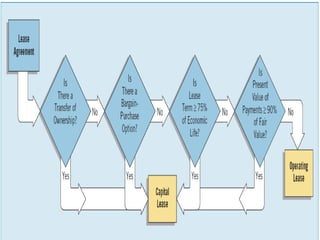
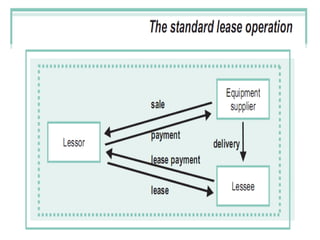
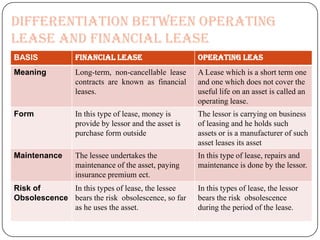
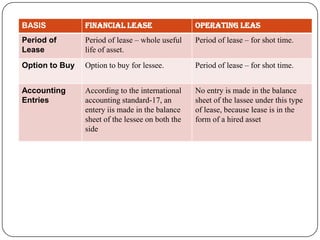
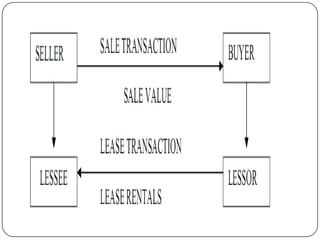
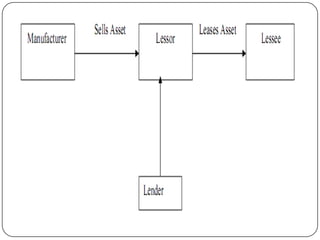
Lease financing involves an arrangement where the owner (lessor) of an asset transfers possession and right to use the asset to another party (lessee) for an agreed period of time in exchange for rental payments. There are two main types of leases: finance leases and operating leases. Finance leases typically involve long-term agreements where the lessee takes on most of the risks and benefits of asset ownership, while operating leases are usually shorter term agreements where the lessor retains responsibility for the asset. Lease financing can provide businesses with an alternative to purchasing assets outright and offers tax benefits compared to other forms of financing.