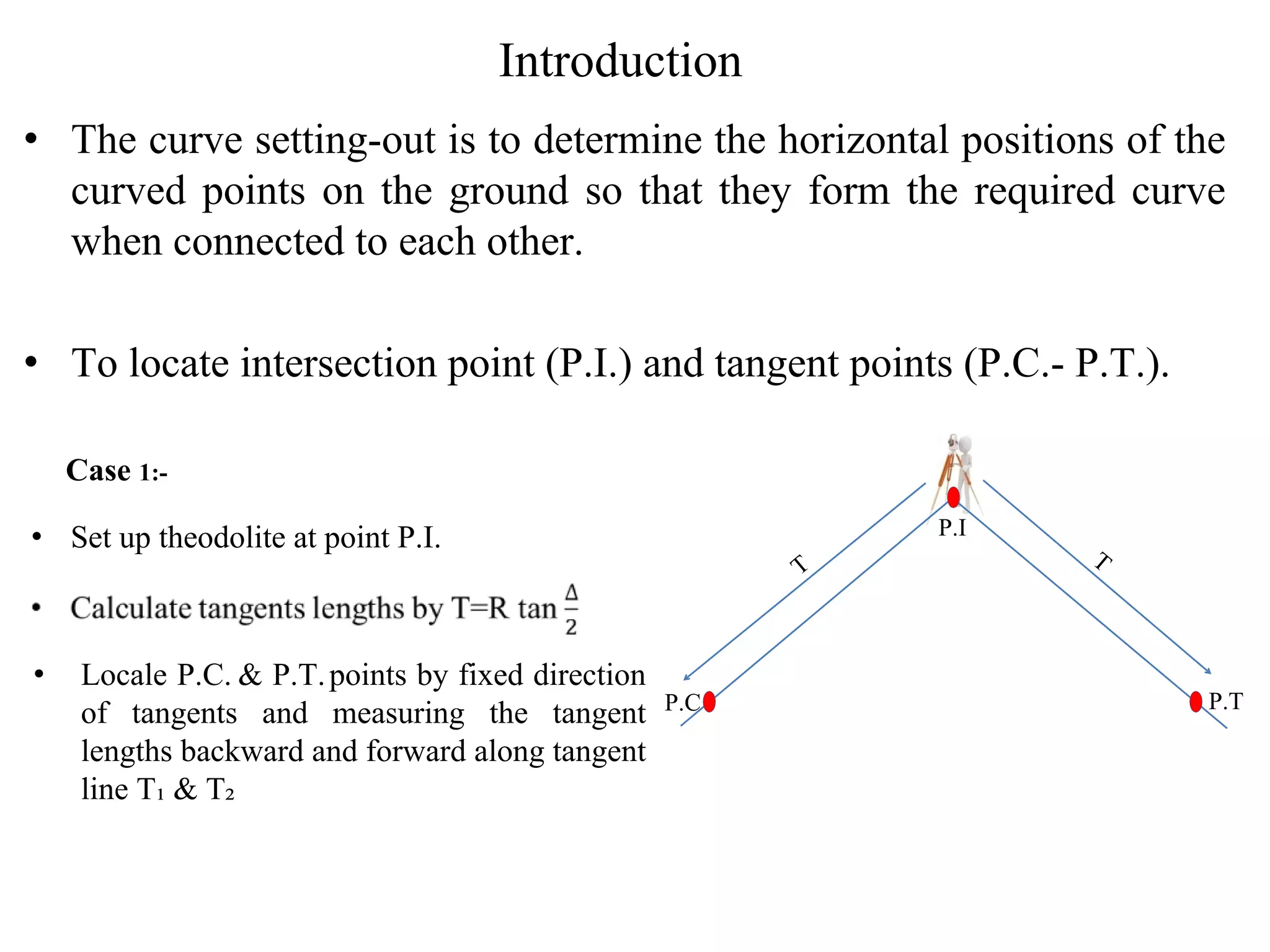
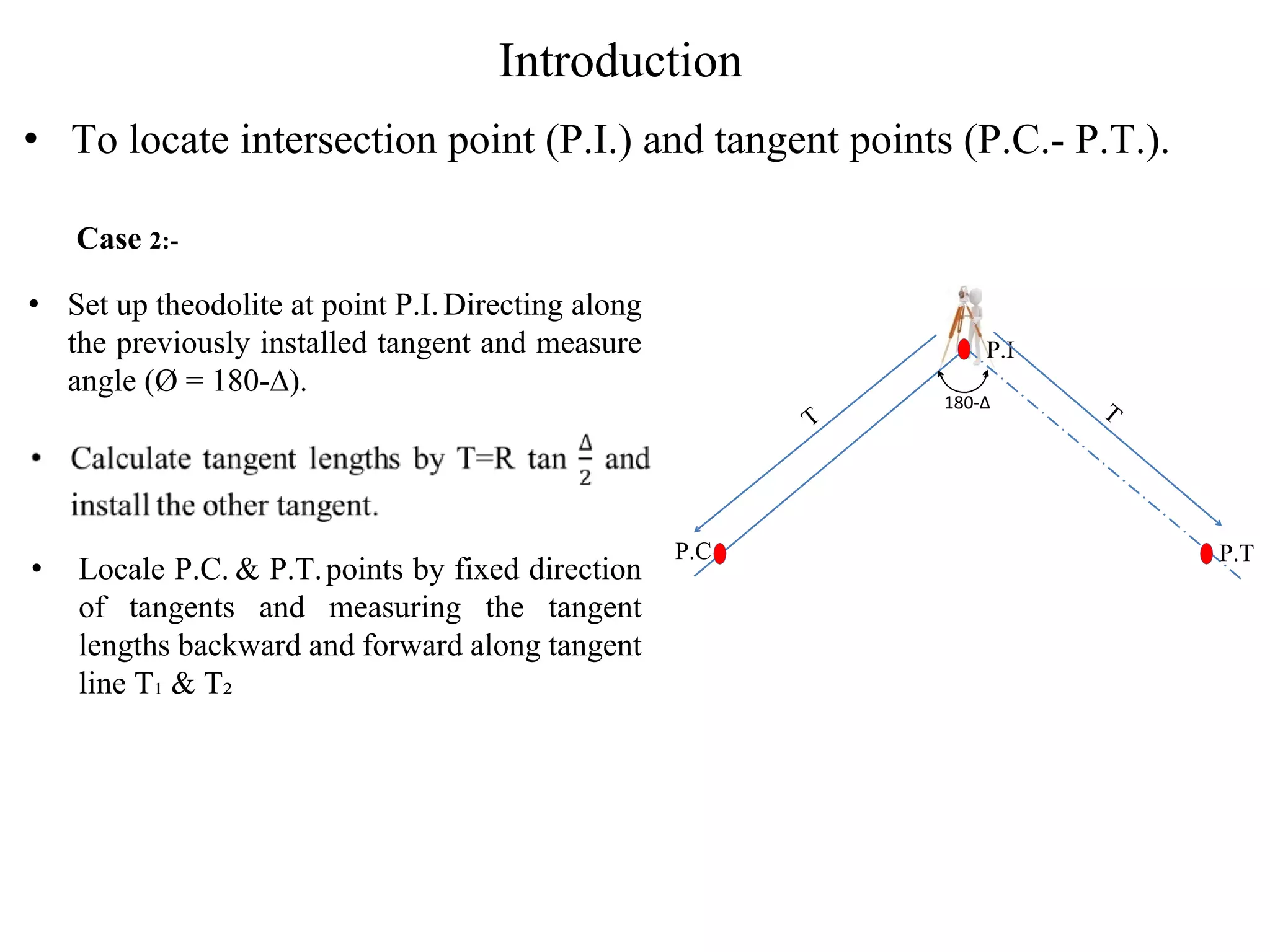
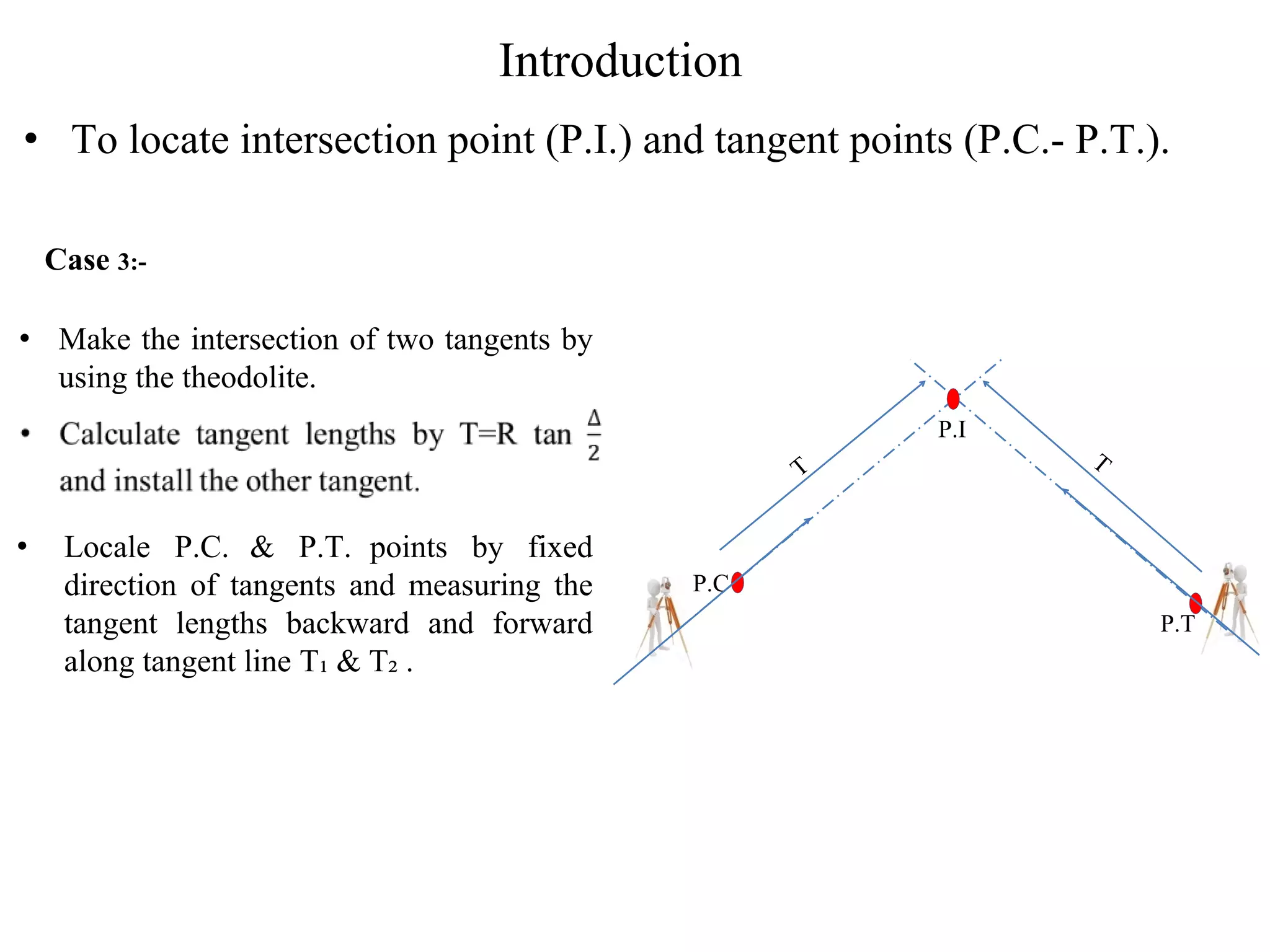
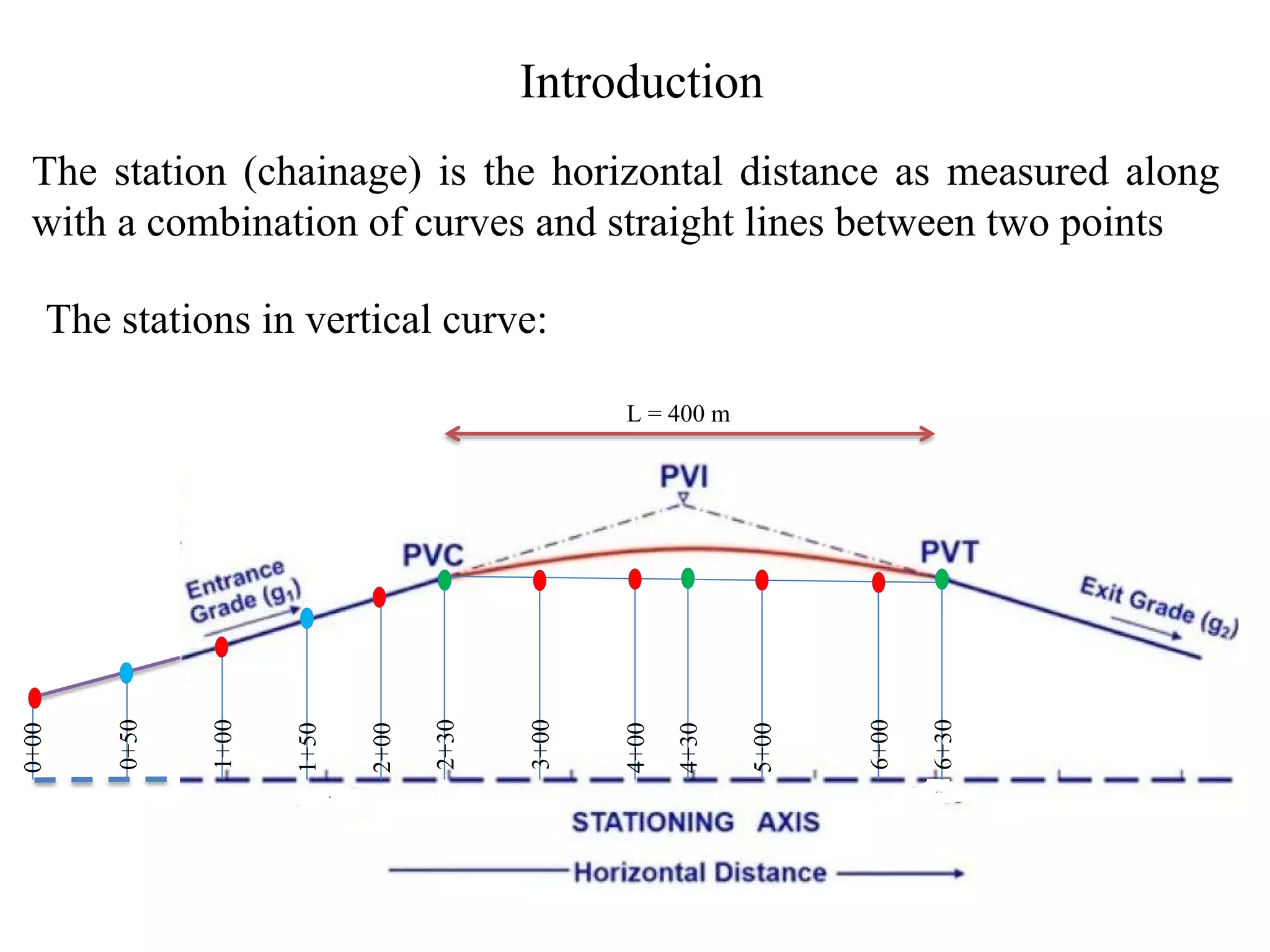
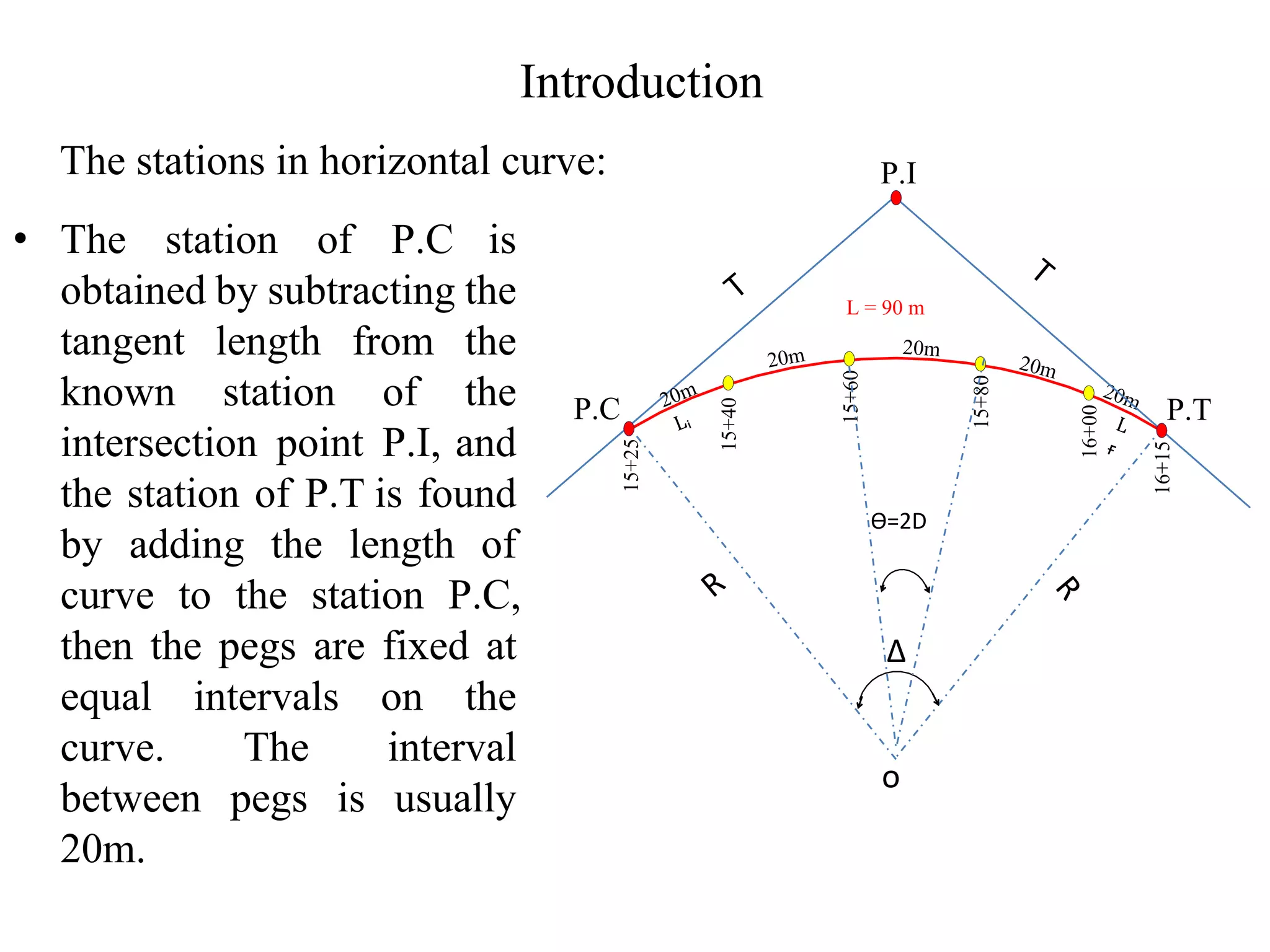
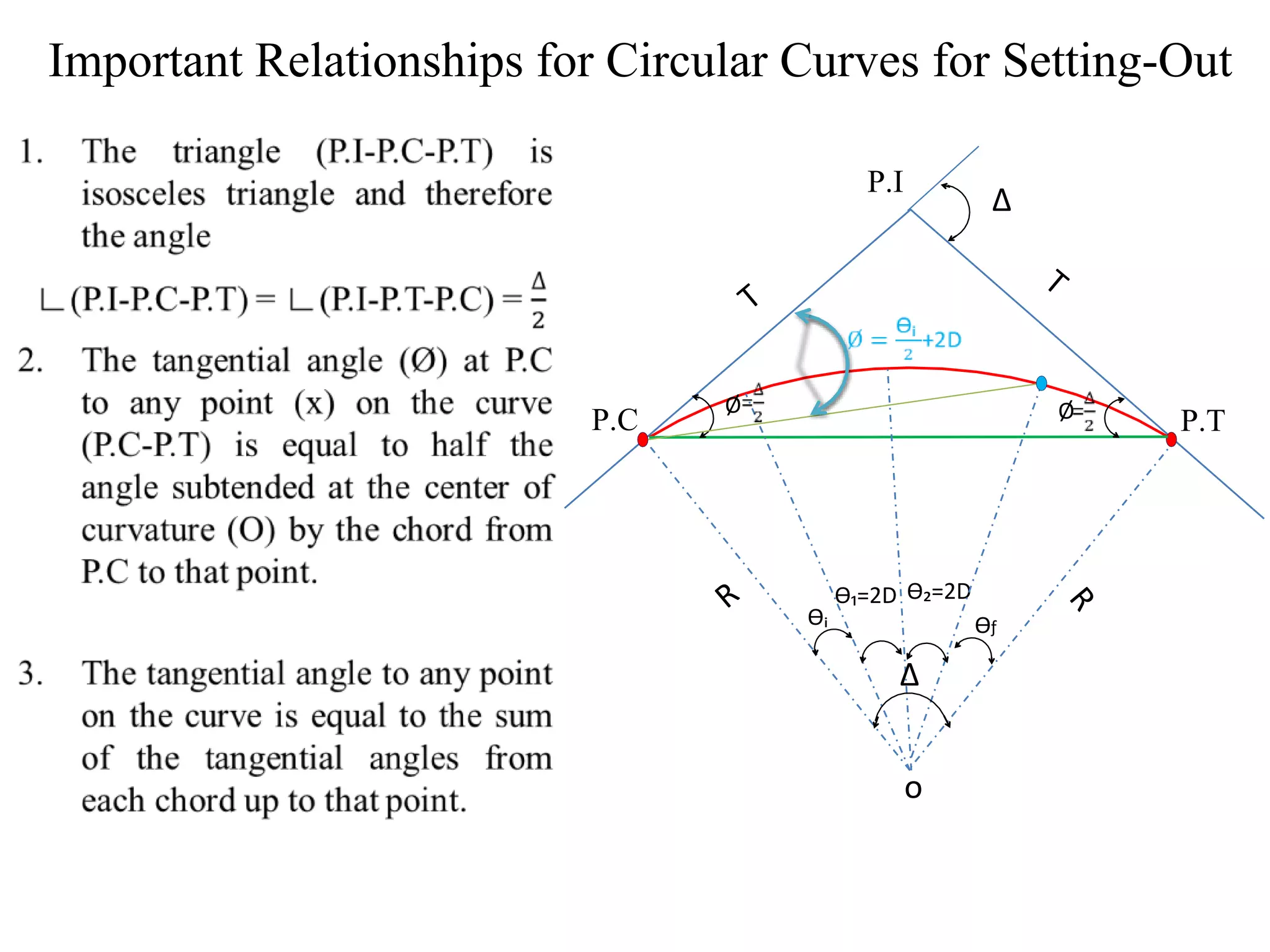
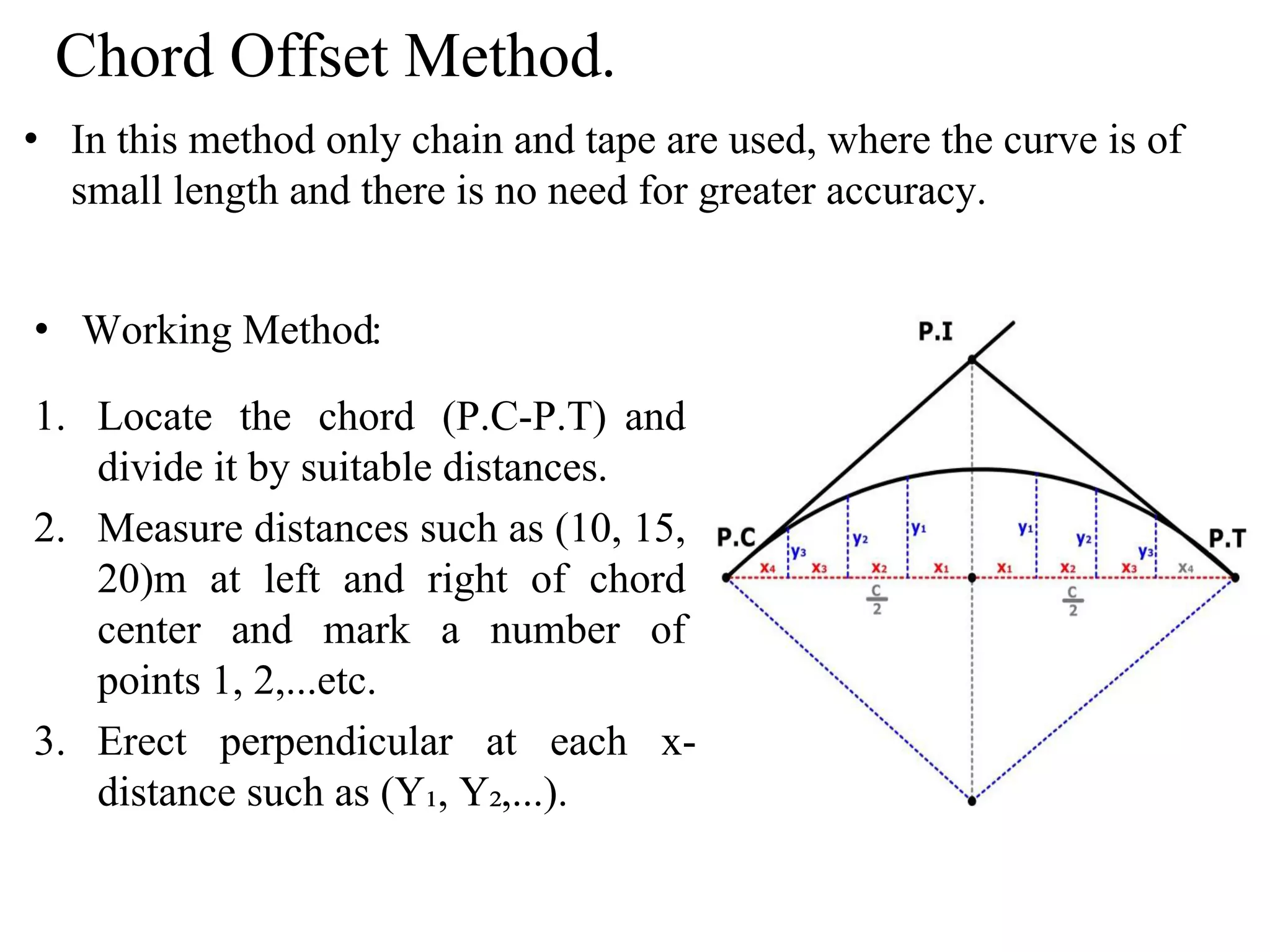
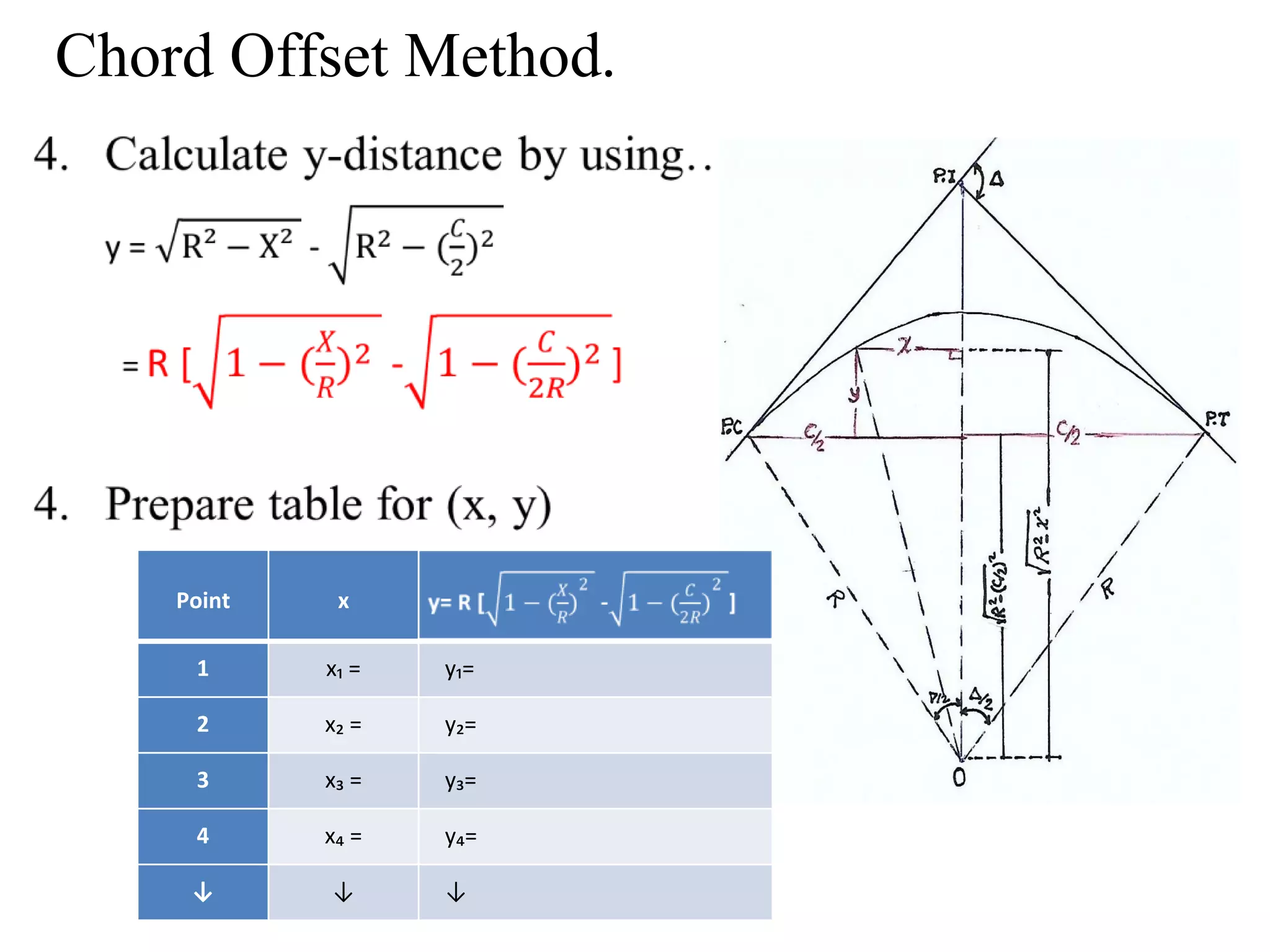
1. The document discusses three methods for setting out a simple circular curve in engineering and surveying projects: the tangential angle method, the tangent offset method, and the chord offset method.
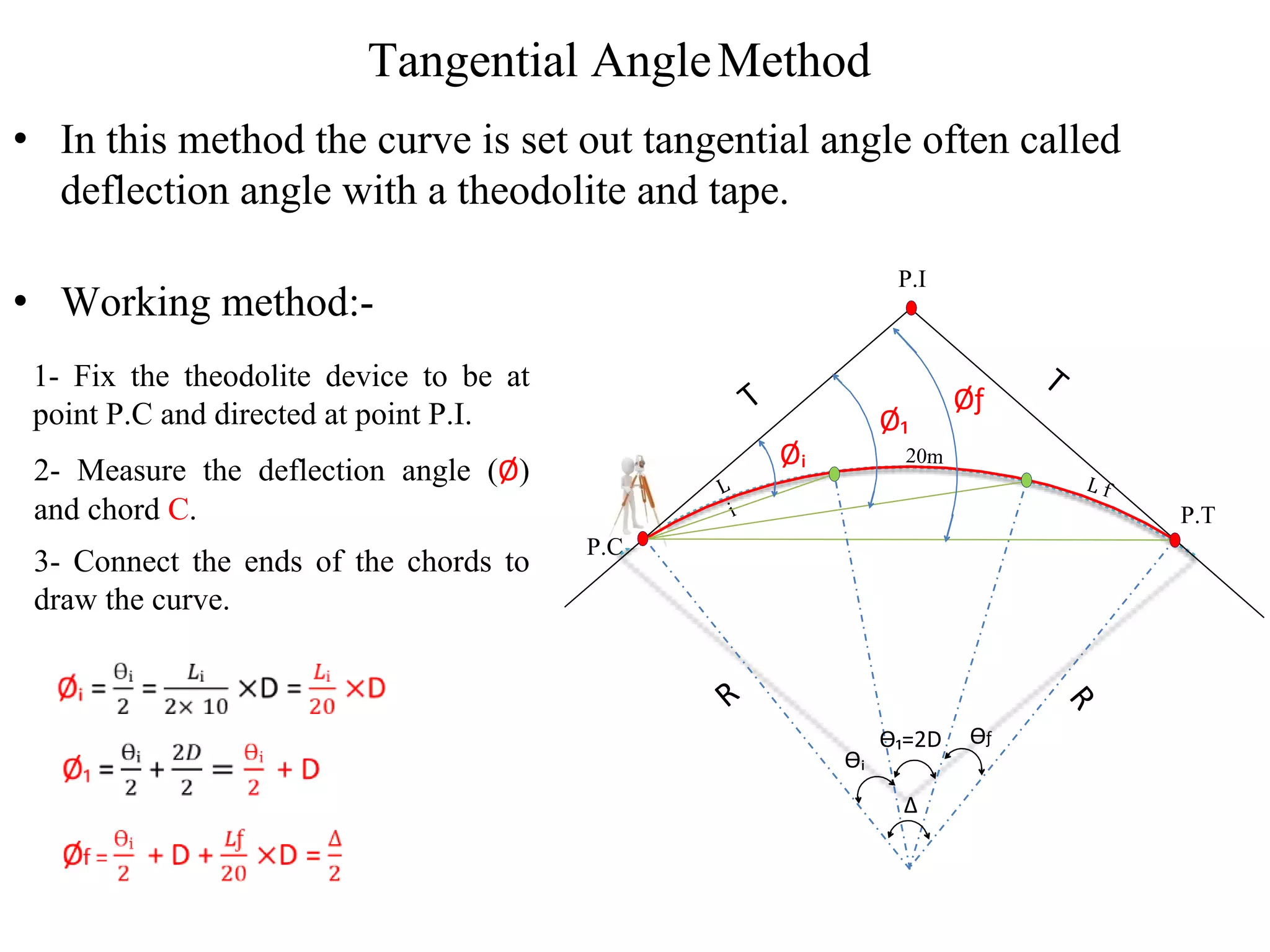
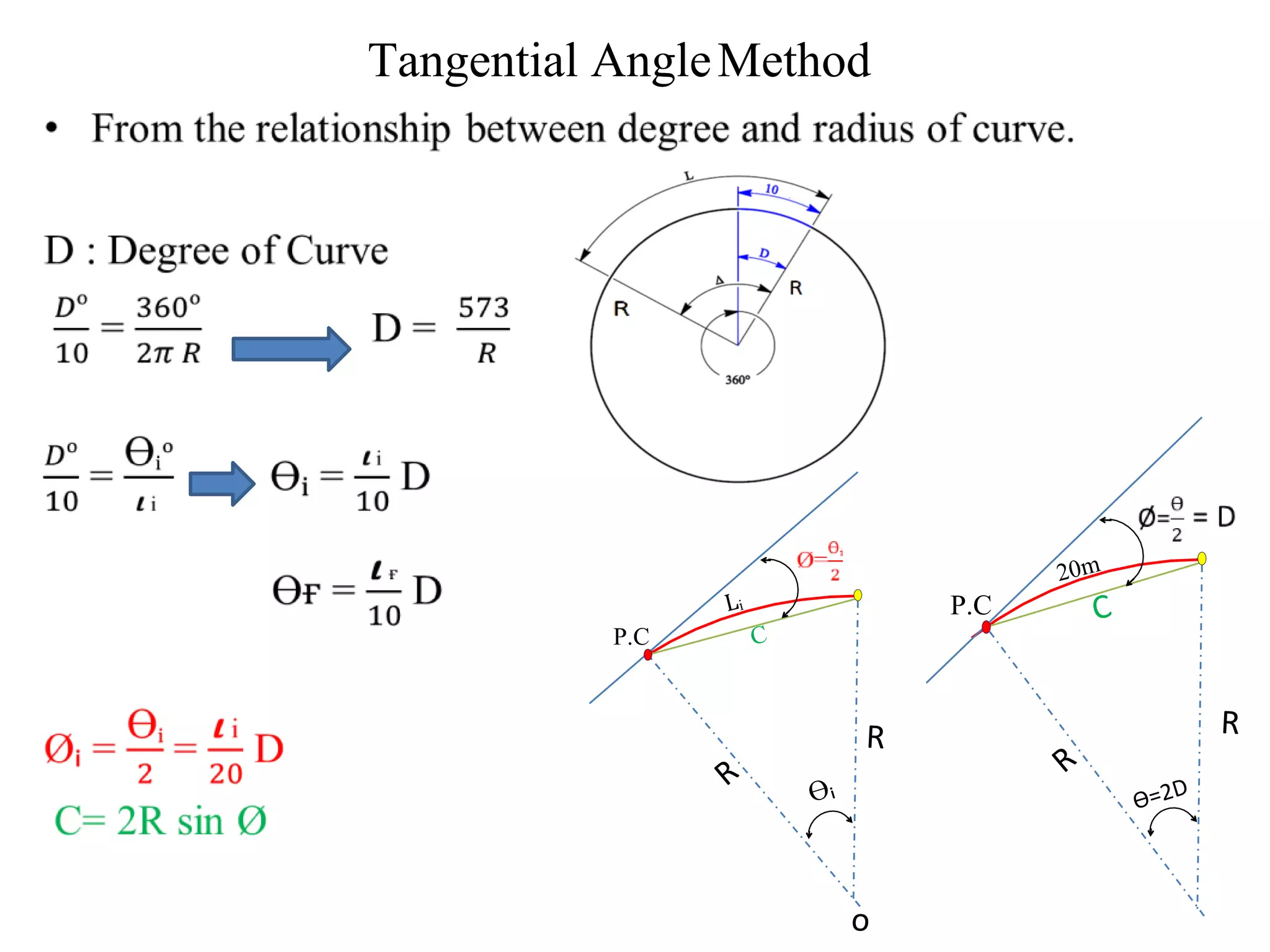
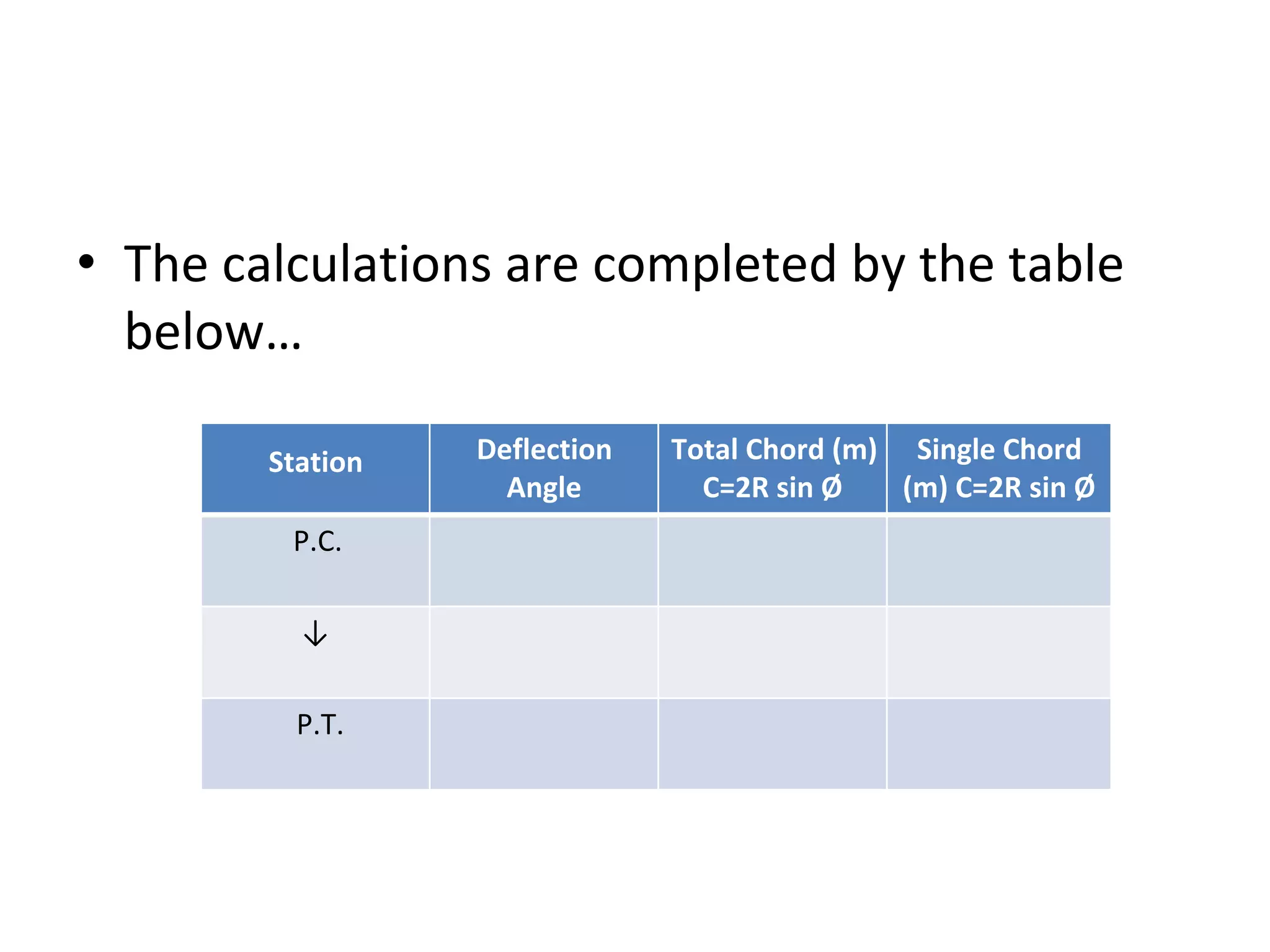
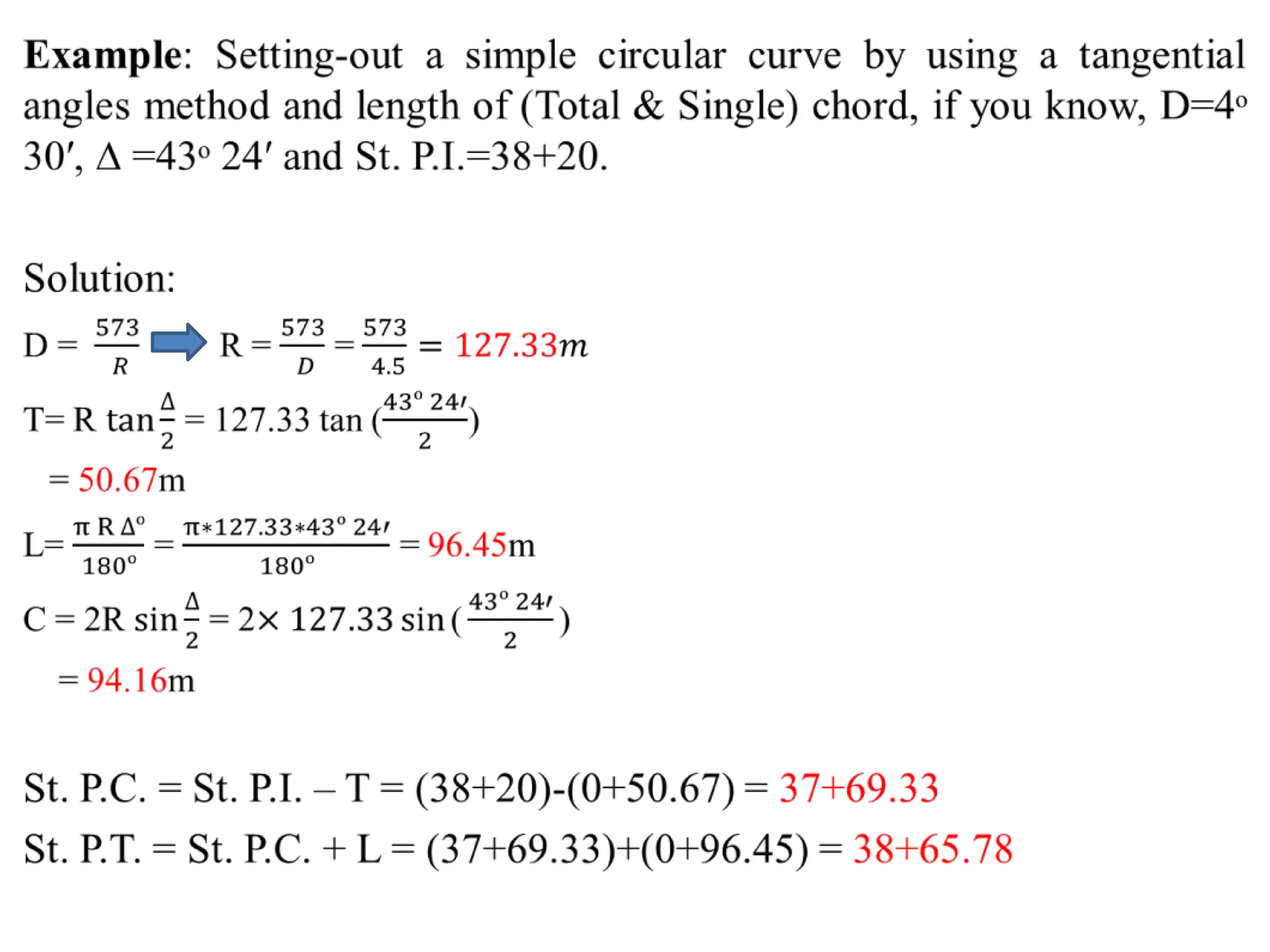
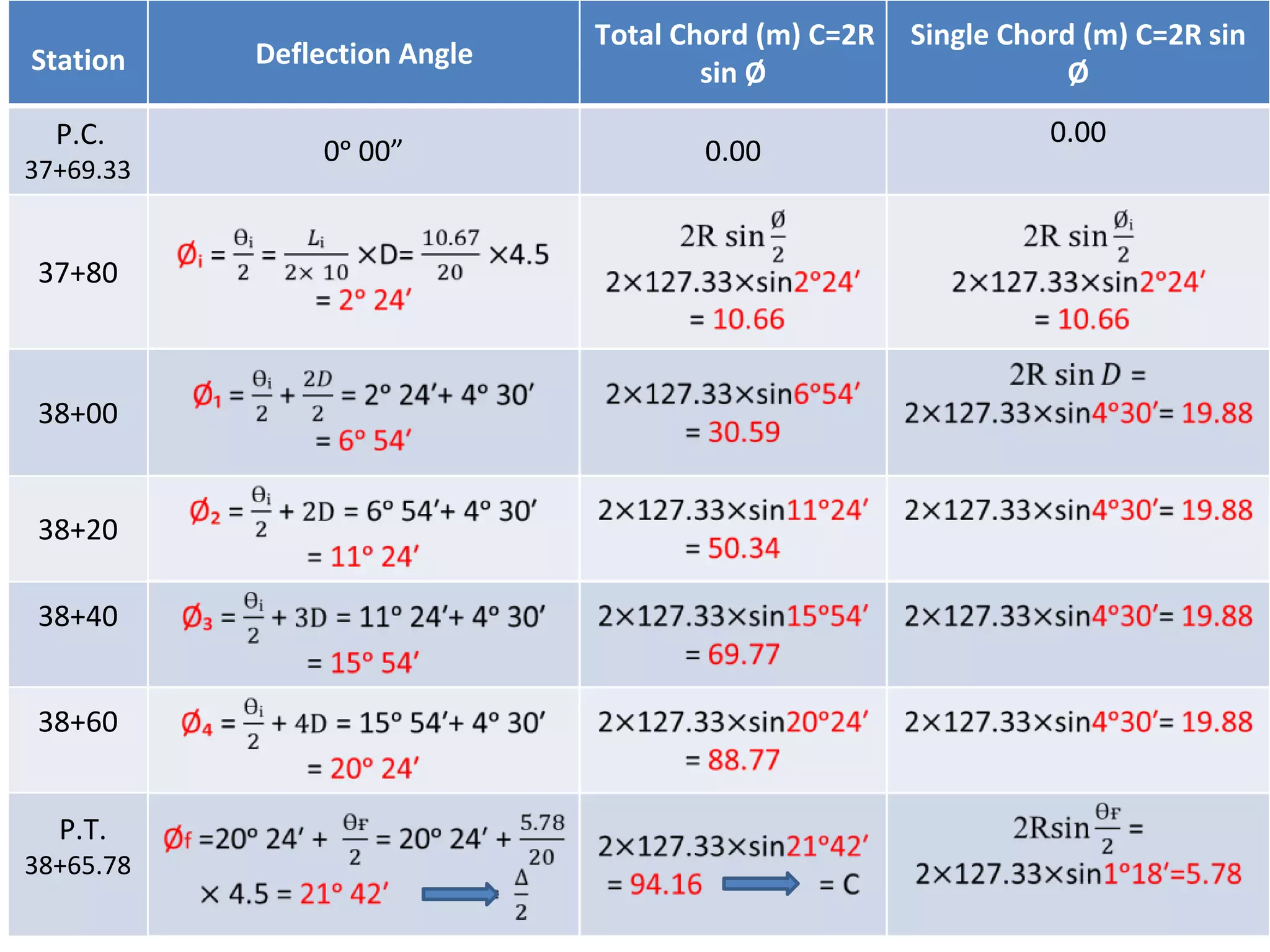
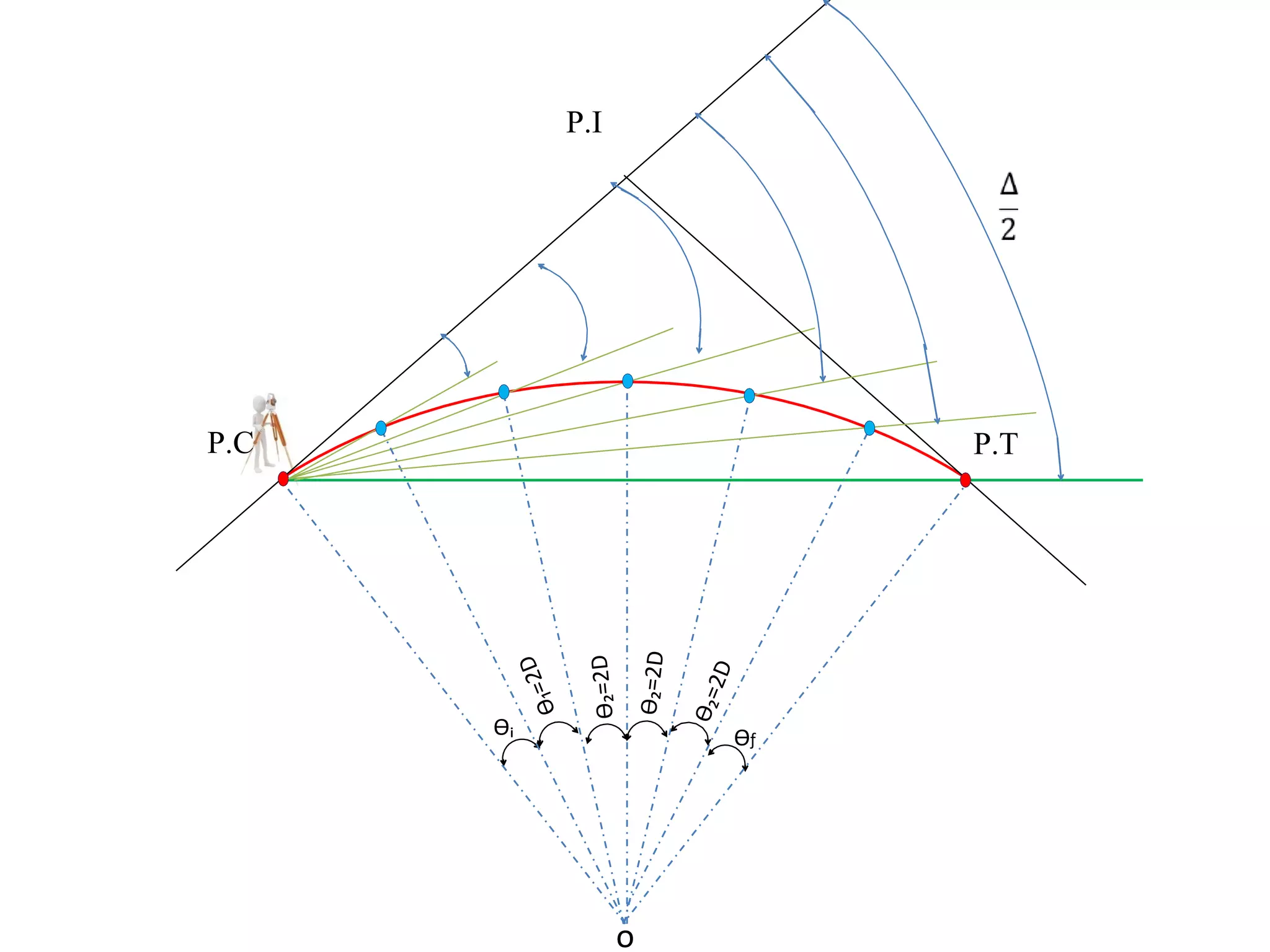
2. The tangential angle method uses a theodolite to measure deflection angles and chords to lay out points along the curve.
3. The tangent offset method uses only a chain and tape, measuring offsets perpendicular to tangents to locate points for small curves where high accuracy is not required.
4. Similarly, the chord offset method divides a chord between the PC and PT into segments and measures offsets perpendicular to locate points along the curve.