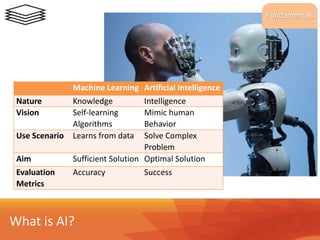
This document provides an overview of a business analytics course. It includes the following key points:
- The objective of the course is to build students' knowledge of applying business analytics in various industrial settings.
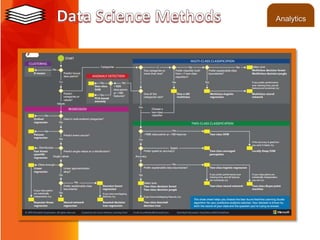
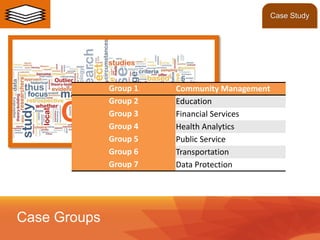
- The course will cover fundamentals, case methodology, and involve analyzing case studies from industries like community management, education, and health analytics.
- Grading will be based on participation, a mid-term exam, and a final essay exam. Students will analyze case studies and apply appropriate data science techniques.