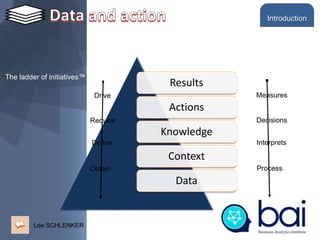
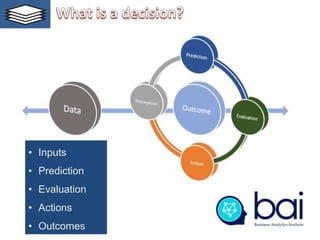
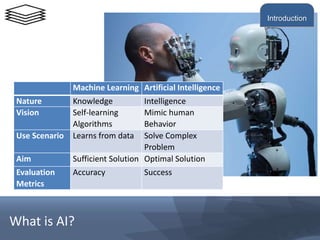
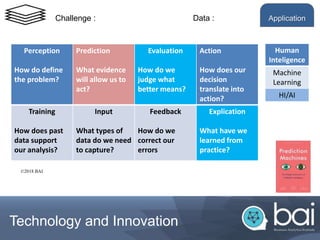
This document provides an introduction to a training module on digital technologies and innovation. It discusses artificial intelligence (AI) and its role in innovation. The training will cover topics like the building blocks of AI, digital economics, the internet of value, decision making, data ethics, and how AI can be used as a lever for innovation. It outlines the course administration, including grading based on a final exam and an innovation project. The introduction discusses using data to help management make better decisions and defines the key elements involved in applying analytics, including defining the problem, making predictions, evaluating outcomes, and taking action. It also outlines the machine intelligence continuum from rule-based automation to developing human-like intelligence.