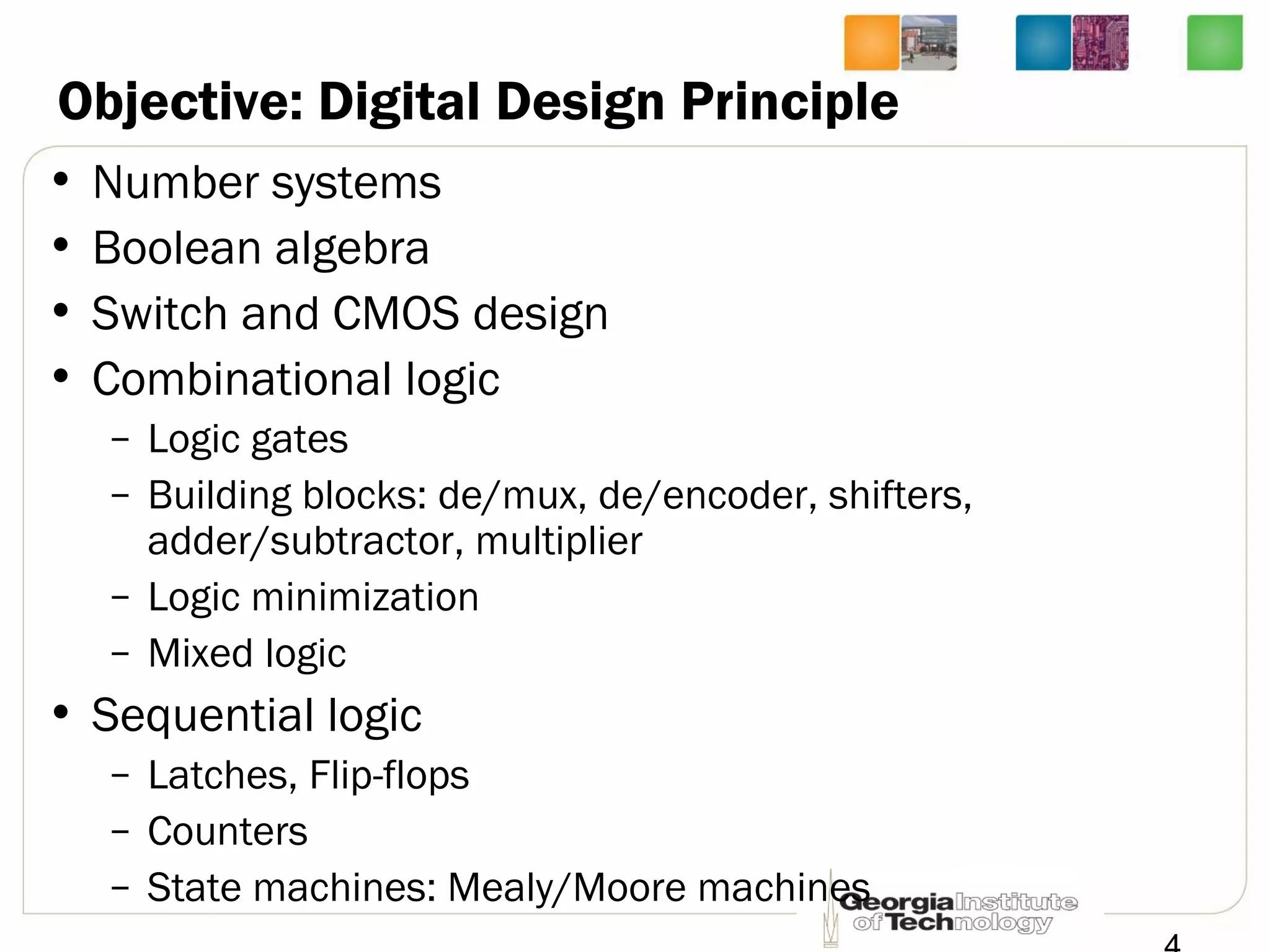
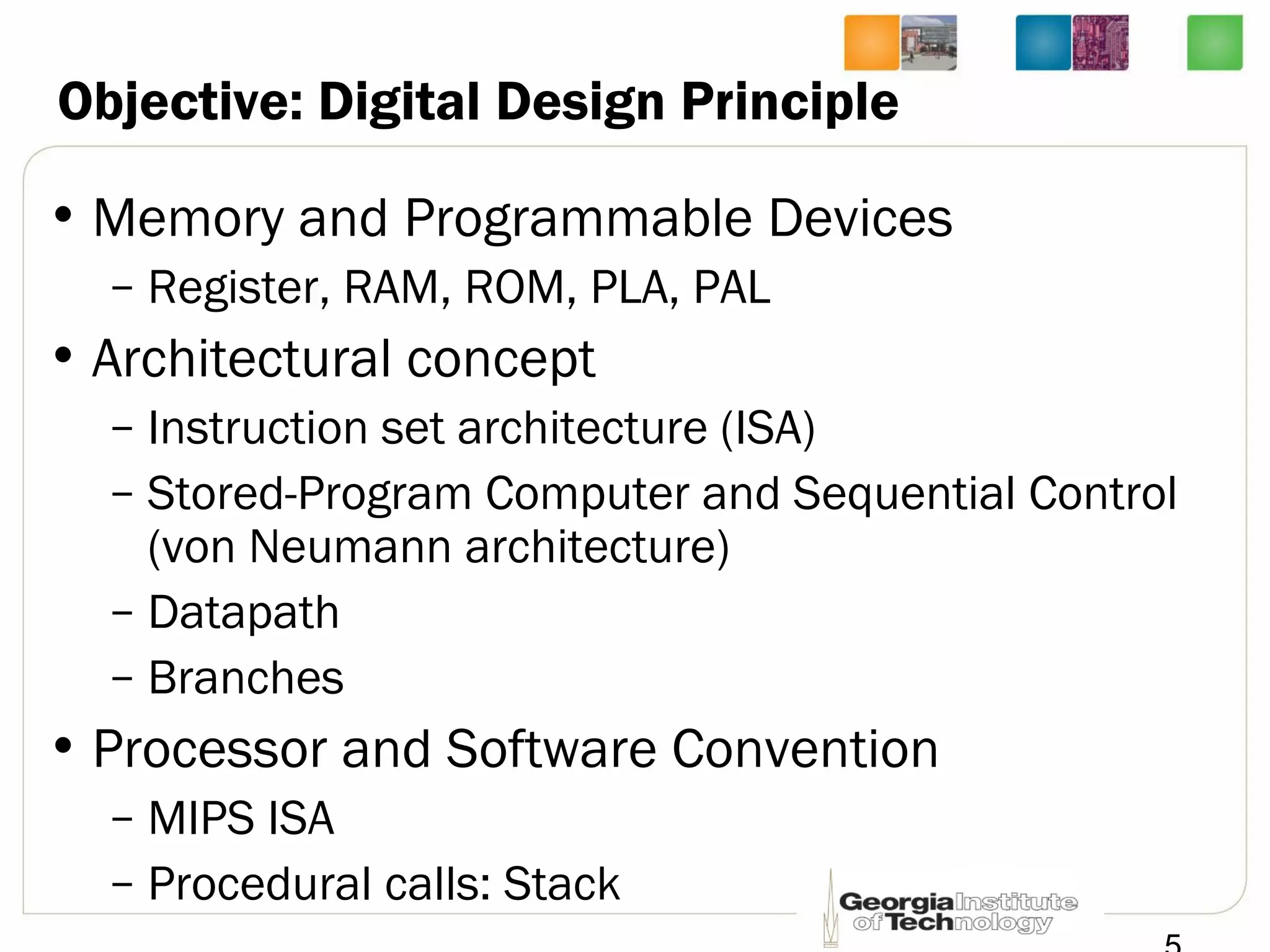
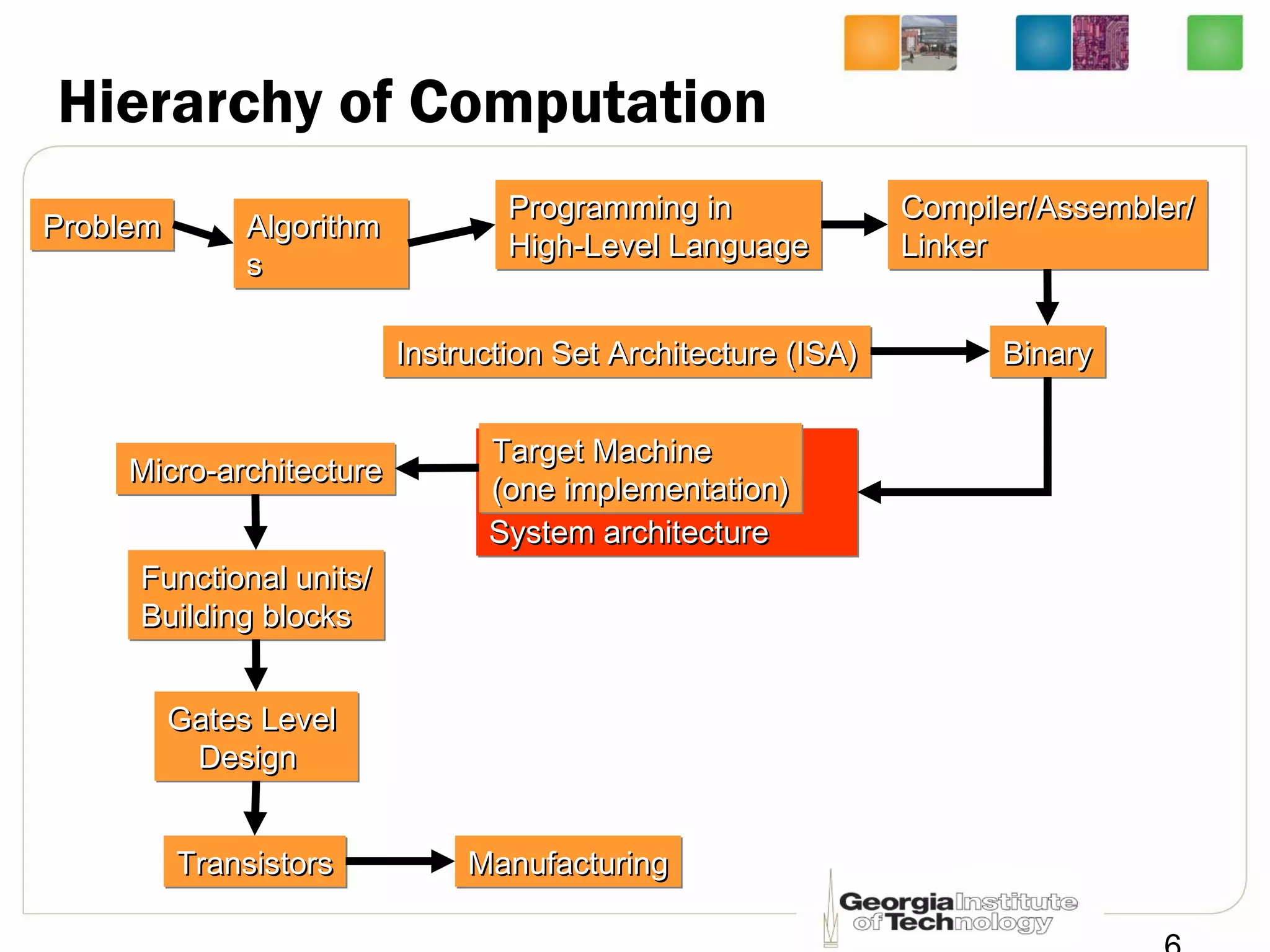
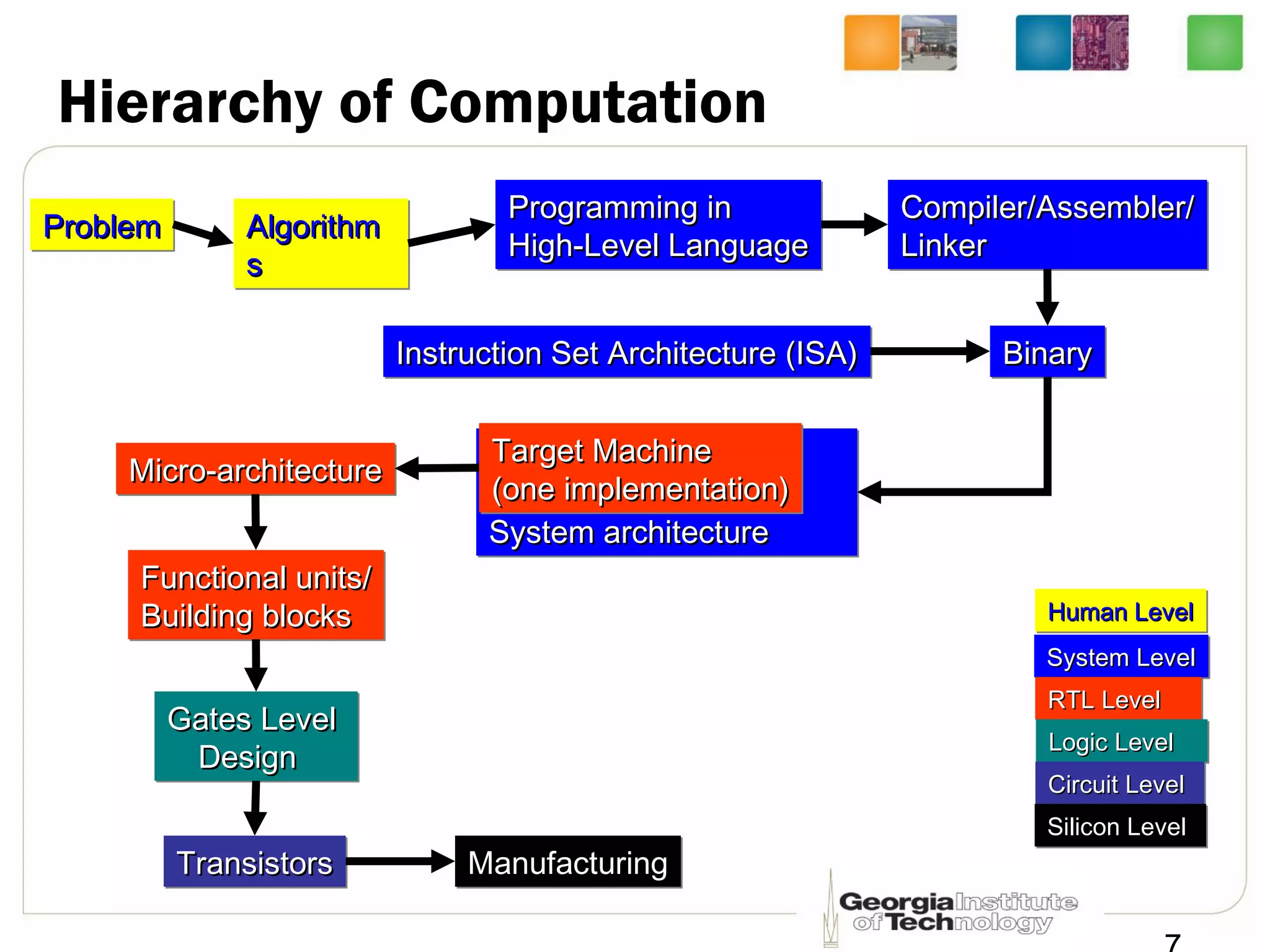
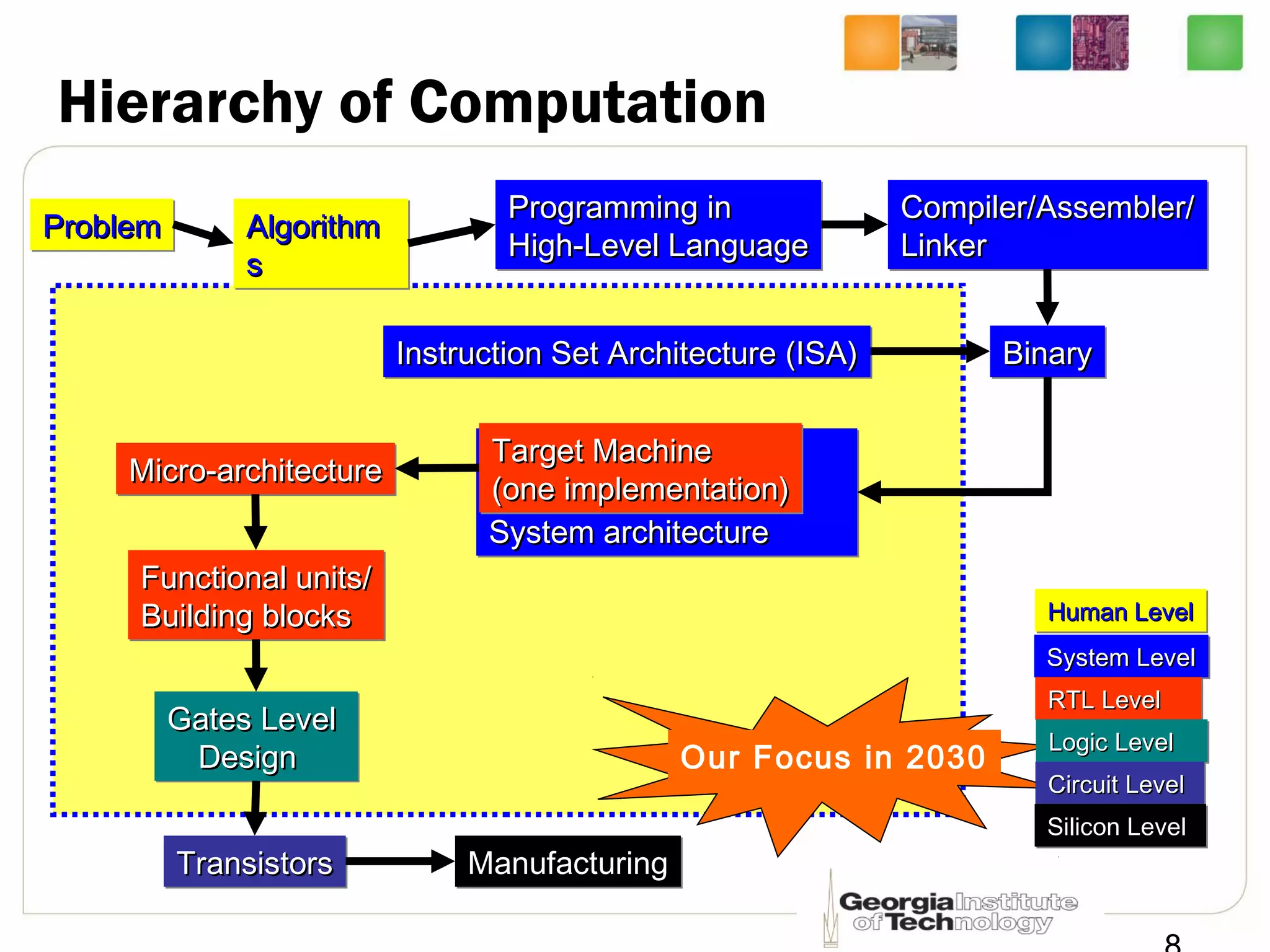
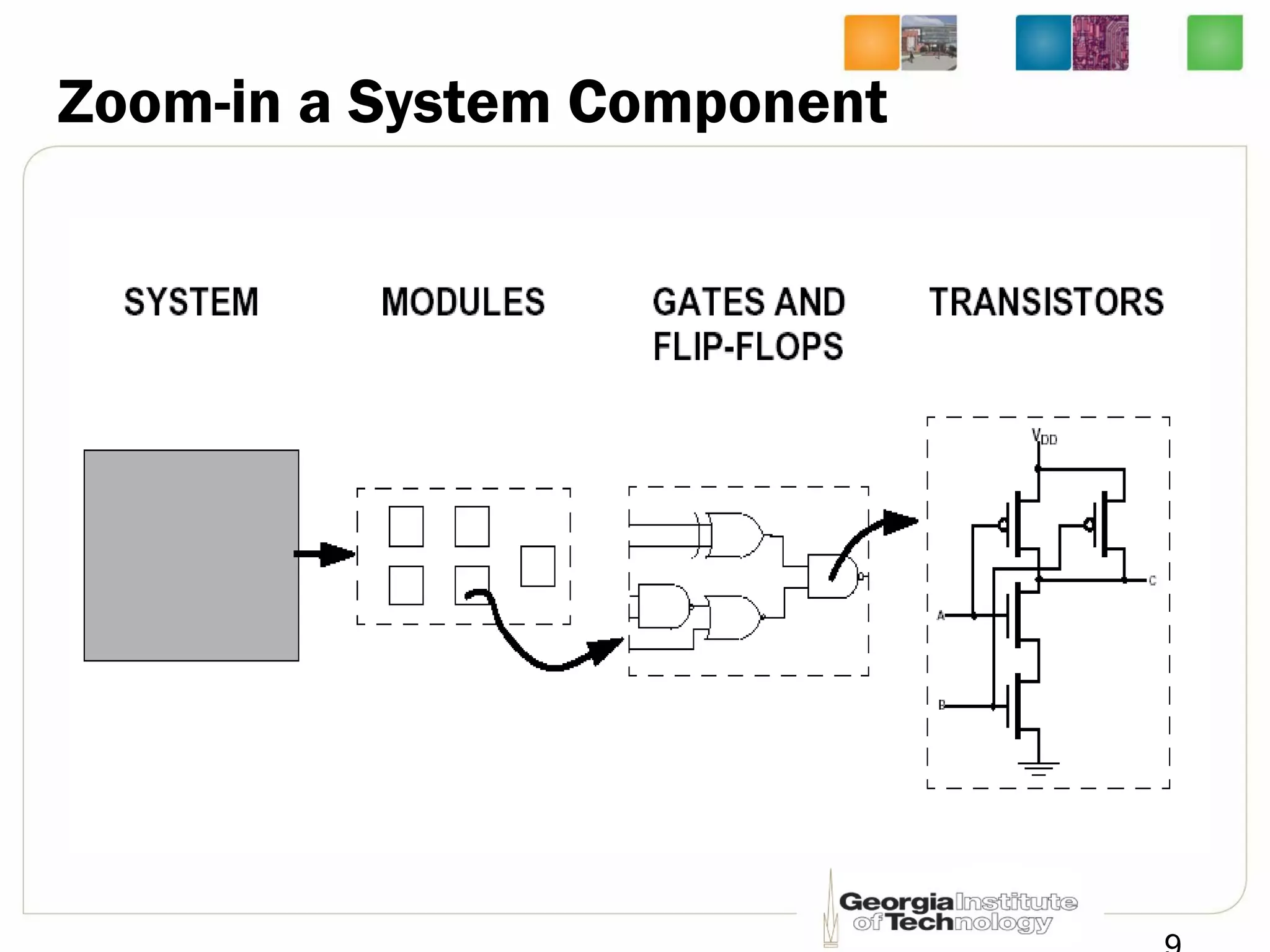
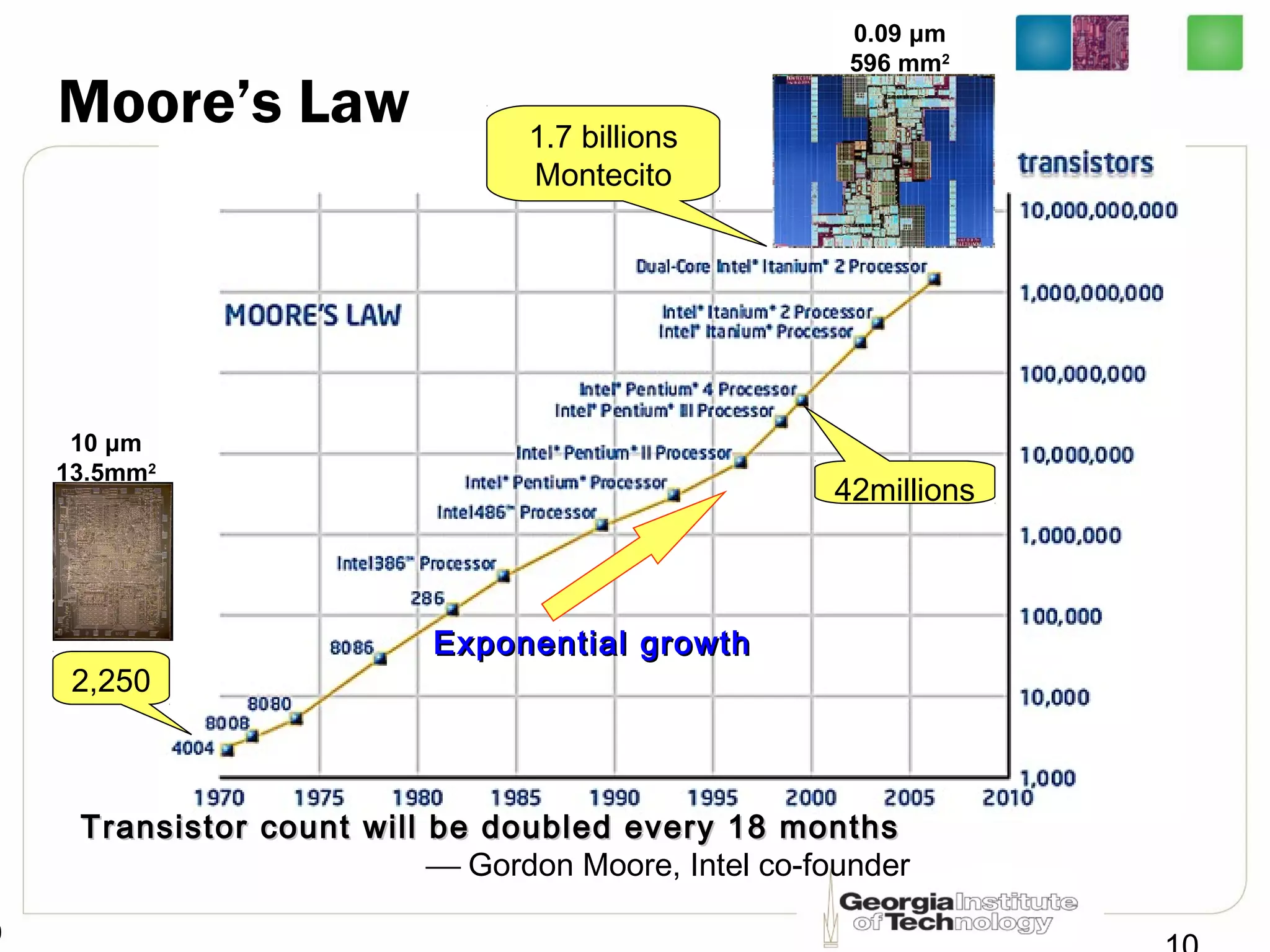
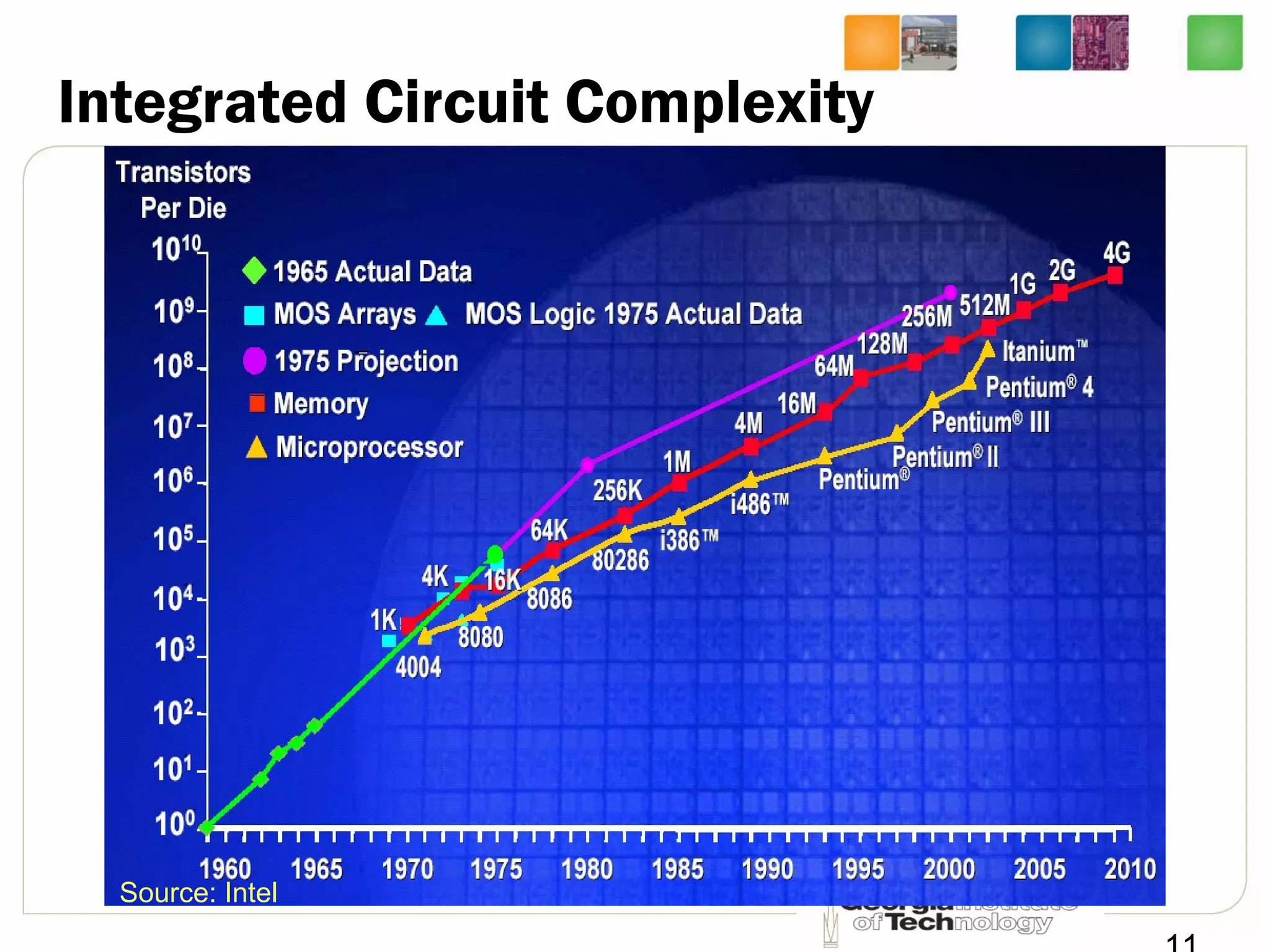
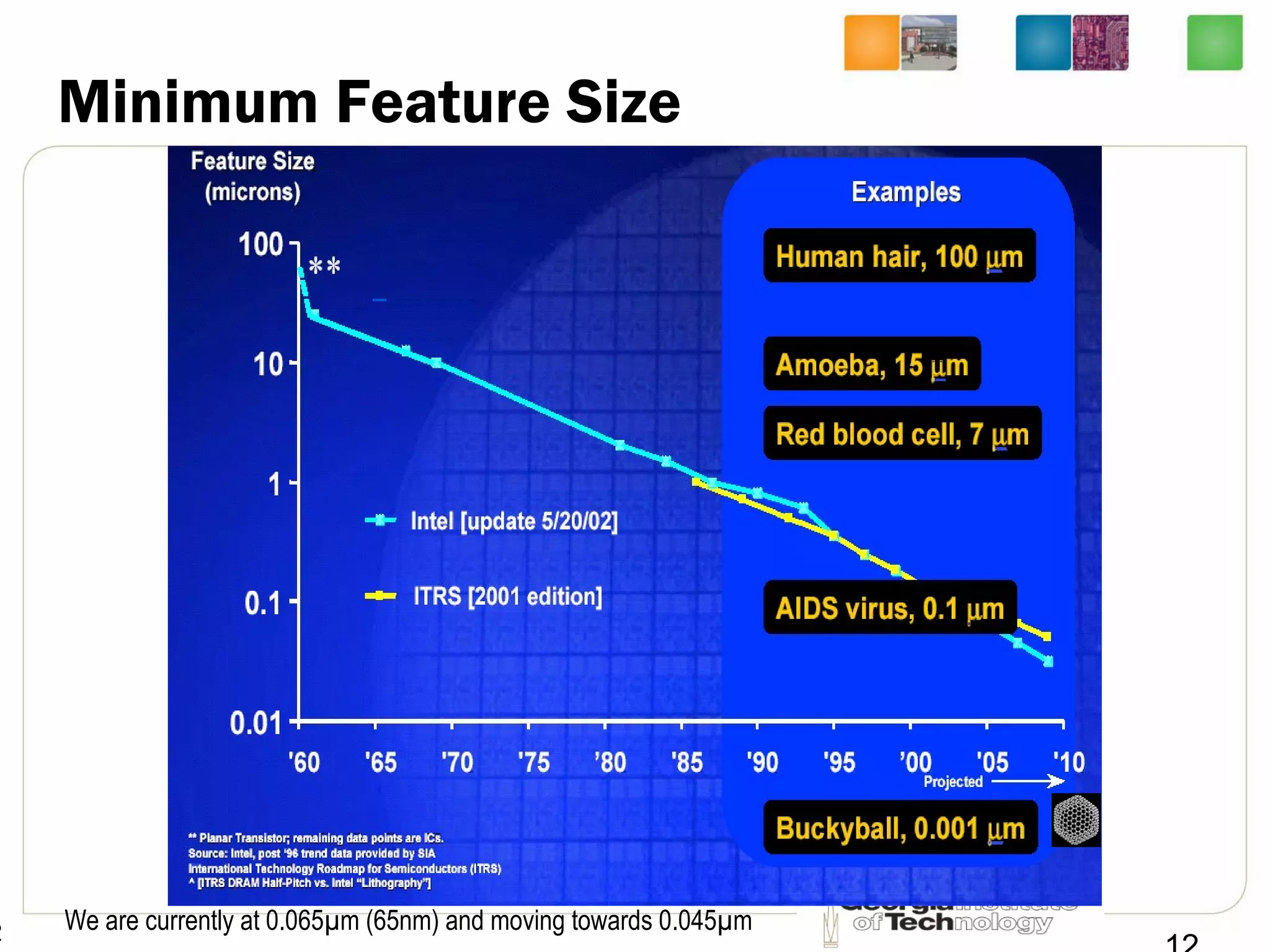
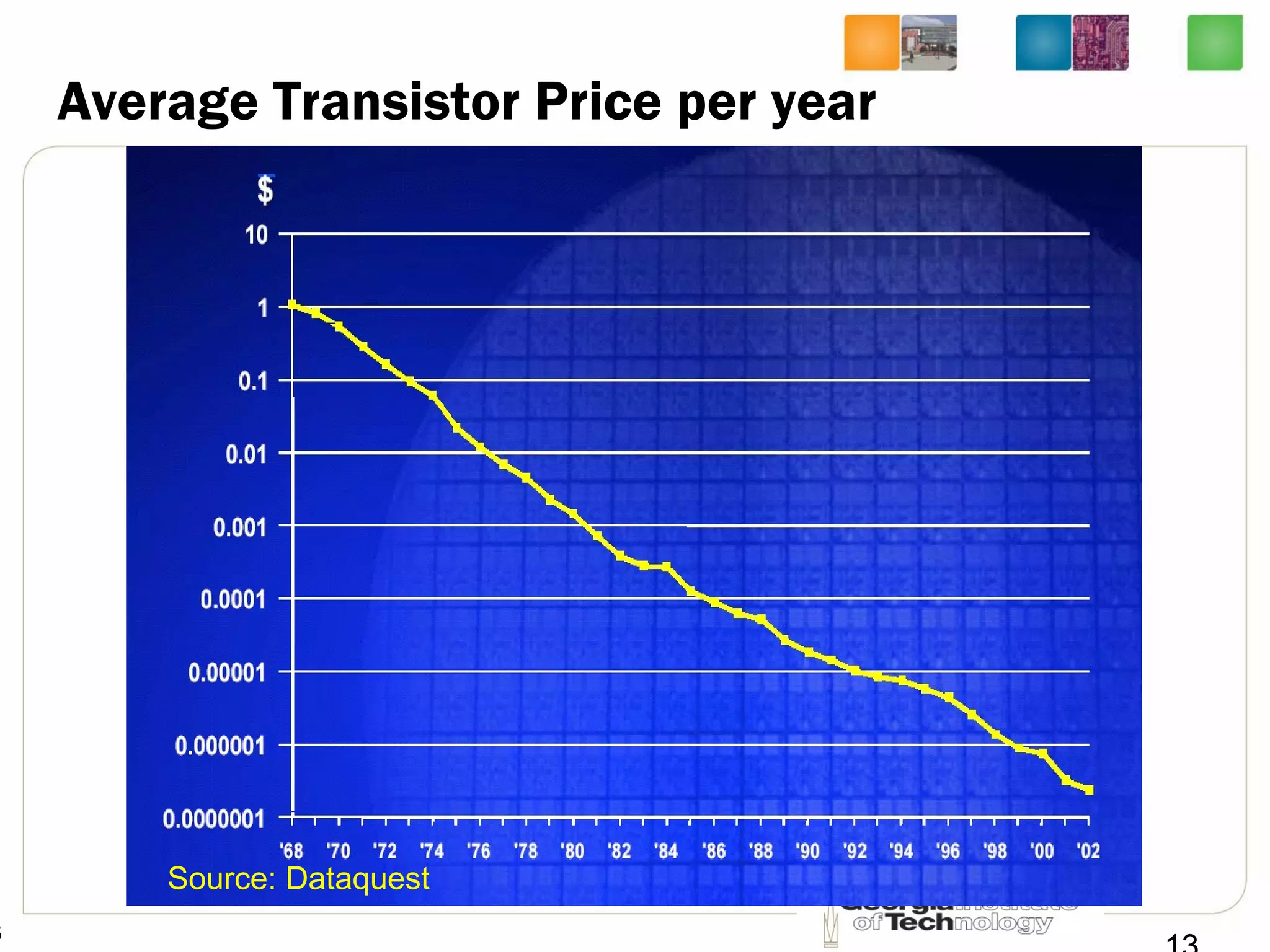
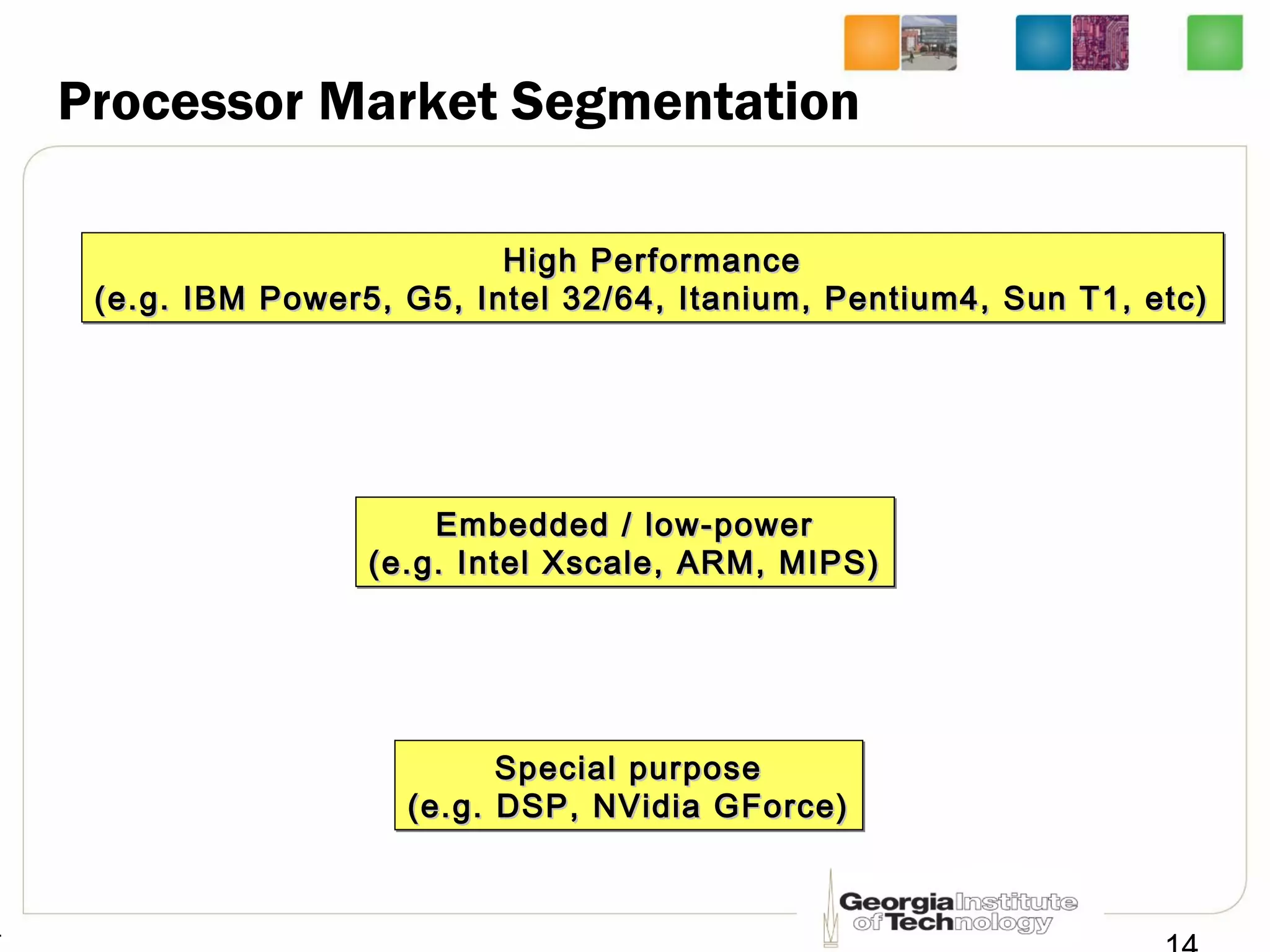
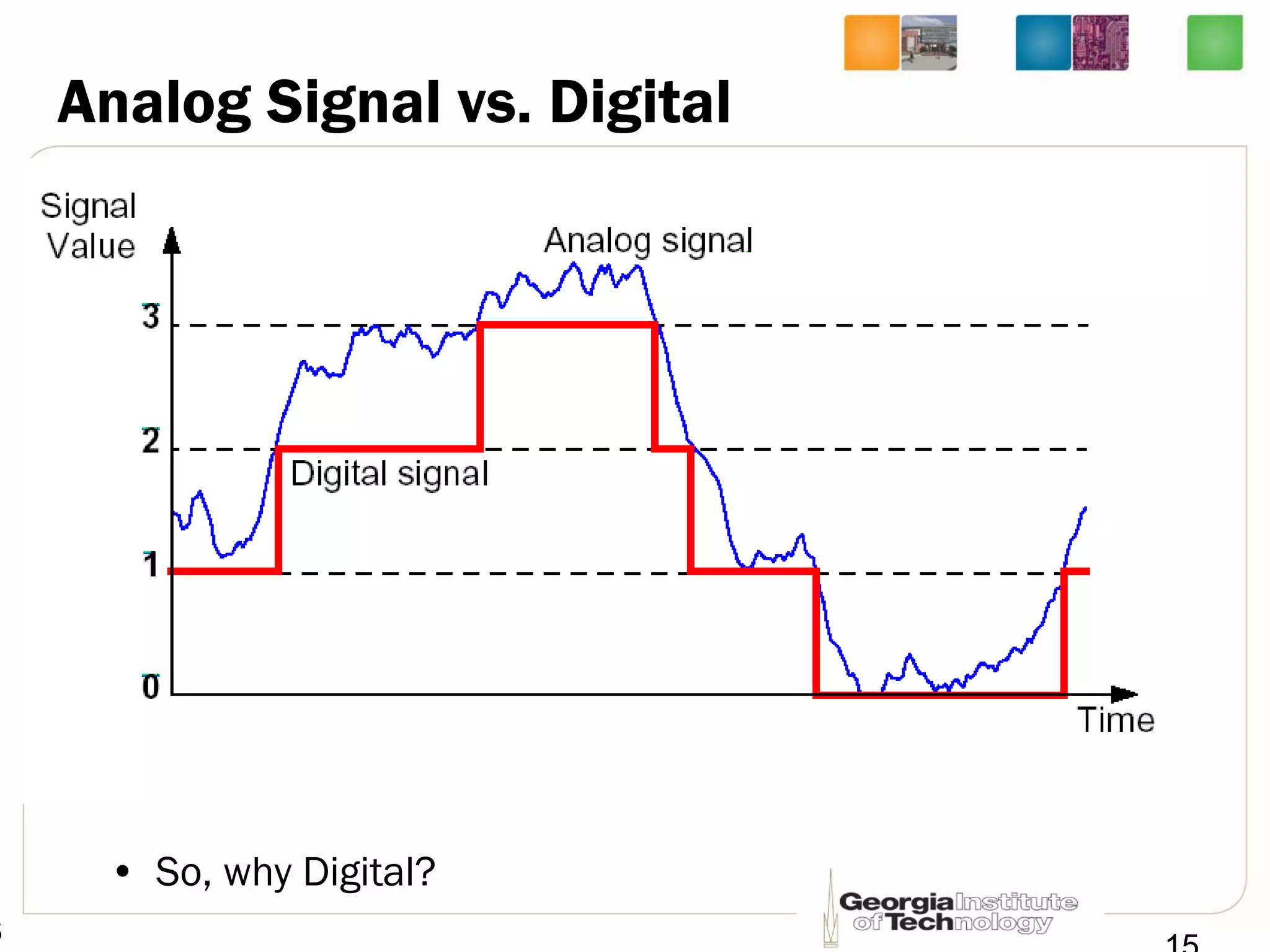
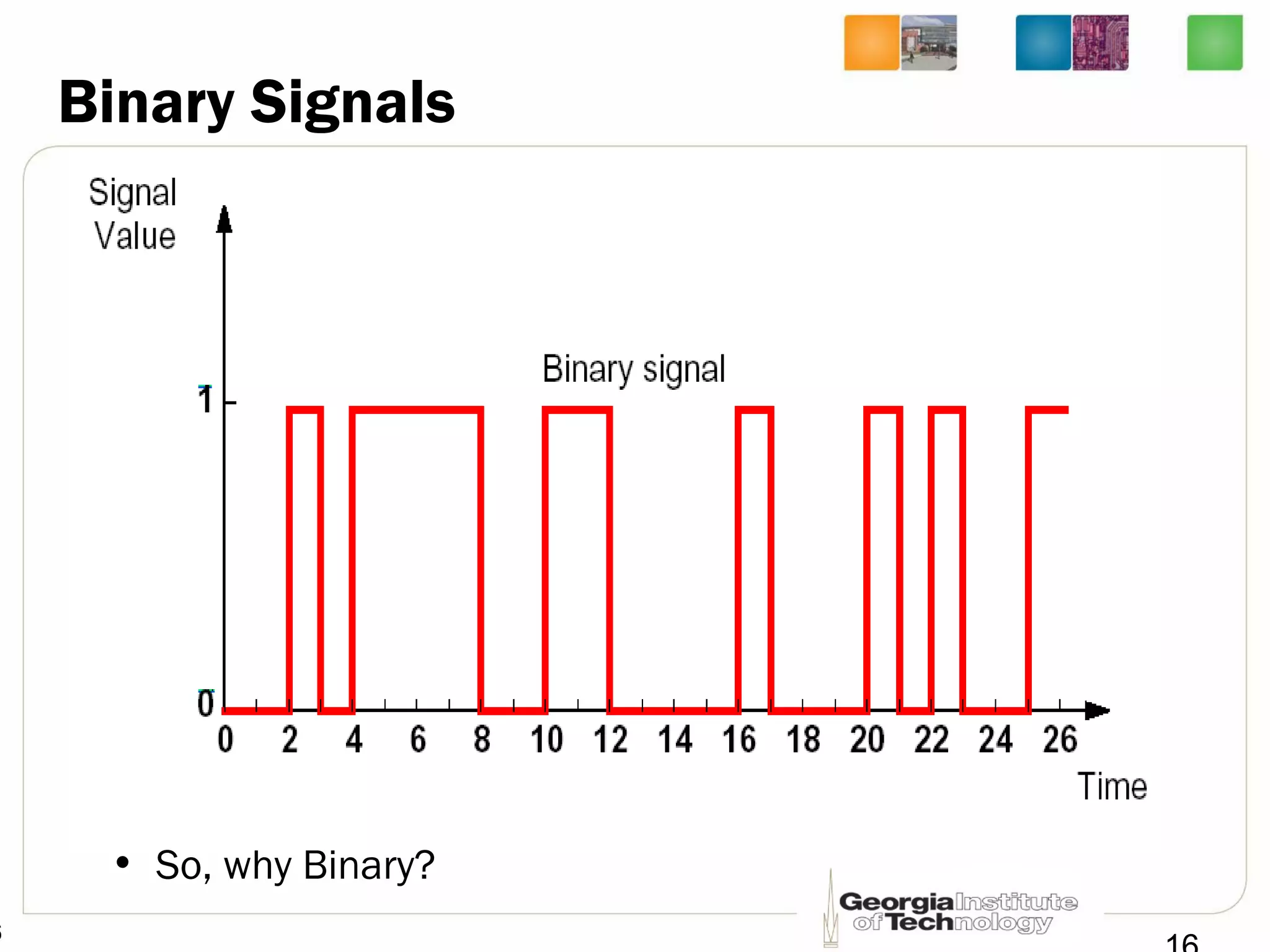
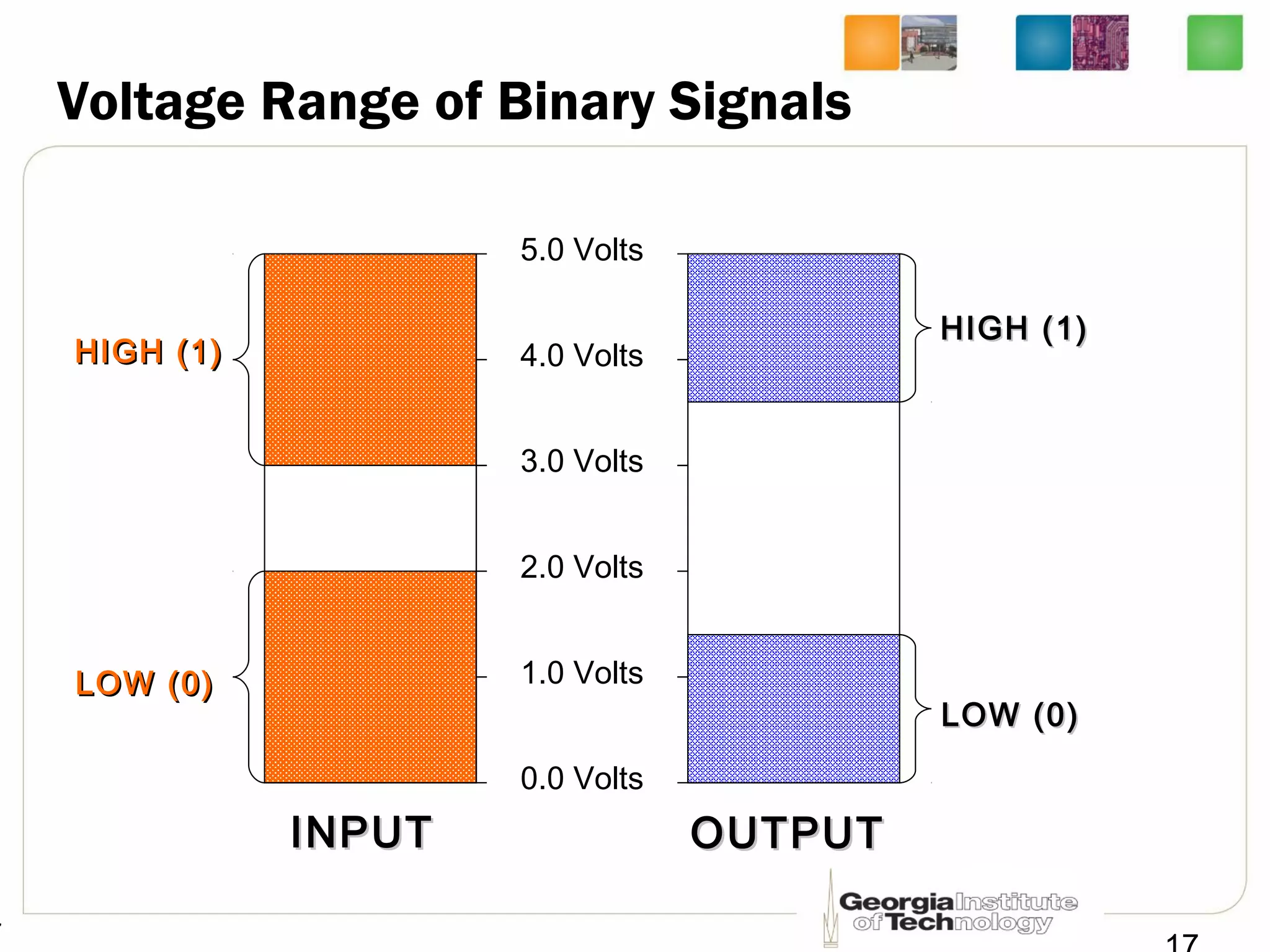
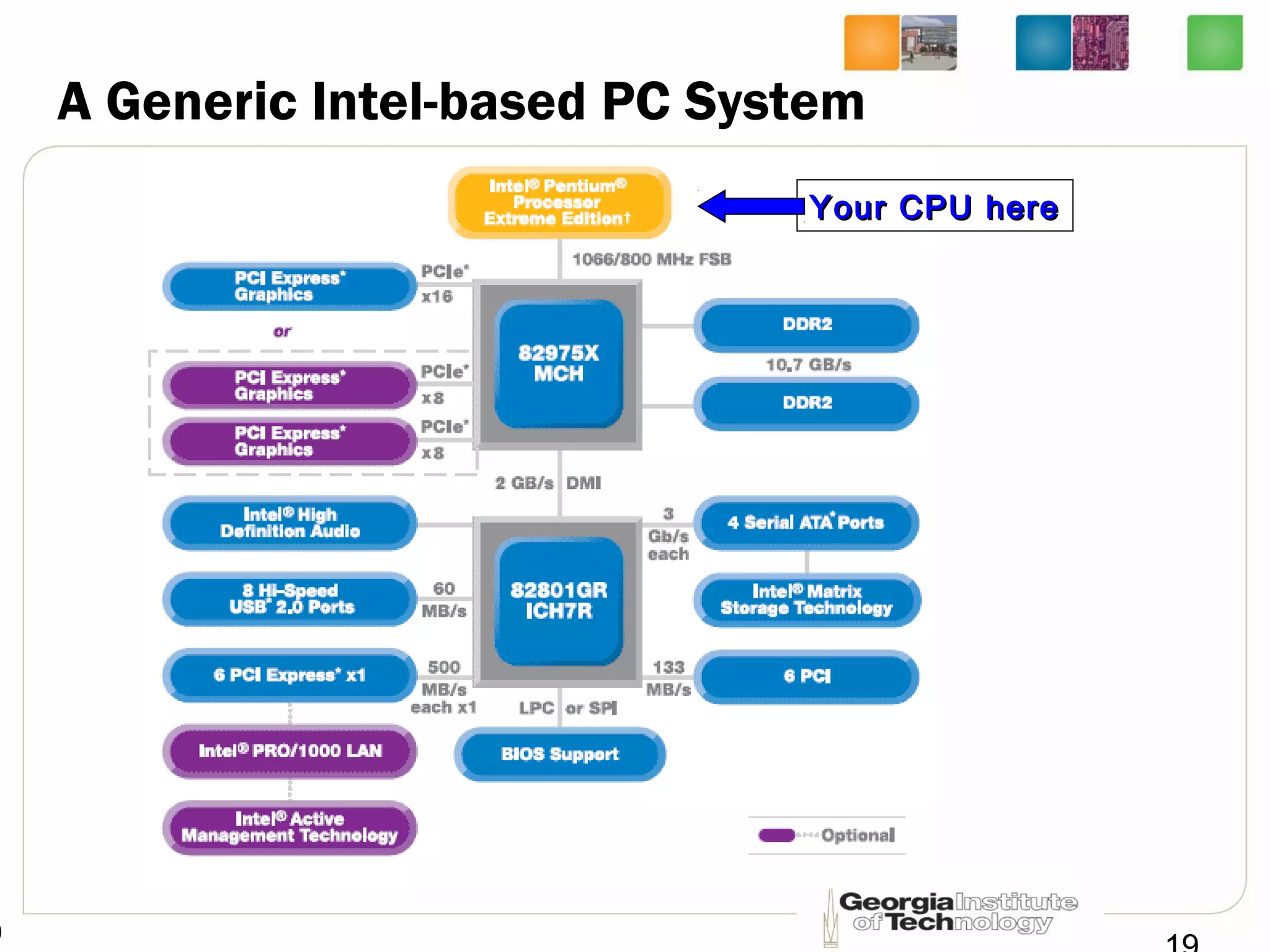
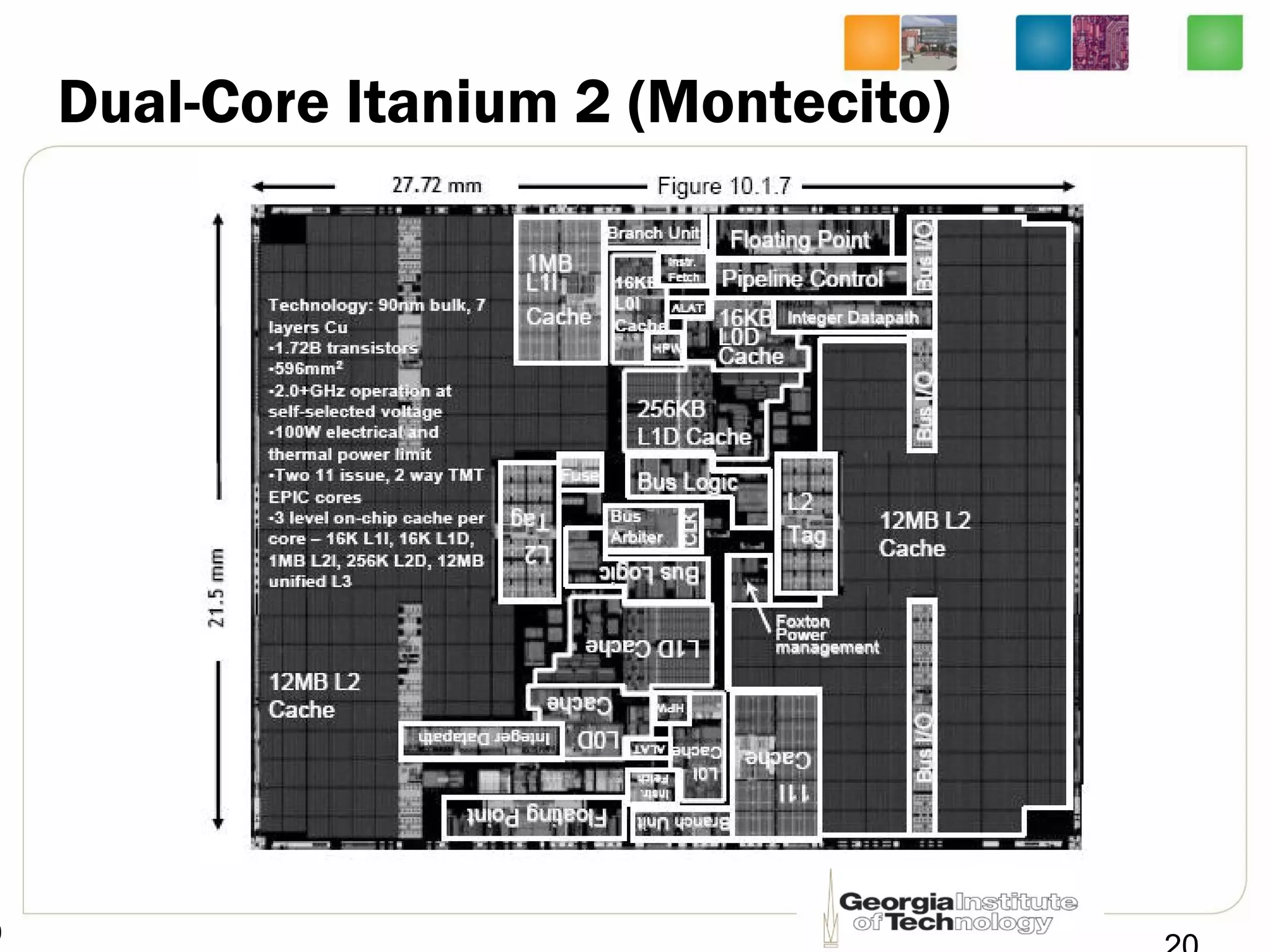
This document provides an overview of ECE2030 Introduction to Computer Engineering course. It introduces the instructor, Prof. Hsien-Hsin Sean Lee, and lists course details such as materials, assignments, exams, grading policy. It outlines the course objectives which include digital design principles like number systems, Boolean algebra, combinational and sequential logic. The focus will be on levels below system architecture like microarchitecture, gates and transistor levels.


![ECE2030 Syllabus
• Grading policy
– 3 Homework assignment: 5% each
– 1 Programming assignment: 10%
– 3 in-class exams: 15% each
– 1 final exam: 30%
– [100,90]=A; (90,80]=B; (80,70]=C,(70,55]=D,(55,0]=F
• All homework: turn-in in the first 5 minutes “in
class” of the due day
• All exams: closed books, closed notes, no calculator
• Honor code
• Use webct (http://webct.gatech.edu) for your
homework and exam grades](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lec1-intro-150829104637-lva1-app6892/75/Lec1-Intro-to-Computer-Engineering-by-Hsien-Hsin-Sean-Lee-Georgia-Tech-Intro-3-2048.jpg)