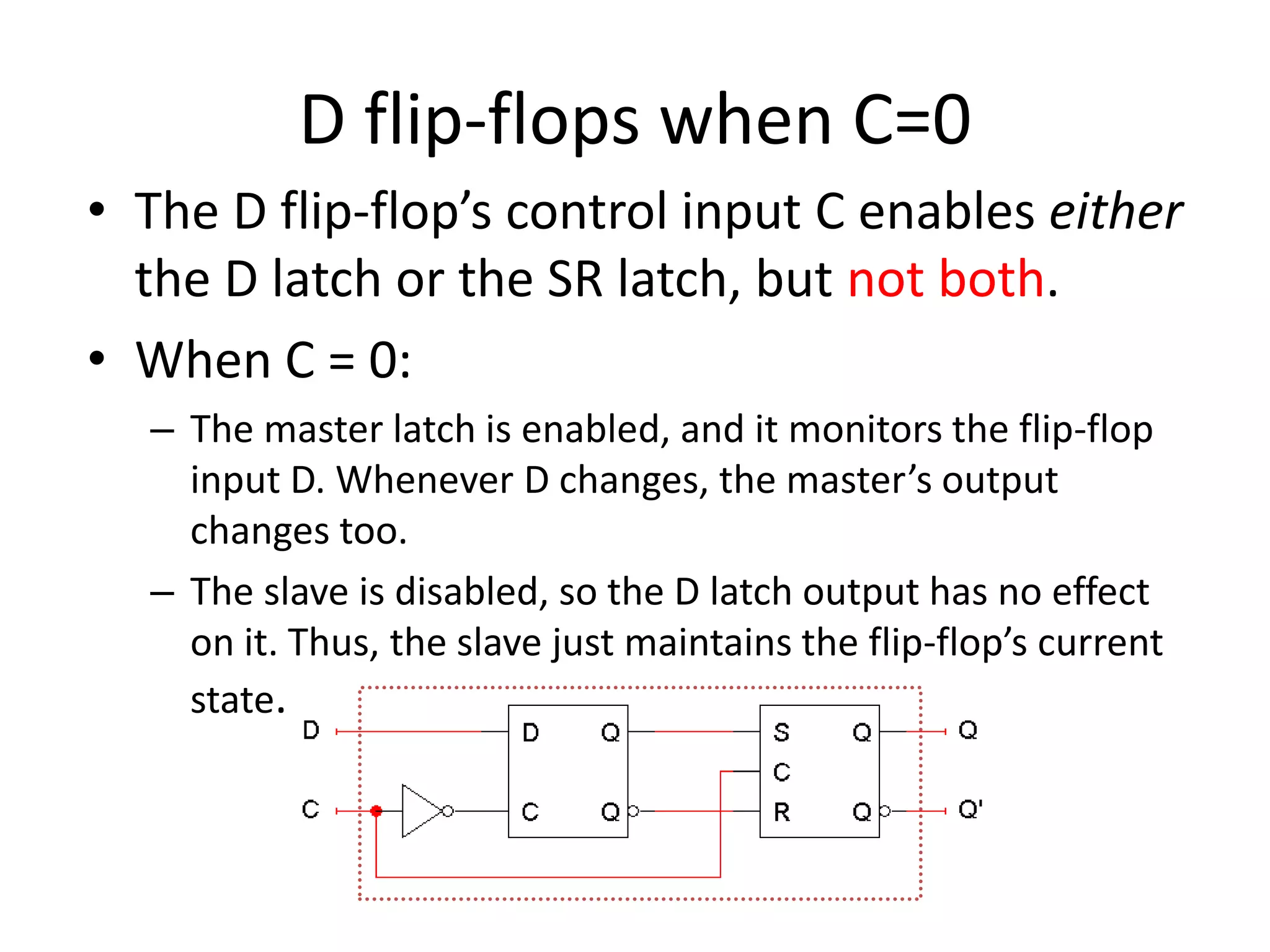
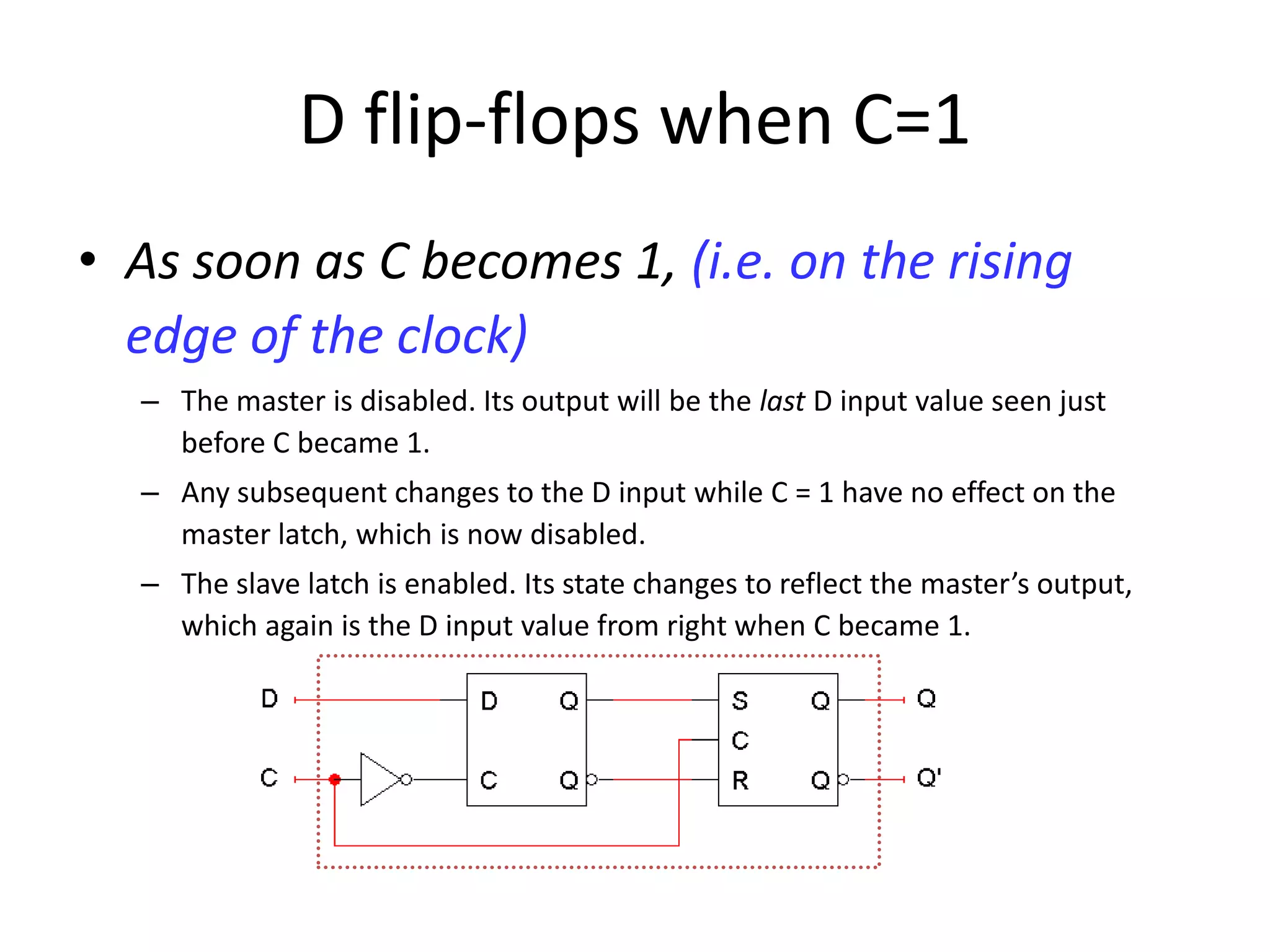
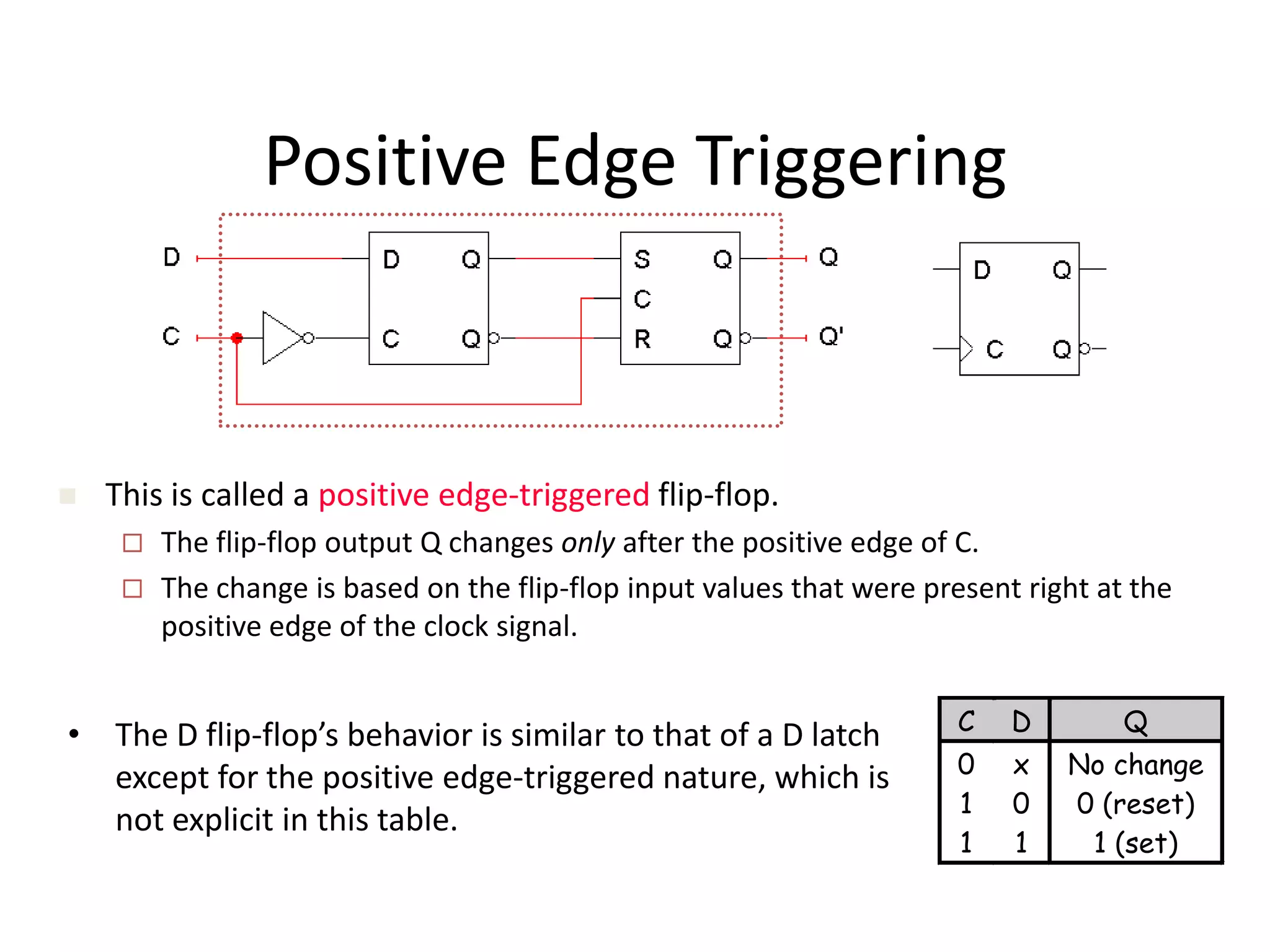
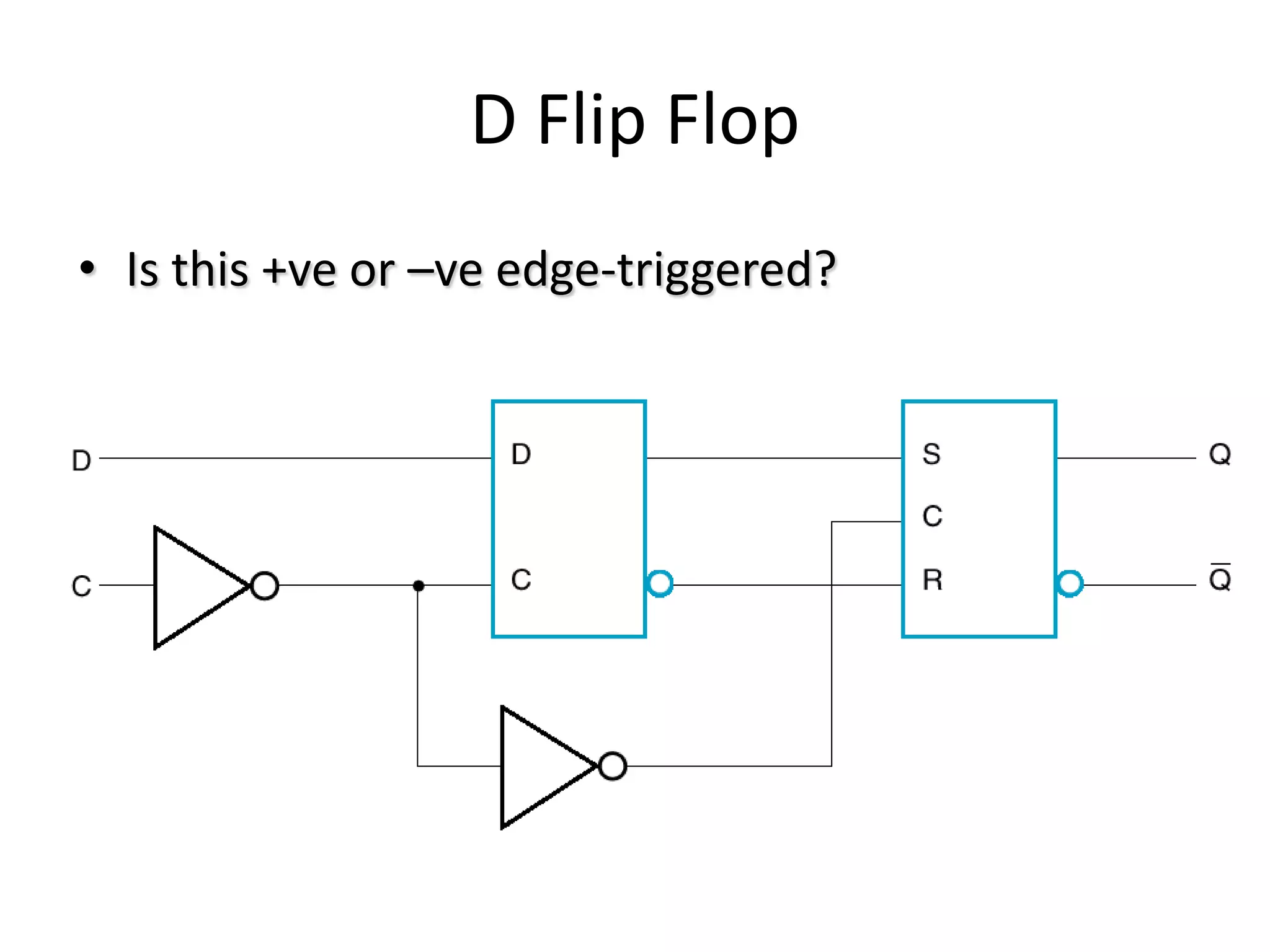
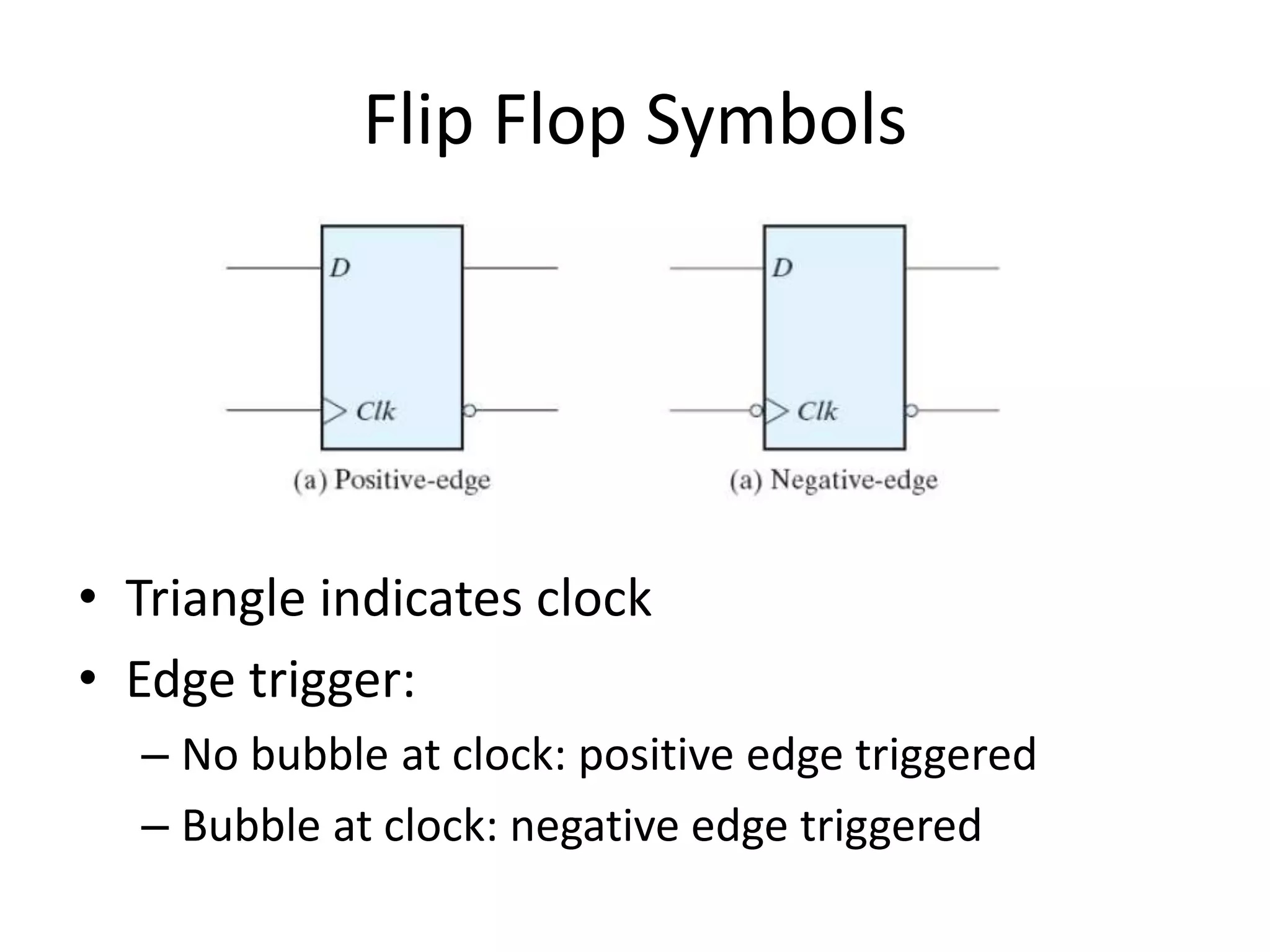
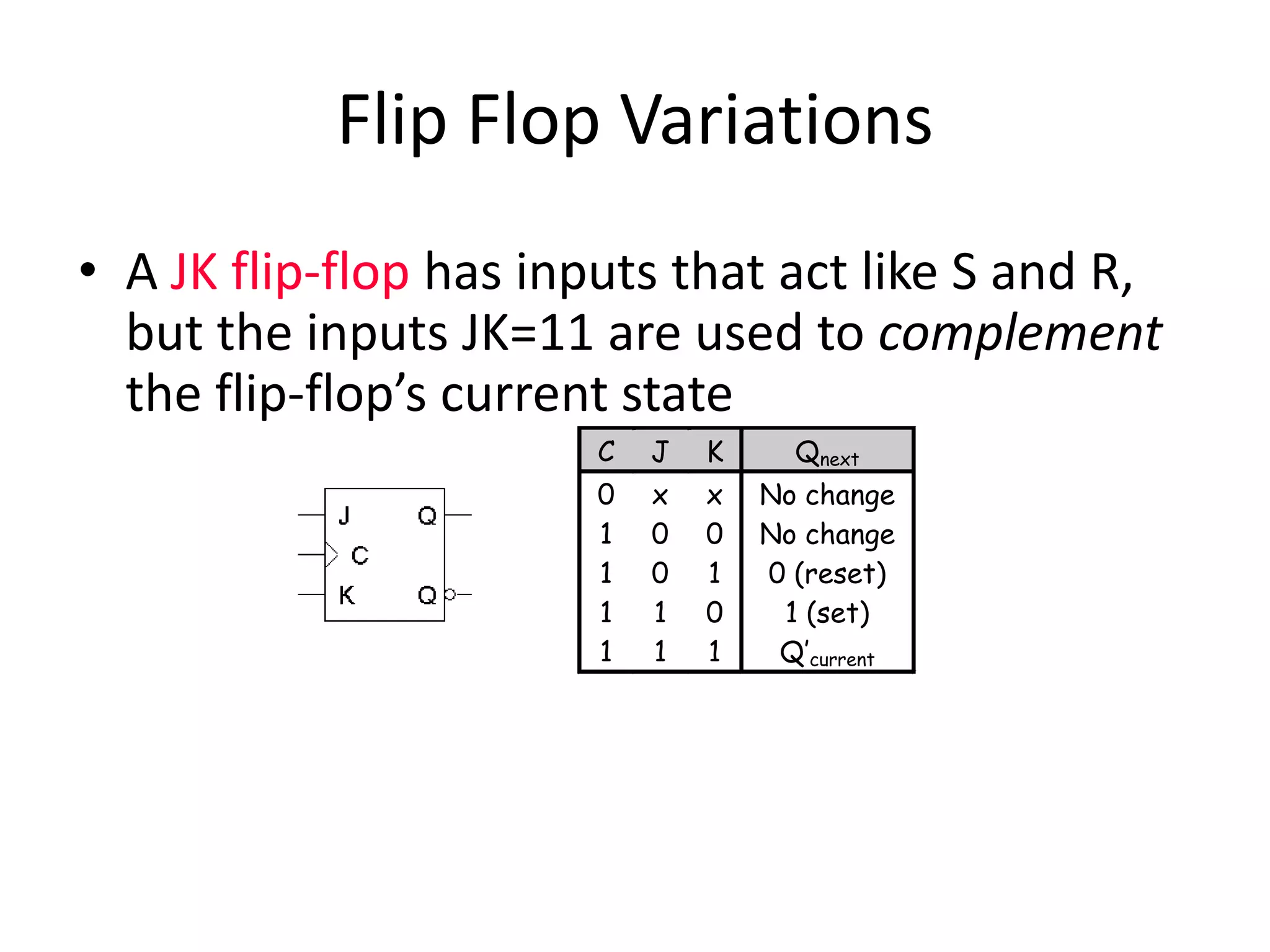
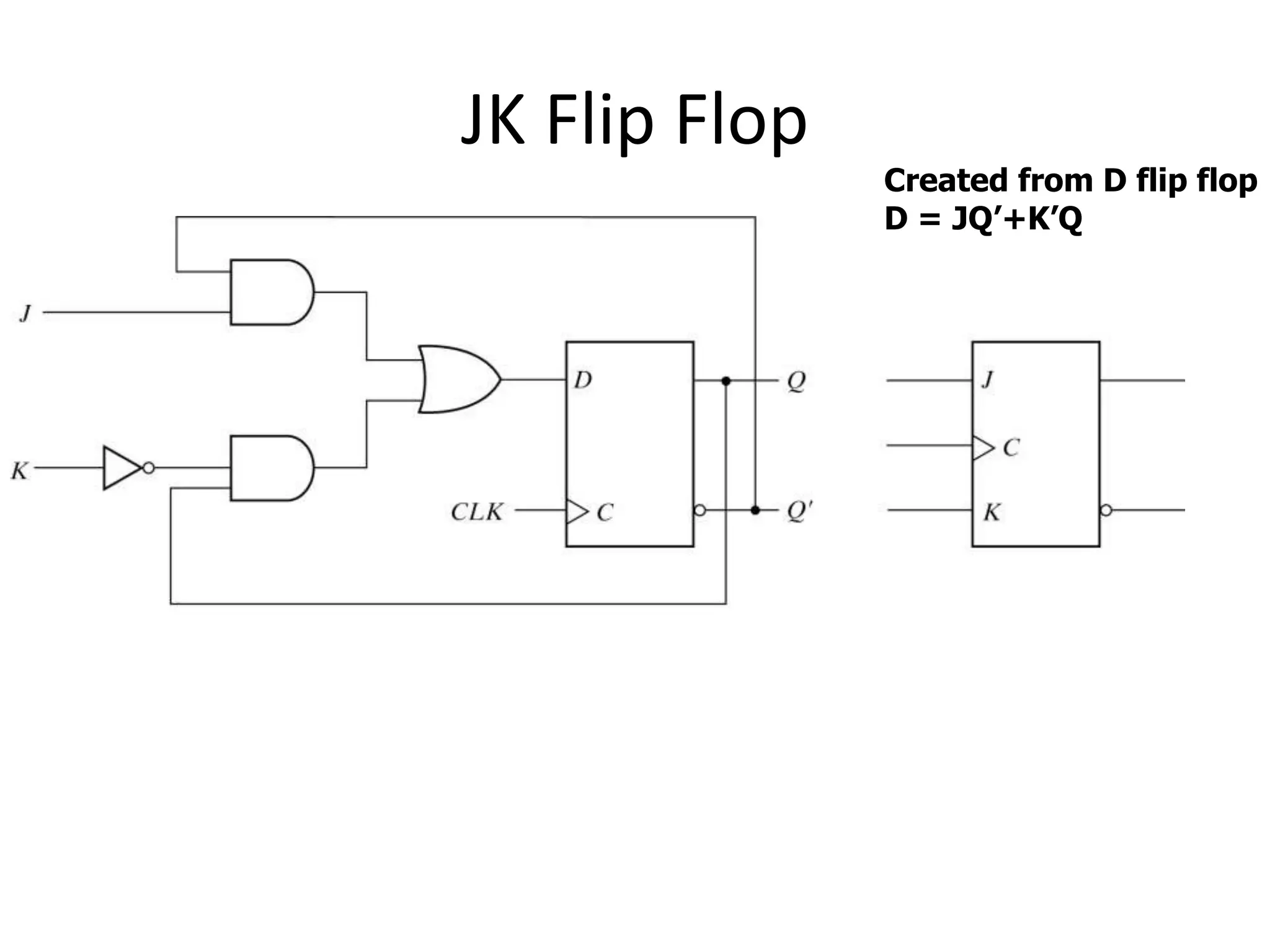
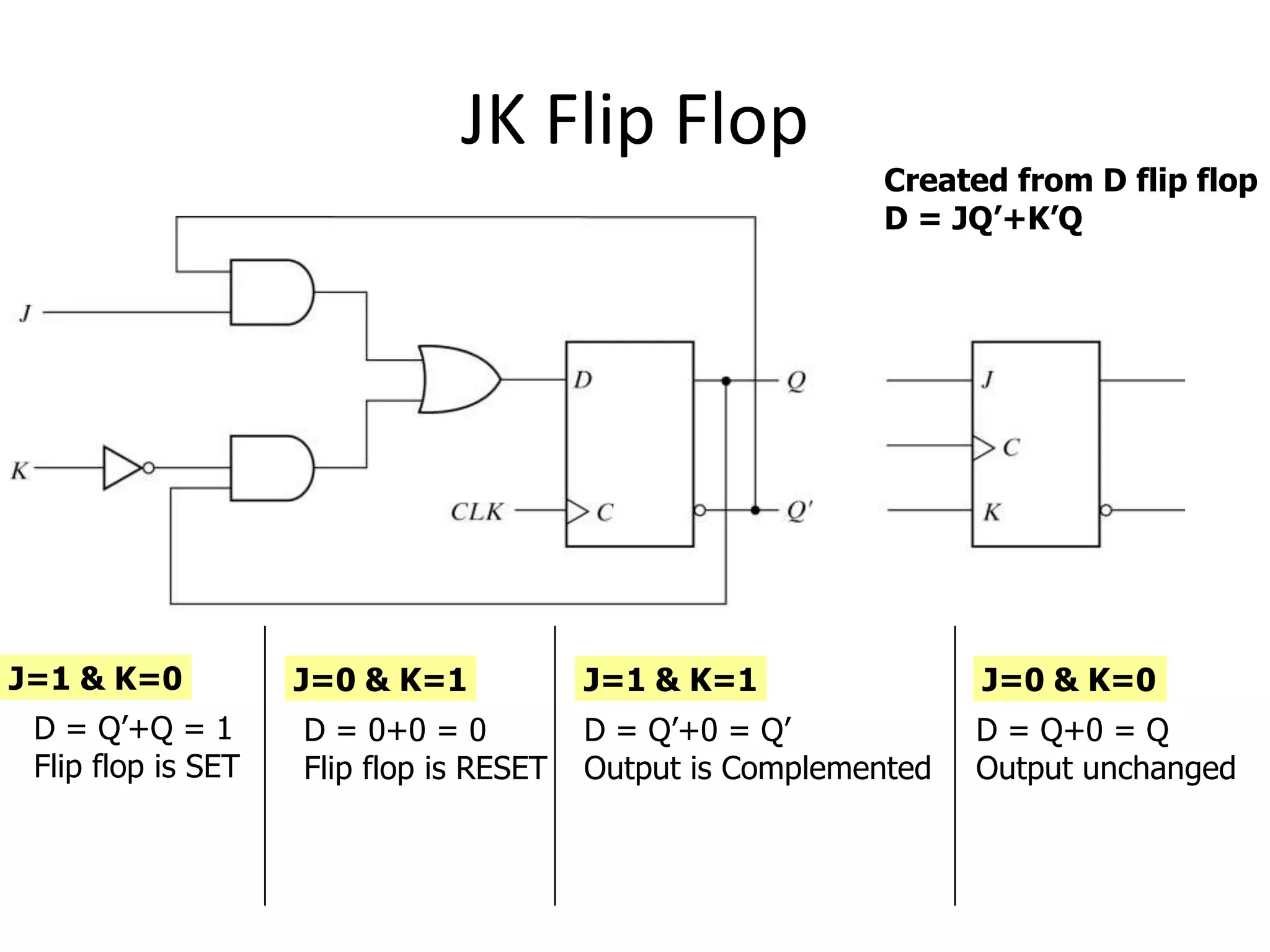
3) Flip-flops are edge-triggered versions of latches that only change state on a clock edge, making them easier to synchronize in larger circuits than latches.