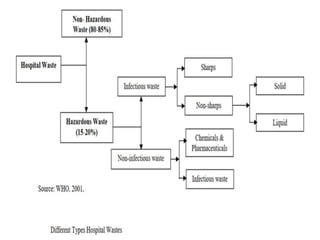
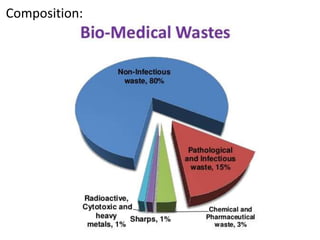
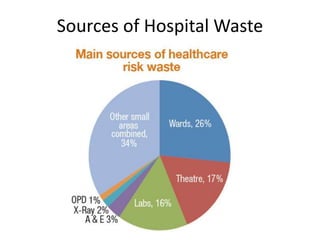
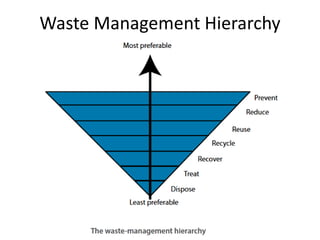
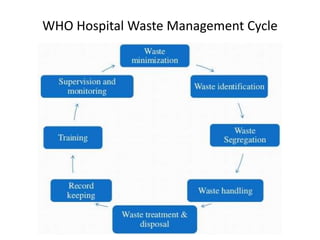
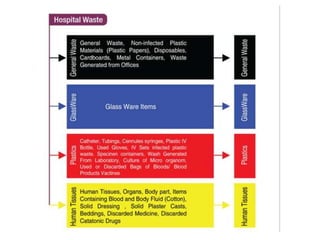
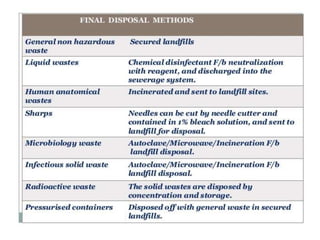
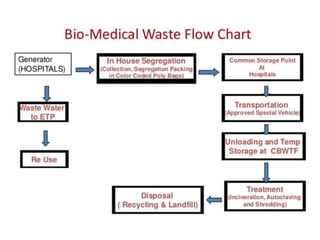
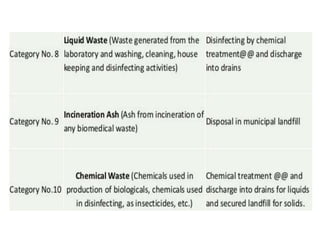
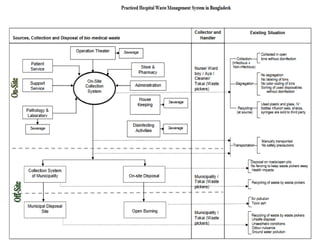
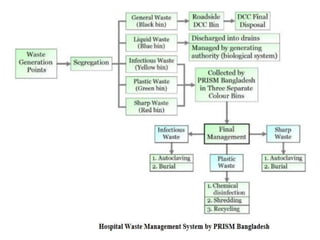
This document defines hospital waste and medical waste generation. It discusses the classification, sources, and health risks of hospital waste. Proper hospital waste management requires policies, legislation, resources, and following best practices like waste minimization, segregation, handling, collection, storage, treatment, and disposal. The waste management hierarchy and WHO guidelines are outlined. Hospital waste management in Bangladesh faces challenges like lack of implementation, gaps in rules and laws, economic constraints, and not prioritizing hazardous waste. A few NGOs are actively working to properly collect, treat and dispose of hospital waste in Bangladesh.