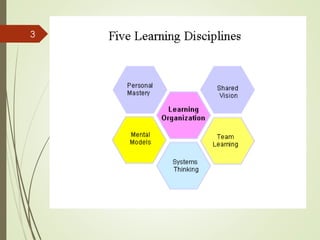
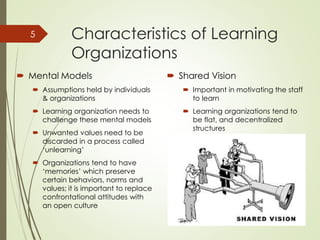
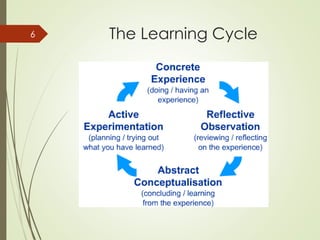
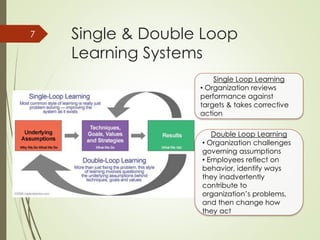
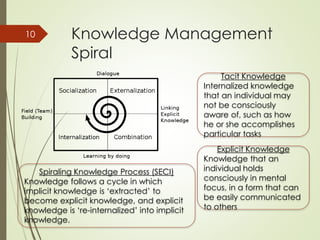
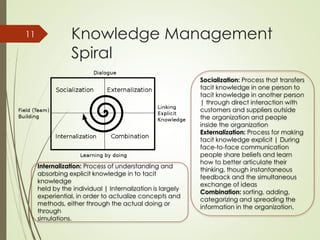
This document discusses organizational learning and learning organizations. It defines learning organizations as those that facilitate continuous learning and transformation among its members to anticipate, respond to, and manage change, complexity and uncertainty. Key characteristics of learning organizations include systems thinking, personal mastery, team learning, shared vision, and challenging mental models. The document also discusses knowledge management, describing it as strategies to identify, create, share and apply insights and experiences. An important model presented is the SECI knowledge spiral model, which illustrates how tacit and explicit knowledge are converted within the organization. Finally, the document outlines some challenges to creating learning organizations, such as problems with leadership mindsets and the long-term focus required.