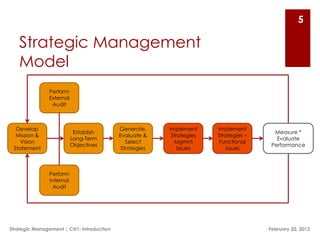
This document provides an overview of strategic management concepts and examples from McDonald's and American General (now Trane). It discusses McDonald's expansion in China and plans to reduce trans fats. It outlines American General splitting into three businesses and renaming itself Trane. It then defines strategic management, discusses its three stages of formulation, implementation and evaluation, and provides key terms like competitive advantage, strategists, and vision and mission statements.