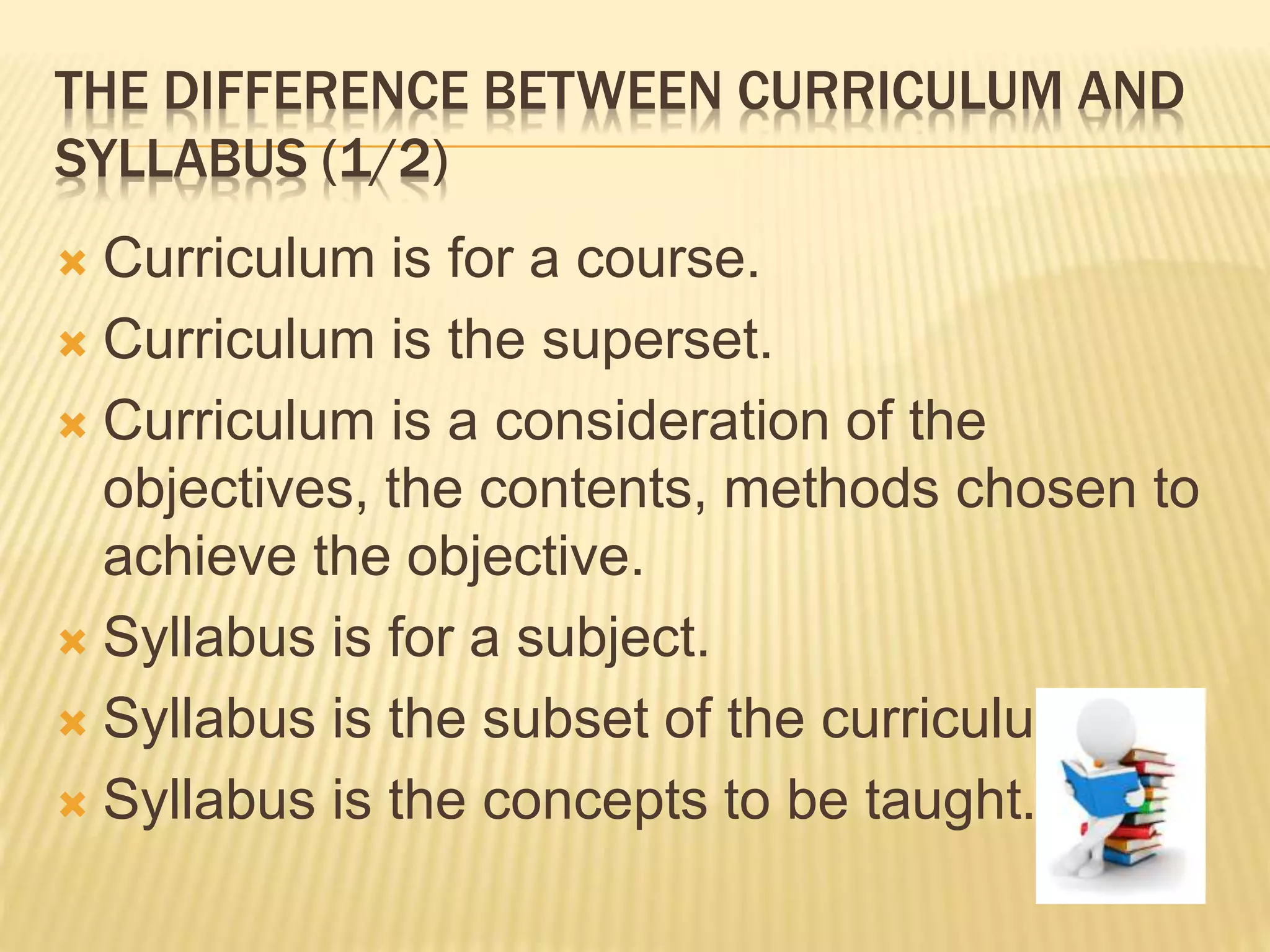
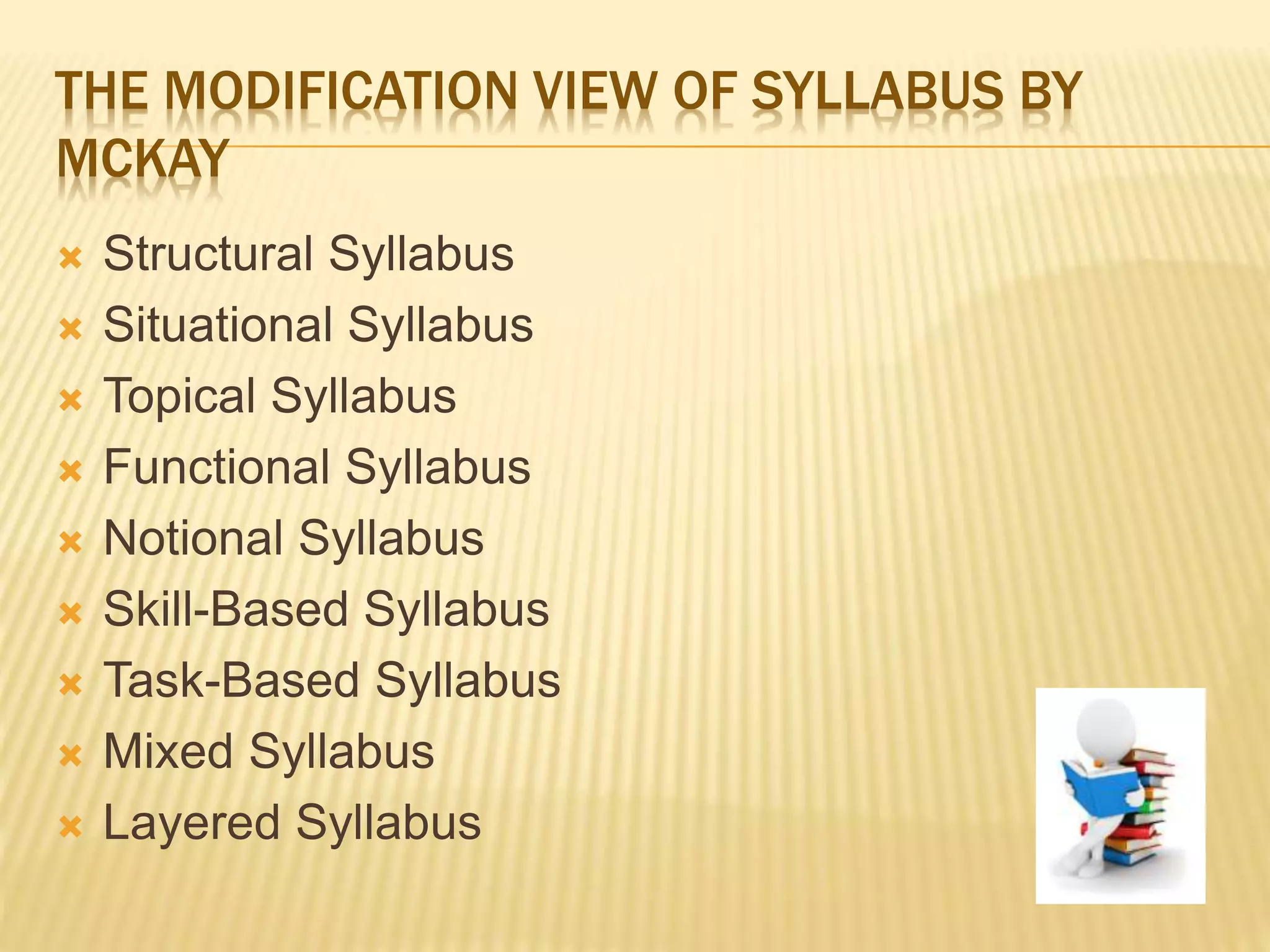
This document outlines key concepts in language curriculum and syllabus design. It discusses the historical development of curriculum, distinguishing between approaches, methods, techniques, and exercises. A curriculum is a broad plan that defines student needs and the overall program, while a syllabus specifies concrete learning objectives and content. The document compares different ways of organizing a syllabus, such as structural and situational models, and examines McKay's modification view incorporating additional syllabus types. It also explores techniques for presenting lessons and exercises for practicing language skills.