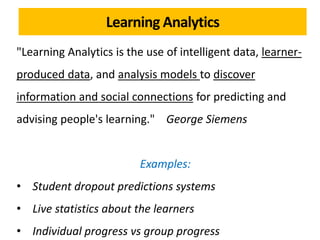
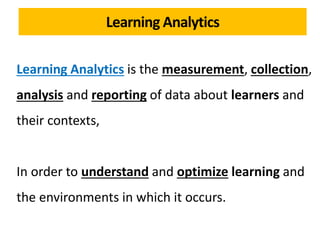
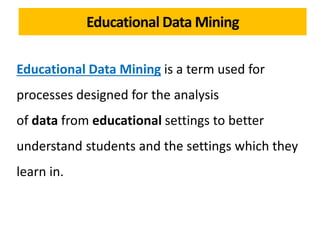
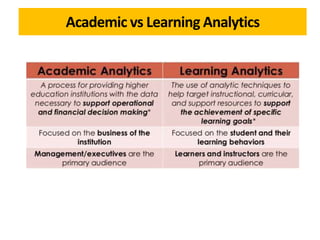
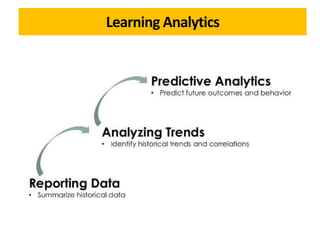
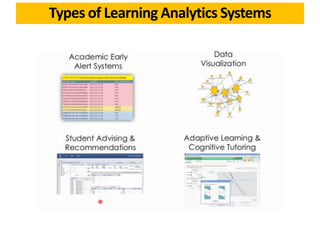
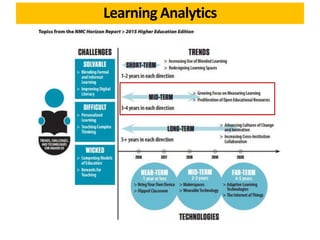
The document discusses the role of learning analytics and big data in education, emphasizing how analyzing student data can enhance teaching and learning outcomes. It outlines what learning analytics can and cannot do, including predicting student performance, personalizing learning experiences, and informing instructional improvements. Key applications, tools, and features related to learning analytics in educational settings are also explored.