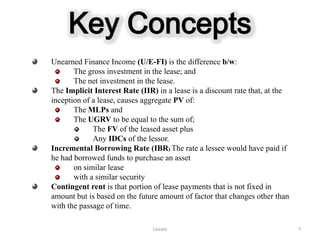
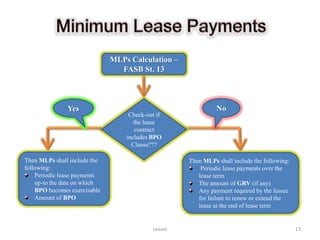
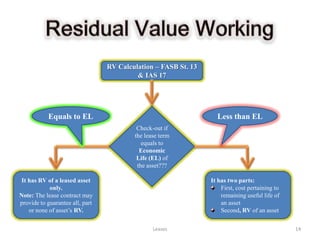
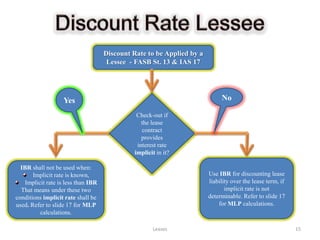
The document provides a comprehensive overview of leasing concepts, including definitions, classifications, accounting treatments, and calculations related to finance and operating leases. Key topics covered include lease assets, minimum lease payments, gross and net investments, and capital versus operating lease criteria as per IAS 17 and FASB Statement 13. Additionally, it discusses various leasing arrangements such as sale and leaseback, and leveraged leasing, along with practical examples and calculations.
![[In accordance with the requirements of IAS 17 &
FASB Statement 13]
Ahmad Tariq Bhatti
FCMA, FPA, MA (Economics), BSc
Dubai, United Arab Emirates](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leases-121106141153-phpapp02/85/Leases-1-320.jpg)








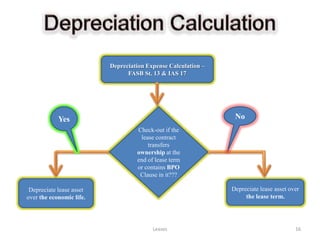
![Lessee’s Books Lessor’s Books
Lease Payable Lease Receivable
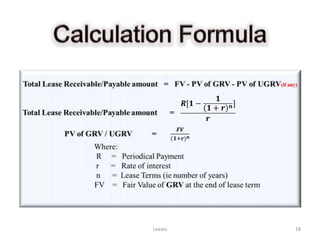
Lease Receivable/Payable Amount = FV - PV of GRV - PV of UGRV (If any)
[Lease Payable amount represents the PV of MLPs from lessee’s perspective]
Leases 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leases-121106141153-phpapp02/85/Leases-17-320.jpg)

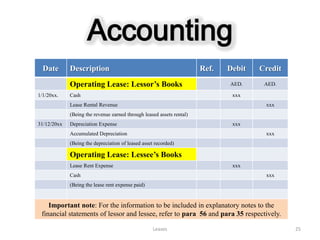
![Accounting
Date Description Ref. Debit Credit
Finance Lease: Lessee’s Books AED. AED.
1/1/20xx Lease Asset xxx
Lease Payable xxx
[Lease asset and lease liability shall be recorded at lower of : (1) PV of MLPs or (2) FV of asset, at
the inception of the lease]
Lease Payable xxx
Cash xxx
31/12/20xx Interest Expense xxx
Lease Payable xxx
Lease Payable xxx
Cash xxx
Depreciation expense xxx
Accumulated Depreciation xxx
Depreciation of an asset is charged over:
The EL of an asset, if ownership transfers to lessee at the end of lease term or there is a BPO
The term of lease, if title does not transfer or there is no BPO
Leases 22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leases-121106141153-phpapp02/85/Leases-22-320.jpg)





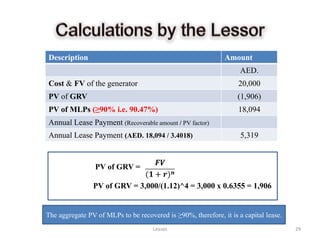
![Lessor’s Books [AAA Co. Books] Lessee’s Books [BBB Co. Books]
Description Dr. Cr. Description Dr. Cr.
1 Lease Receivable 20,000 1 Lease Asset- Generator 20,000
Lease Asset - Generator 20,000 Lease Liability 20,000
(To record capital lease on 01/01/08) (To record capital lease on 1/1/08)
2 Cash 5,319 2 Lease Liability 5,319
Lease Receivable 5,319 Cash 5,319
(To record the 1st lease payment on 01/01/2008) (To record lease payment on 1/1/08)
3 Lease Receivable 1,762 3 Interest Expense 1,762
Interest Revenue 1,762 Lease Liability 1,762
(To record interest earned on 31/12/08.) (To record interest expense on 31/12/2008)
4 Depreciation Expense 4,250
Accumulated Depreciation 4,250
To record Depreciation [(20,000-3000)/4 = 4,250 p.a.]
Leases 31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leases-121106141153-phpapp02/85/Leases-31-320.jpg)
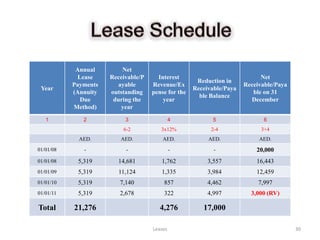
![Lessor’s Books [AAA Co. Books] Lessee’s Books [BBB Co. Books]
Description Dr. Cr. Description Dr. Cr.
1 Cash 5,319 1 Lease Liability 5,319
Lease Receivable 5,319 Cash 5,319
(To record the last lease payment) (To record lease payment on 01/01/2011)
2 Lease Receivable 322 2 Interest Expense 322
Interest Revenue 322 Lease Liability 322
(To record interest earned on 31/12/11) (To record interest expense on 31/12/2011)
3 Lease Asset – Generator 3,000 3 Depreciation Expense 4,250
Lease Receivable 3,000 Accumulated Depreciation 4,250
(Final Settlement entry 31/12/11) To record Depreciation [(20,000-3000)/4 = 4,250 p.a.]
4 Accumulated Depreciation 17,000
Lease Liability 3,000
Lease Asset 20,000
(Final settlement entry on 31/12/11)
Leases 32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leases-121106141153-phpapp02/85/Leases-32-320.jpg)