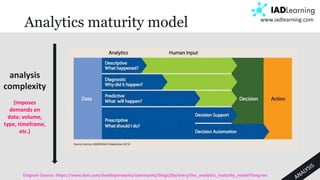
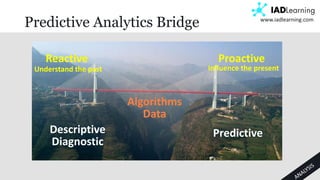
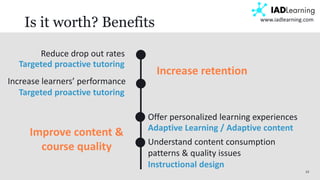
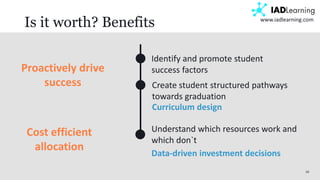
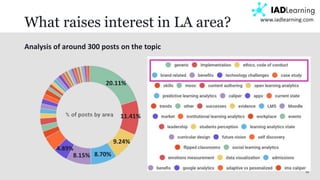
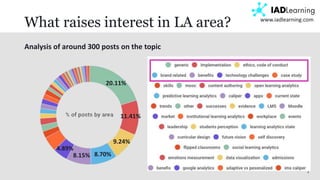
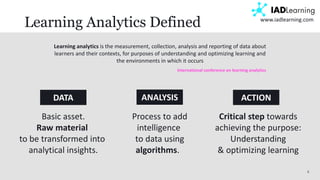
The document discusses learning analytics, defined as the measurement and analysis of learner data to optimize educational environments. It highlights the importance of data sources, the implementation process, and ethical considerations. Key takeaways include the necessity for actionable insights and stakeholder involvement to effectively enhance student success and institutional competitiveness.



![6
www.iadlearning.com
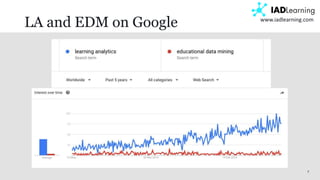
Learning Analytics and EDM
Educational Data Mining (EDM)
EDM focuses on the development of methods for exploring the
unique types of data that come from an educational context. […]
the objective of data mining in education is largely to improve
learning […]
Handbook of educational data mining
Educational Data Mining (EDM) ≈ Learning Analytics](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/highereducation-learninganalytics-jaomedes-170517140956/85/Learning-Analytics-in-Higher-Education-6-320.jpg)