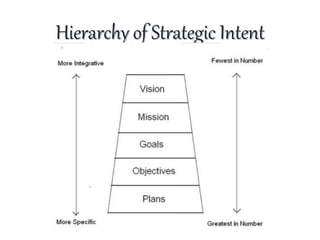
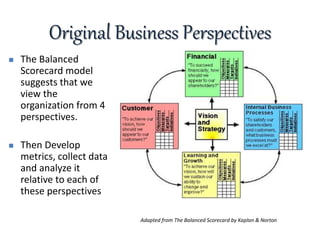
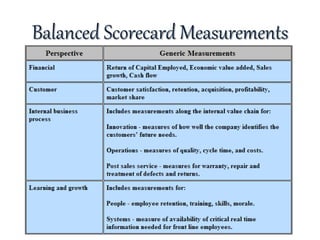
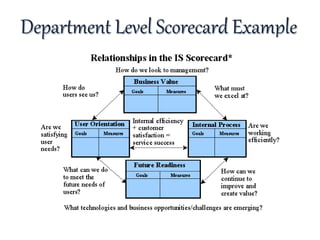
The document discusses strategic intent and the balanced scorecard approach to strategic management. It defines strategic intent as the purpose and direction an organization aims to achieve. Key elements of strategic intent include vision, mission, goals, and objectives. These elements form a hierarchy with the vision at the top as the long-term goal, followed by the mission which articulates how the vision will be achieved, then specific goals and objectives with metrics to evaluate performance. The balanced scorecard framework translates strategic intent into objectives and measures across financial, customer, internal process, and learning/growth perspectives.