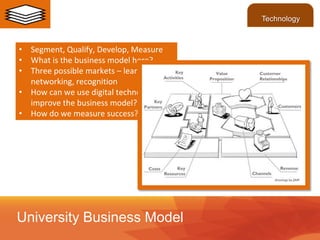
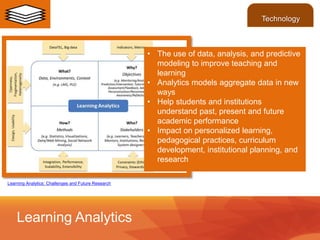
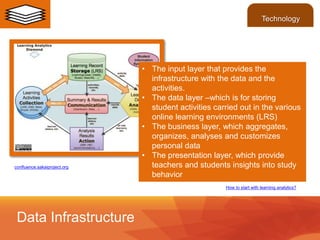
This document discusses the use of learning analytics in higher education. It begins with definitions of key terms and an overview of how learning analytics works. Specifically, it collects and analyzes student data from various systems to generate insights about performance and risk of failure. Examples are given of universities that have implemented learning analytics to improve outcomes like graduation rates. Challenges discussed include privacy concerns and integrating diverse data sources. The future may see broader use of learning data and standards to further personalize learning.