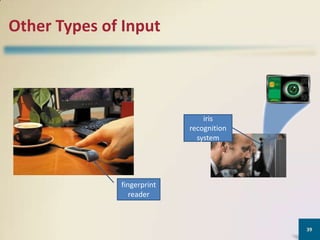
This document provides an overview of various computer input and output devices. It describes common keyboard types and features found on desktop and mobile keyboards. It also discusses different pointing devices like mice, touchpads, trackballs and touch screens. Other types of input covered include graphics tablets, digital cameras, scanners, biometric devices and terminals. The document outlines categories of output such as displays, printers, speakers and data projectors. It provides details on LCD and CRT monitors as well as inkjet, laser and impact printers.