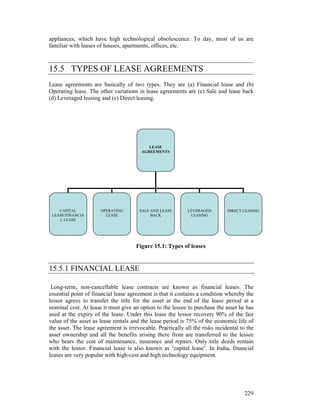
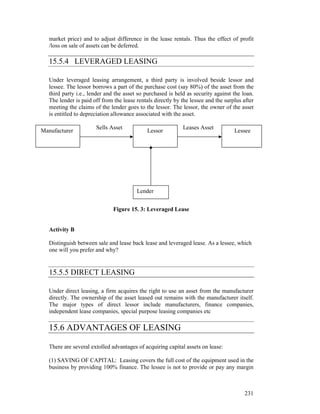
This document provides an overview of lease financing, hire purchase, and factoring. It defines lease financing as procuring assets through a lease agreement where the lessor finances the asset and the lessee uses it. Key types of leases include financial leases, operating leases, sale and lease back, and leveraged leasing. Hire purchase allows a purchaser to acquire an asset through installment payments with ownership transferring after full payment. Factoring involves the sale of receivables to a factor who provides financing against receivables and collects on debts.