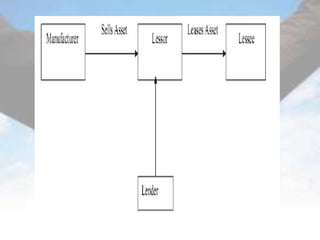
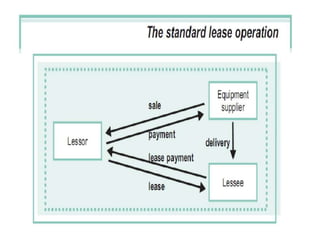
This document defines leasing and describes its key features and types. It begins with defining leasing as a written agreement where a property owner allows a tenant to use the property for a specified period in exchange for fixed installment payments. It then discusses the main features of leasing, including that it allows use of an asset without paying the full upfront cost. The document also outlines the main advantages and disadvantages of leasing. Finally, it describes the main types of leasing, including finance leases, operating leases, leveraged leases, sale and lease back, and direct leasing.