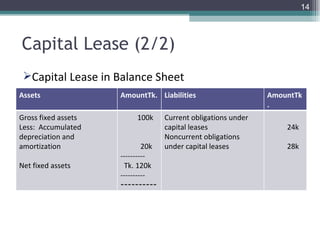
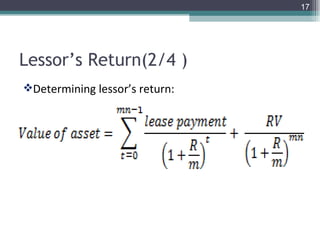
This document discusses different types of lease financing. It describes financial leasing, operating leasing, sale and leaseback leasing, direct leasing, and leveraged leasing. Financial leasing involves the lessor retaining title to the asset, transferring risk and reward to the lessee, and having non-cancelable leases that cover most of the asset's economic life. Operating leasing involves shorter terms than the asset's life, maintenance by the lessor, and cancelability by the lessee. Sale and leaseback leasing involves selling an asset to a lessor who then leases it back to the original owner.