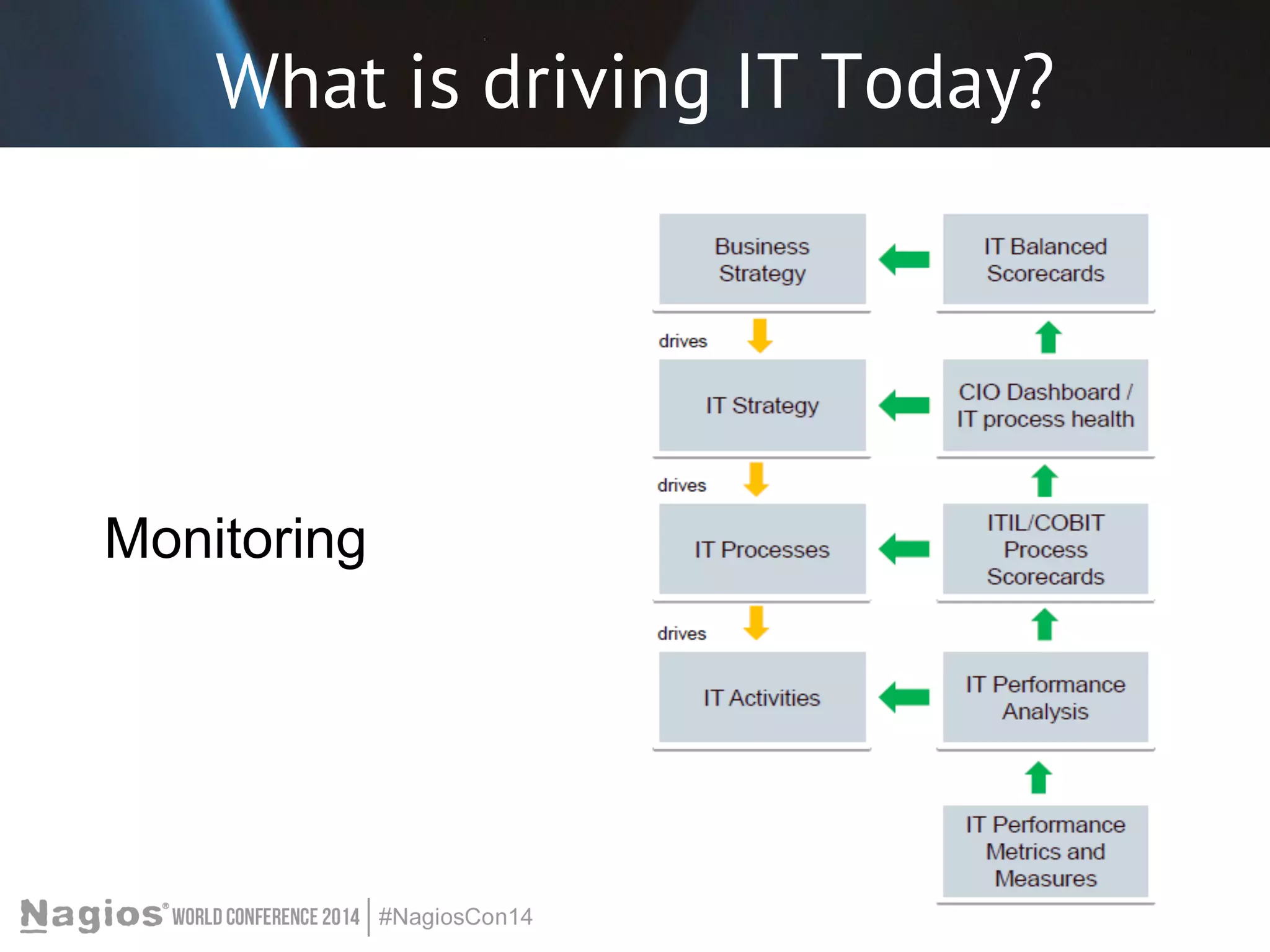
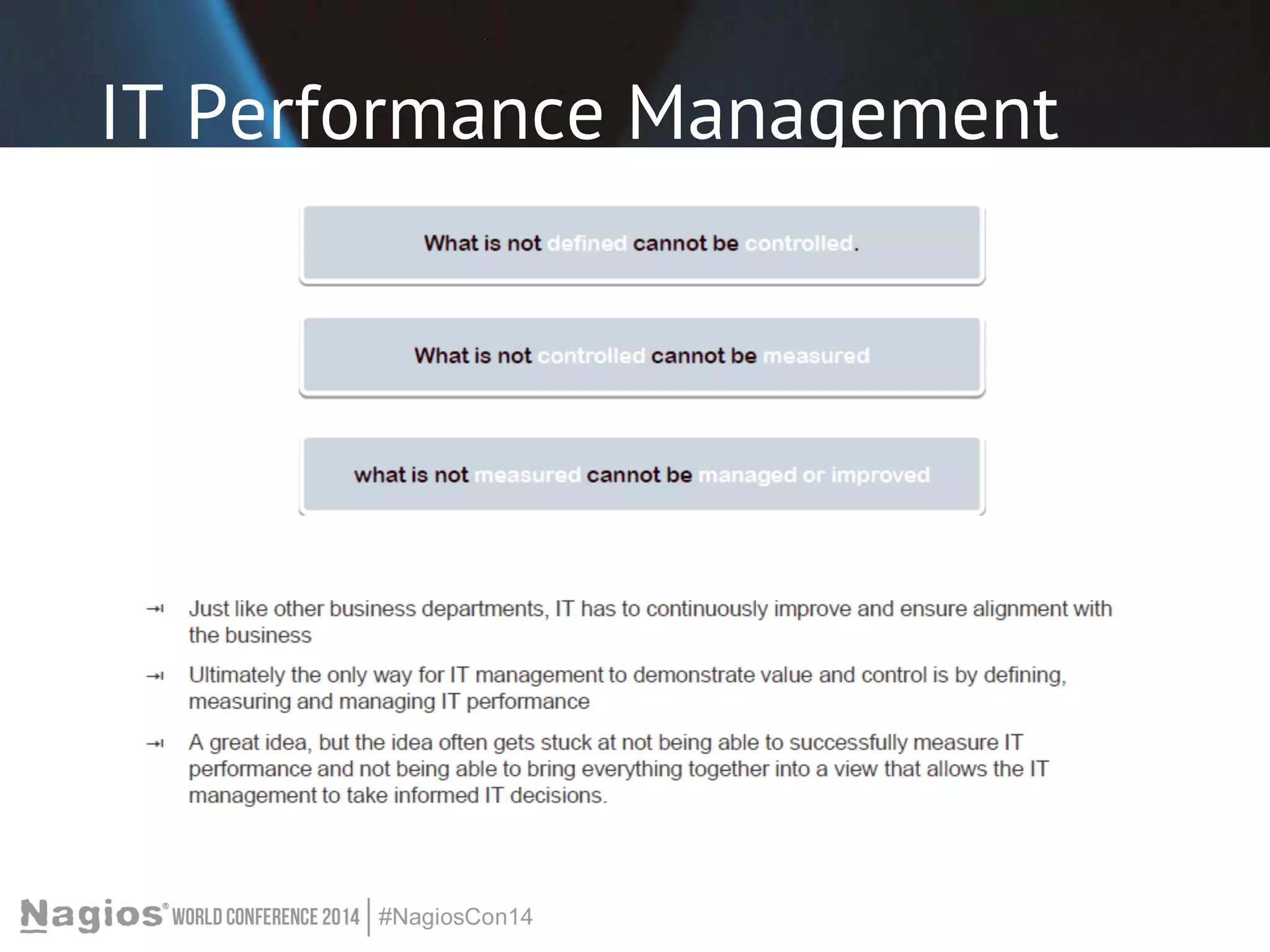
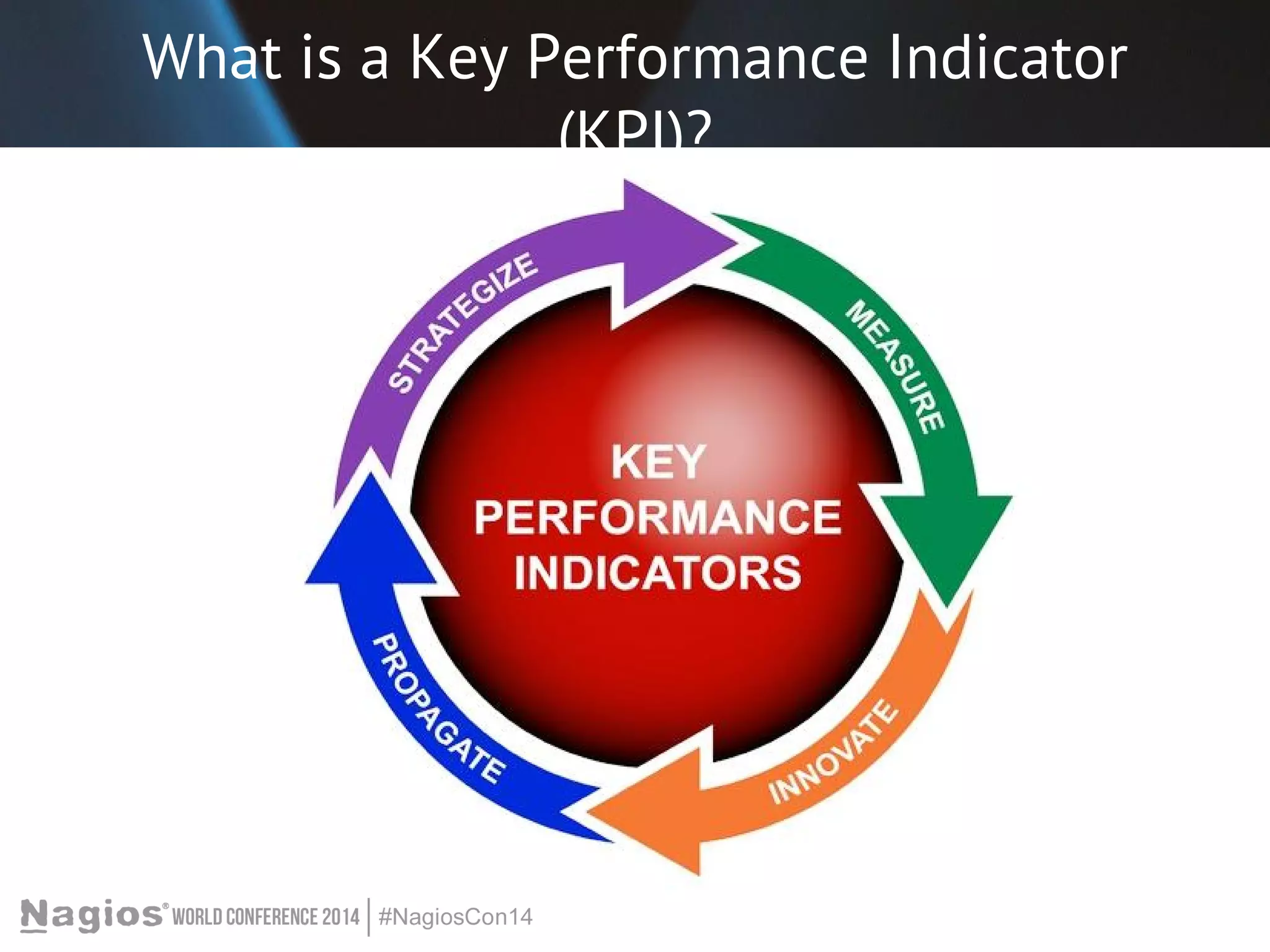
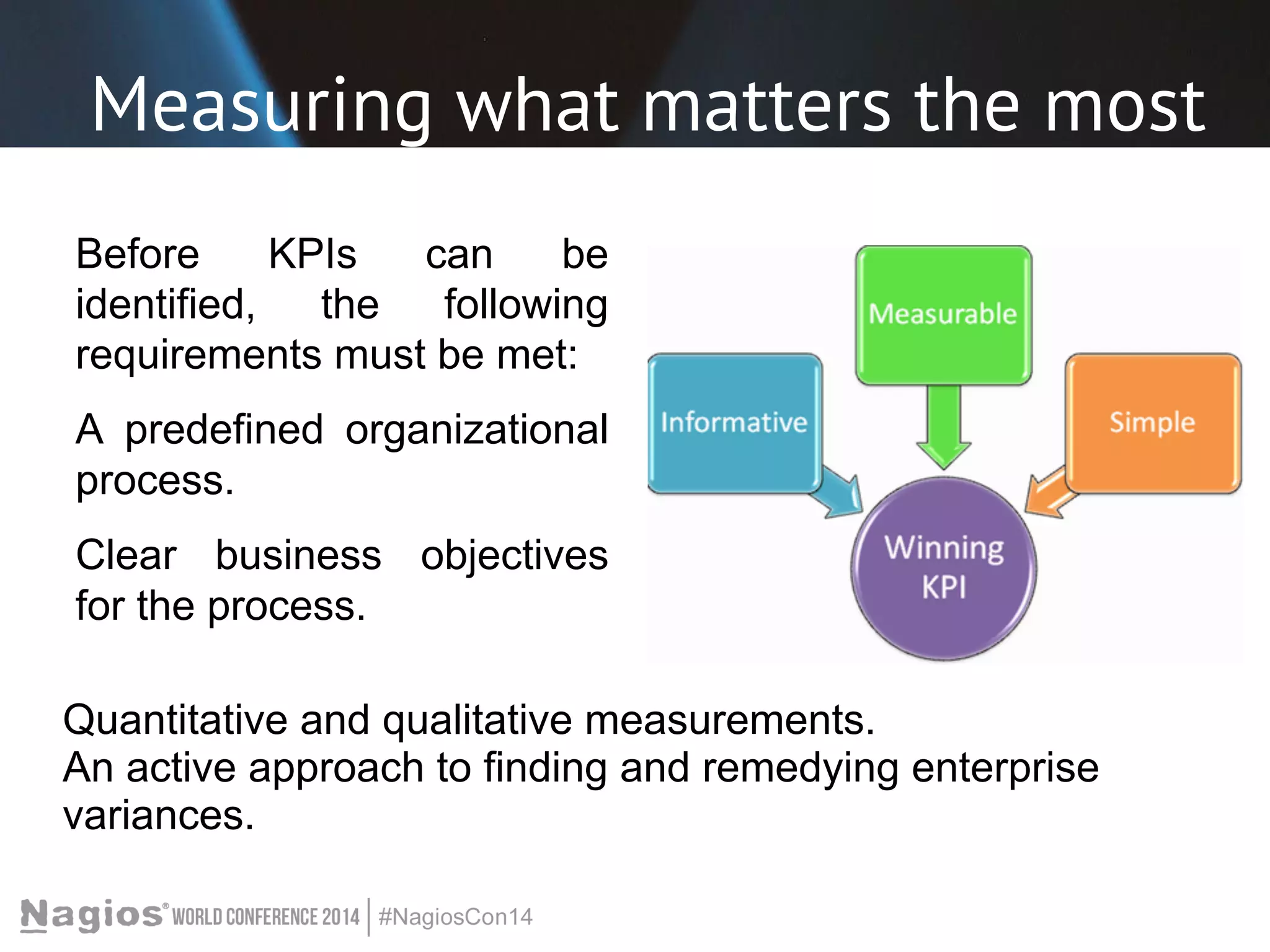
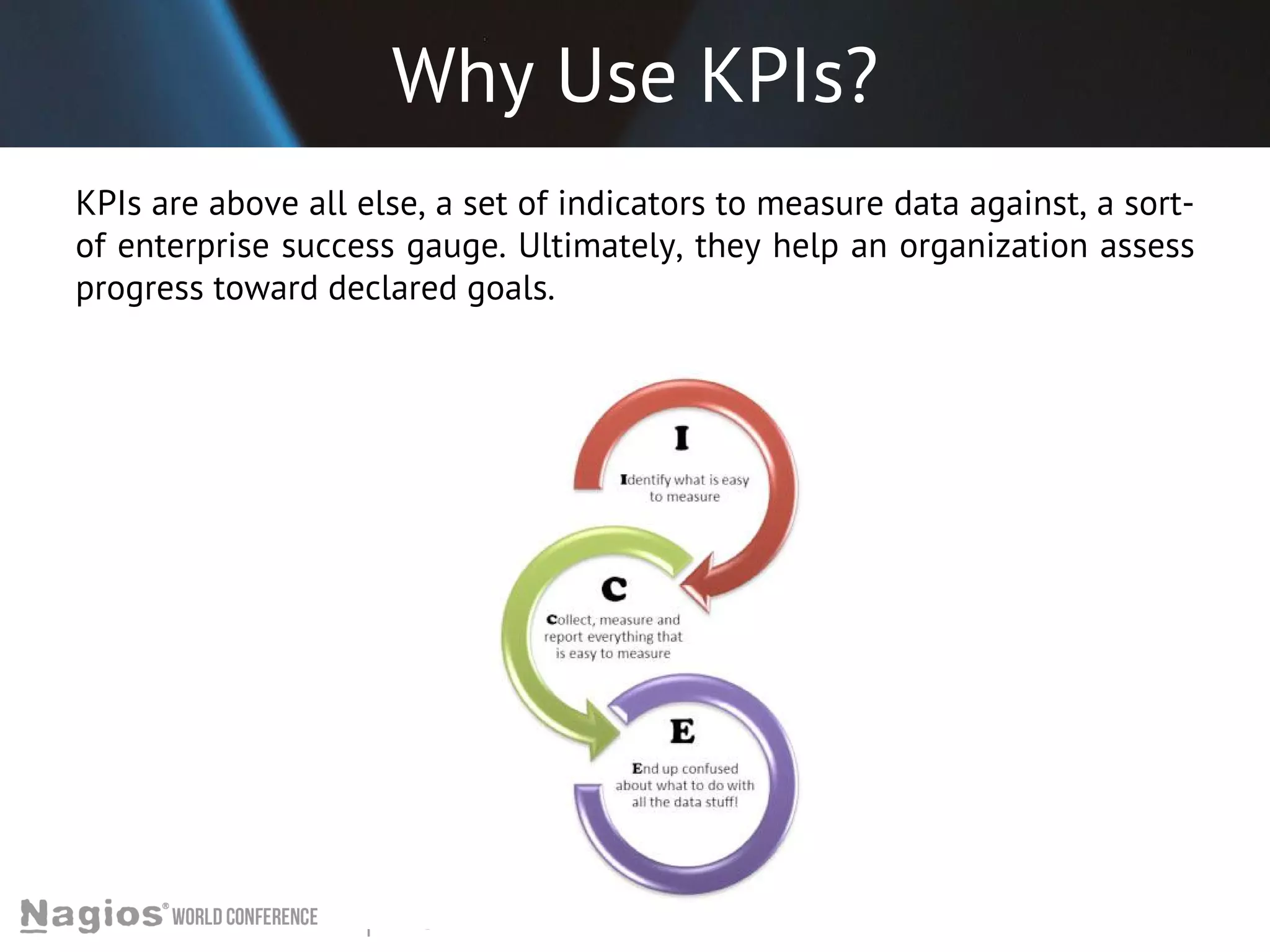
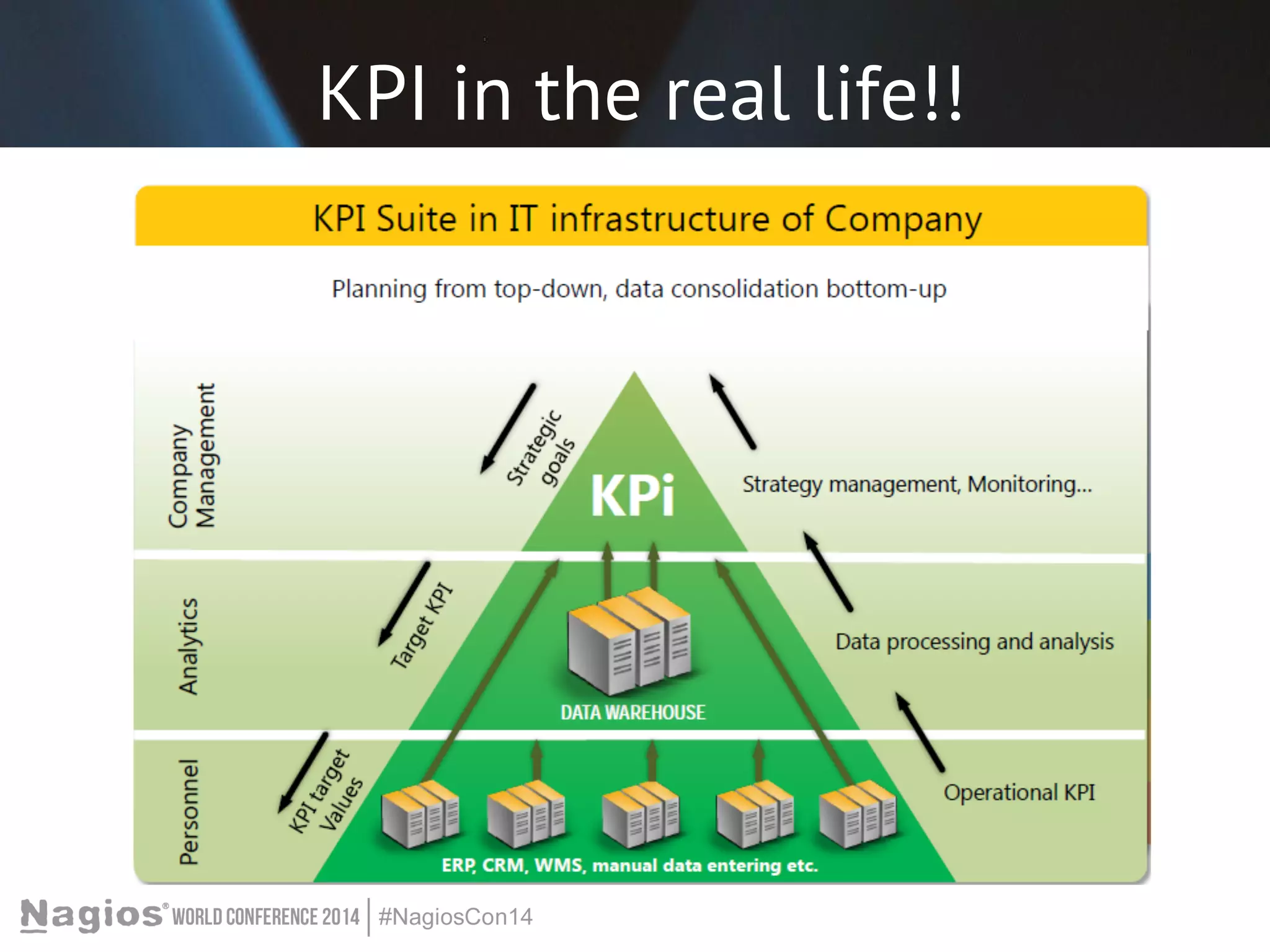
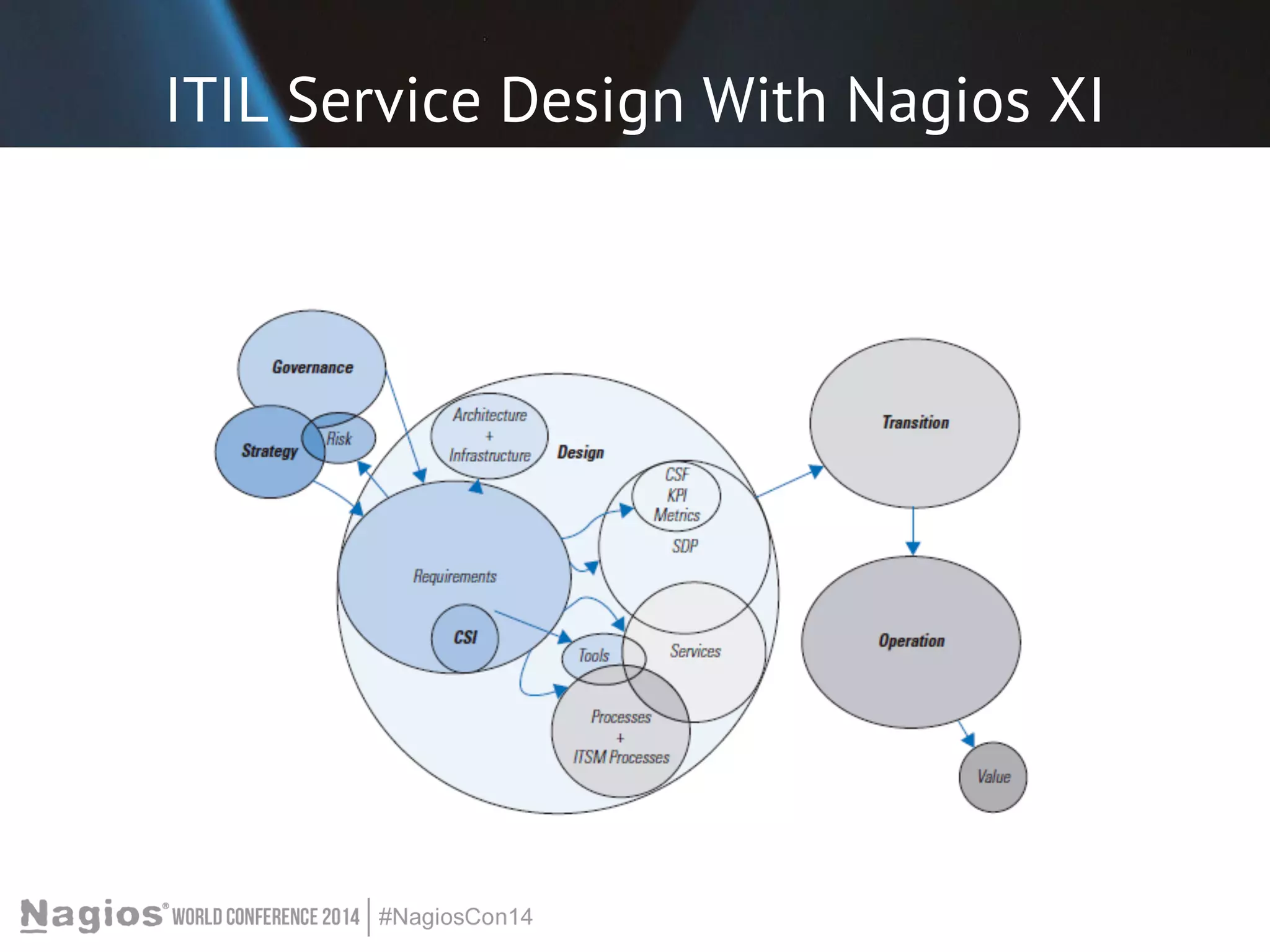
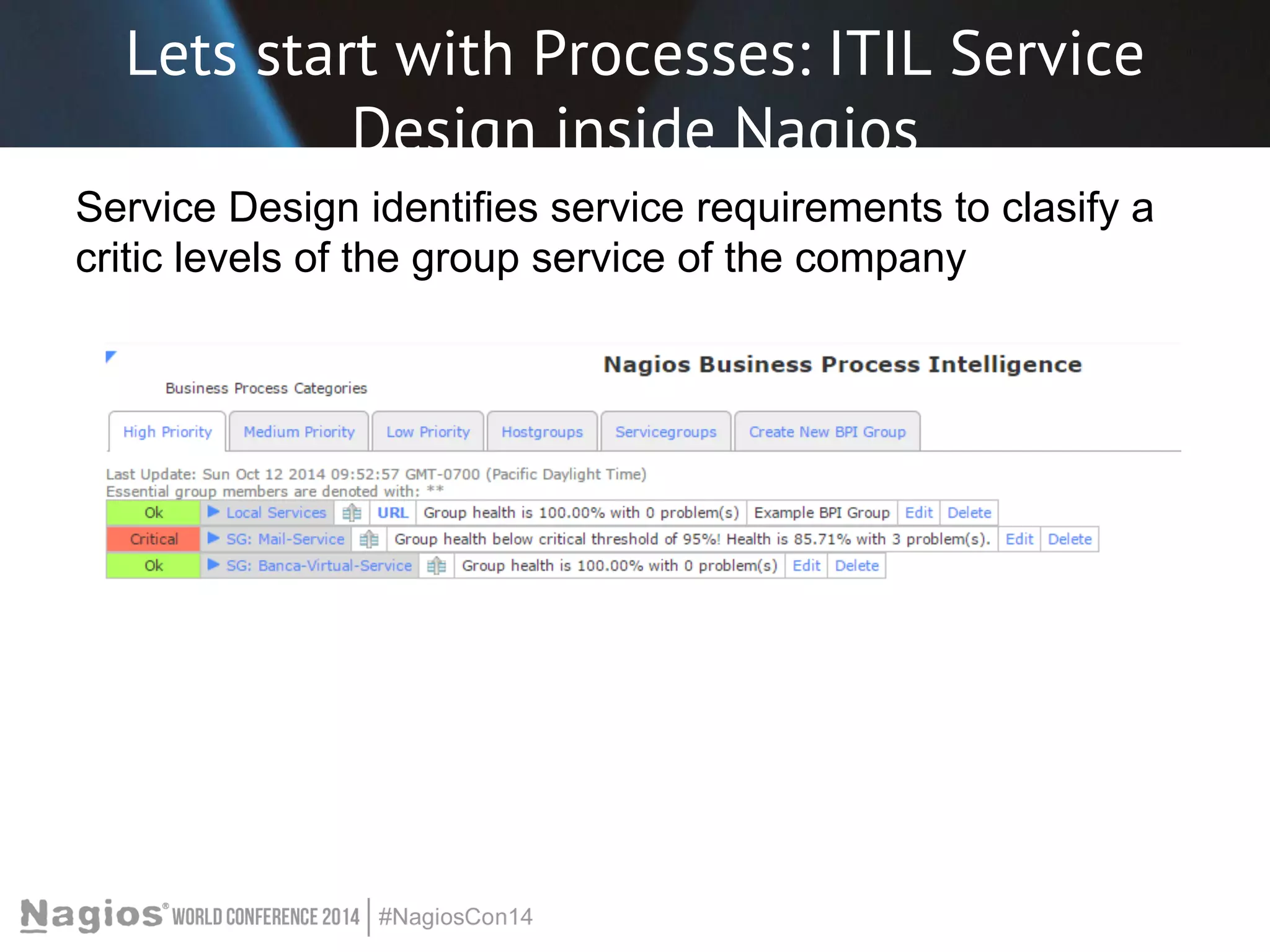
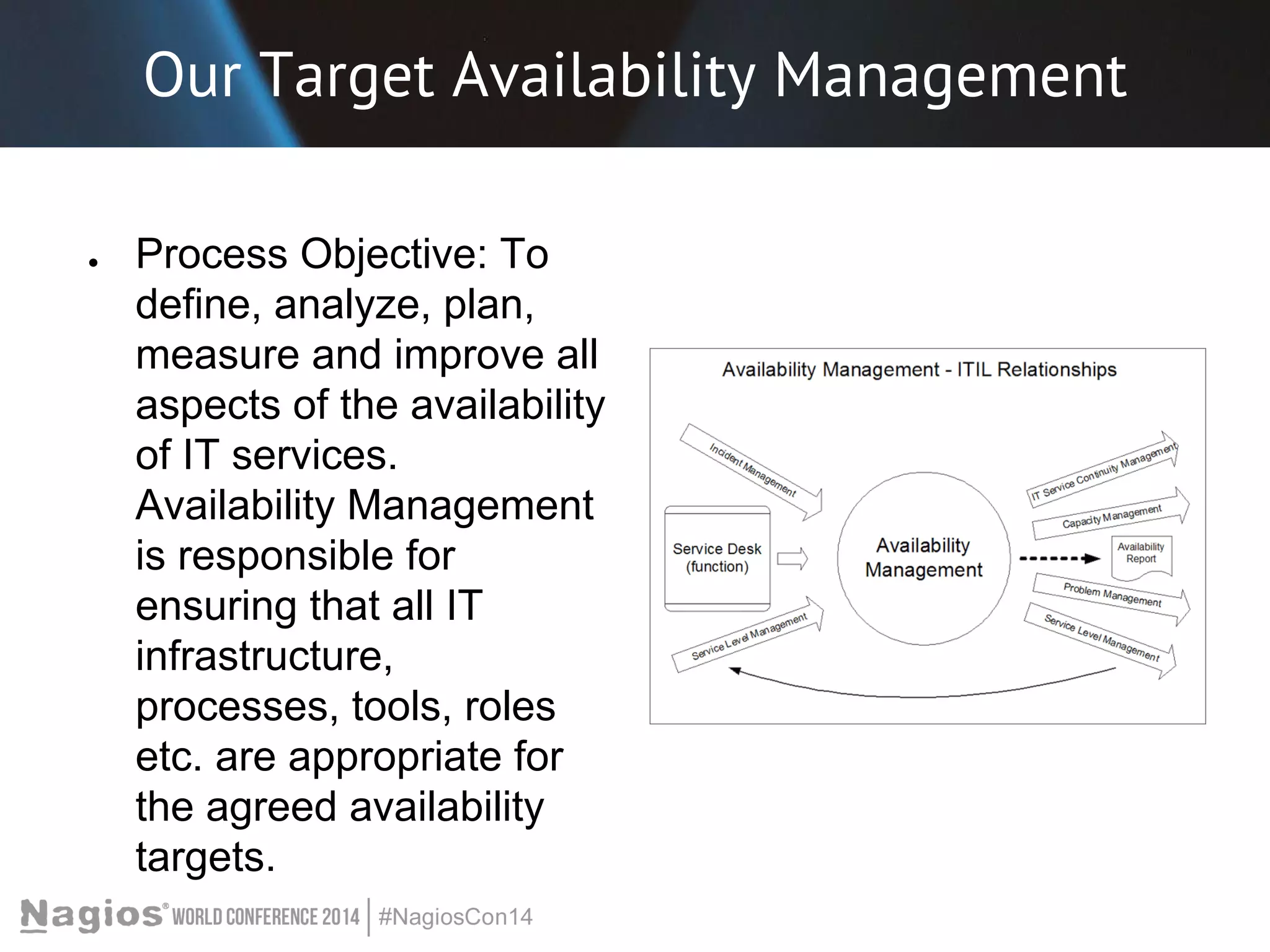
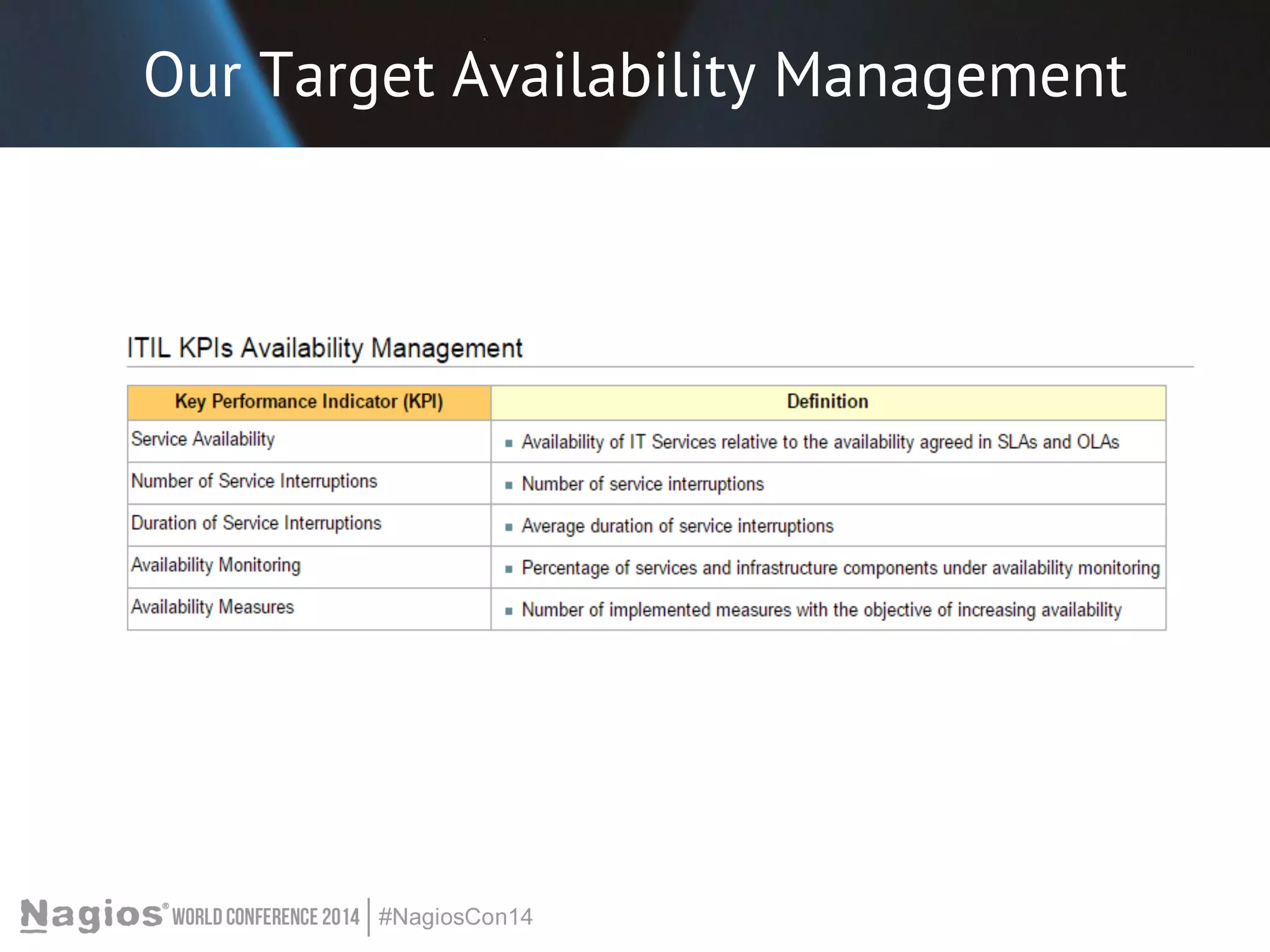
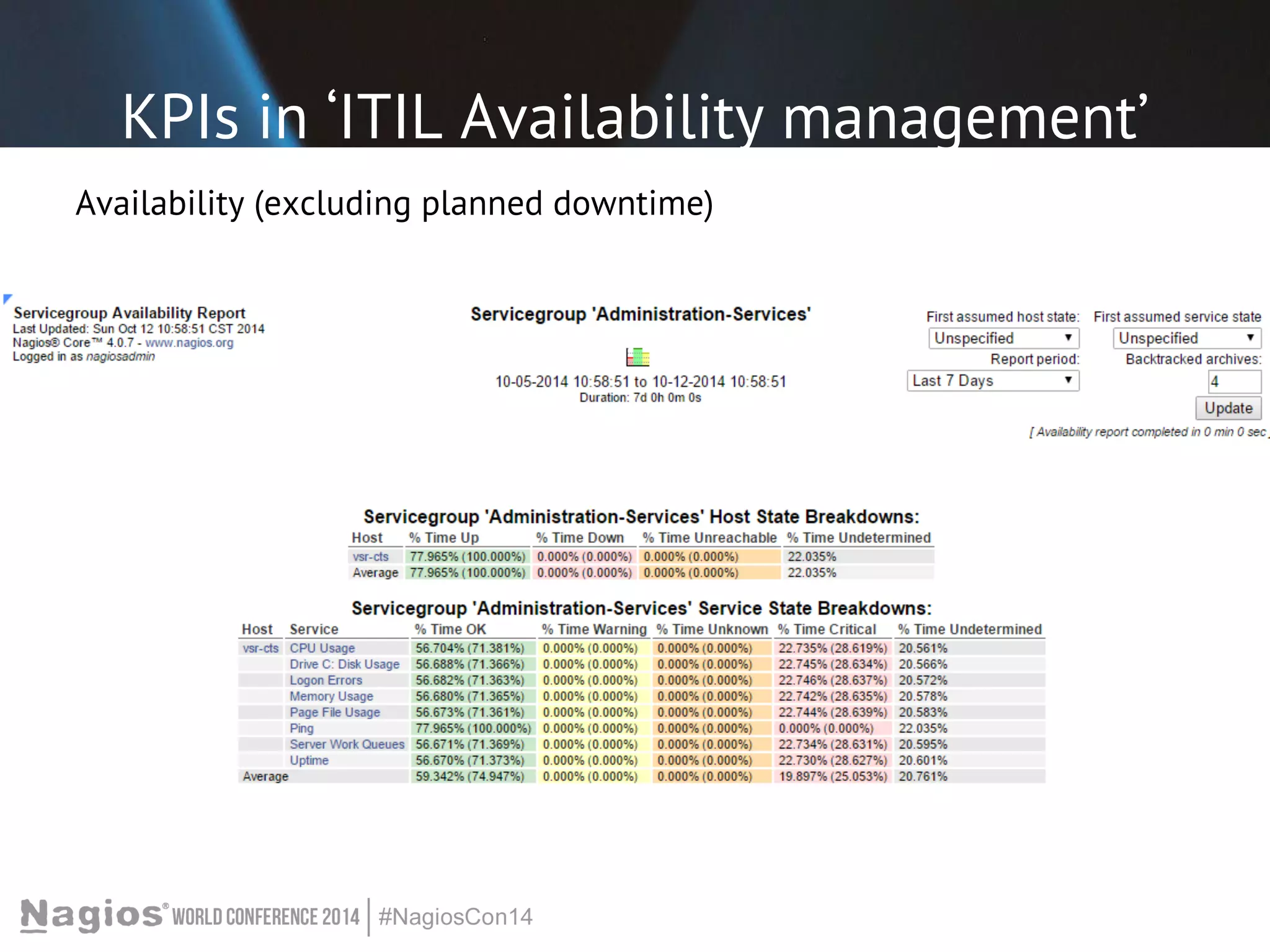
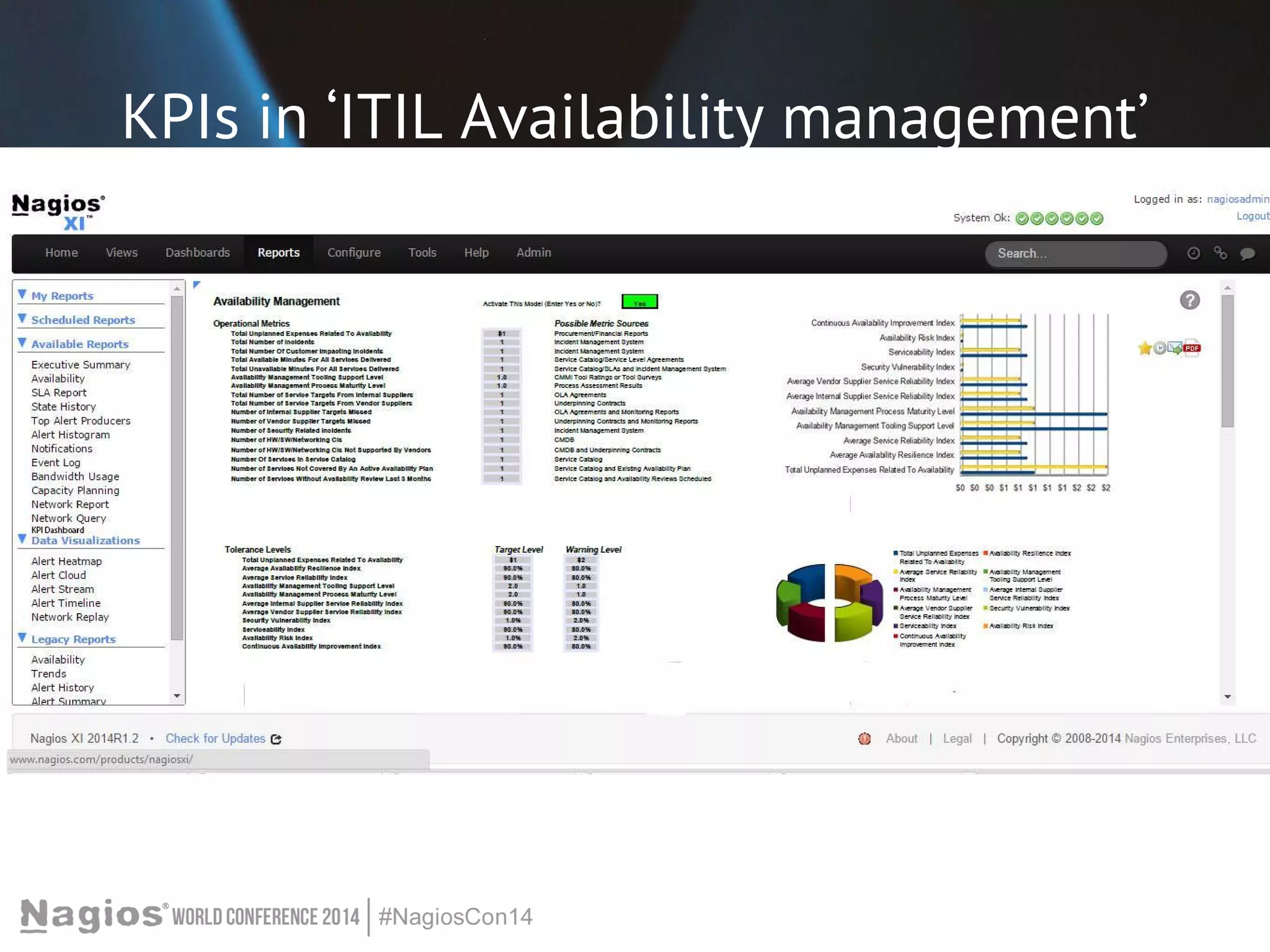
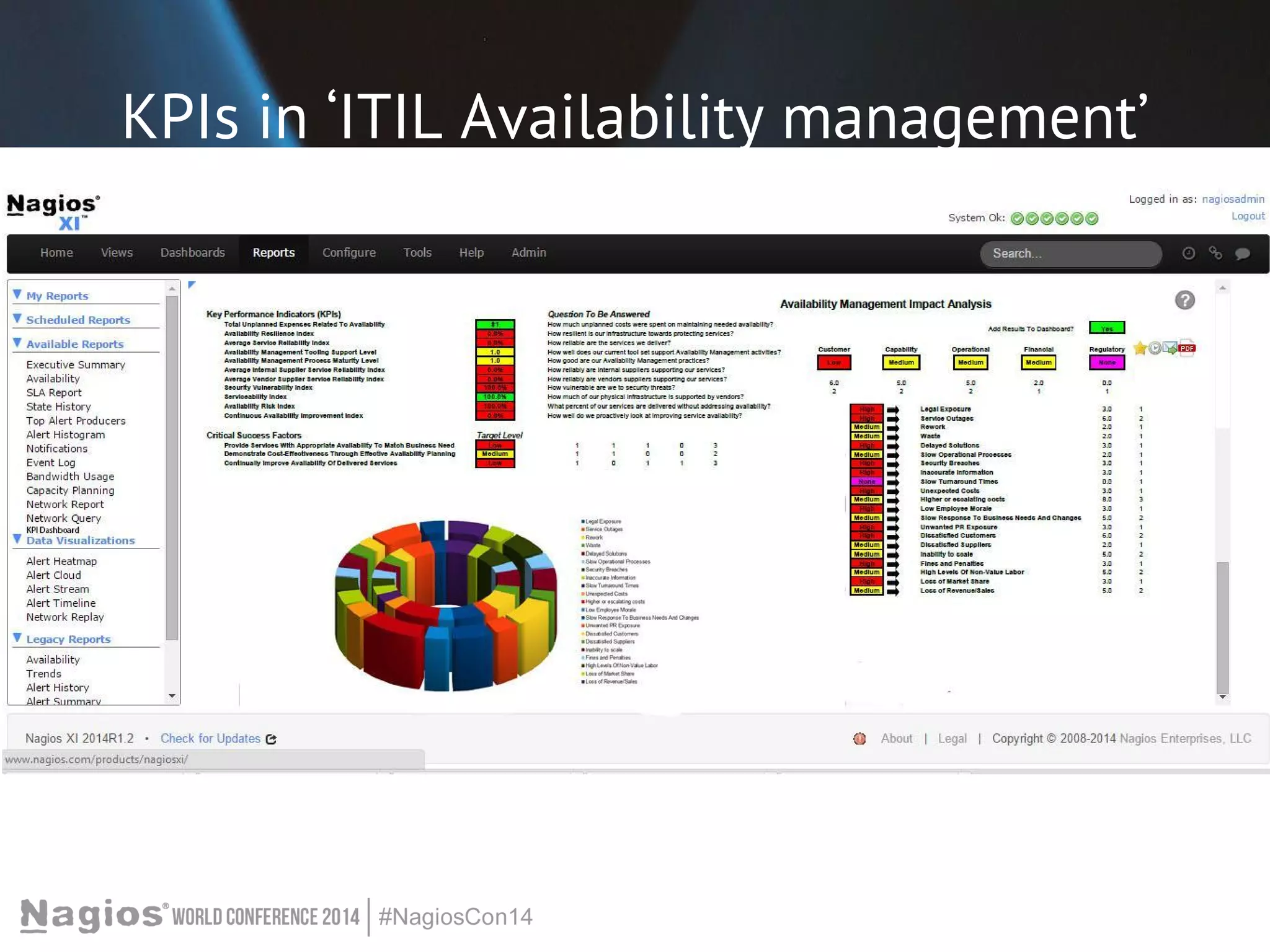
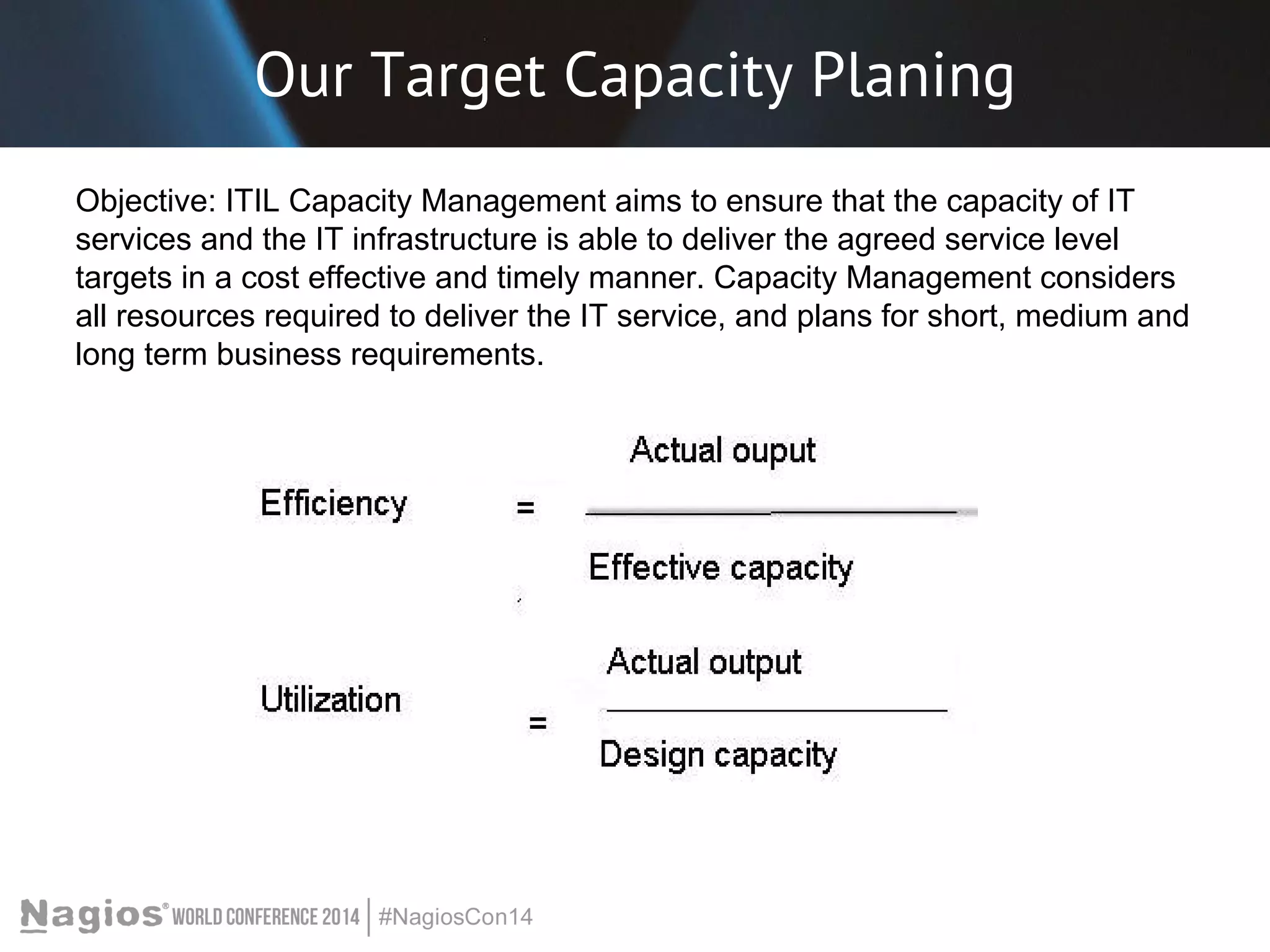
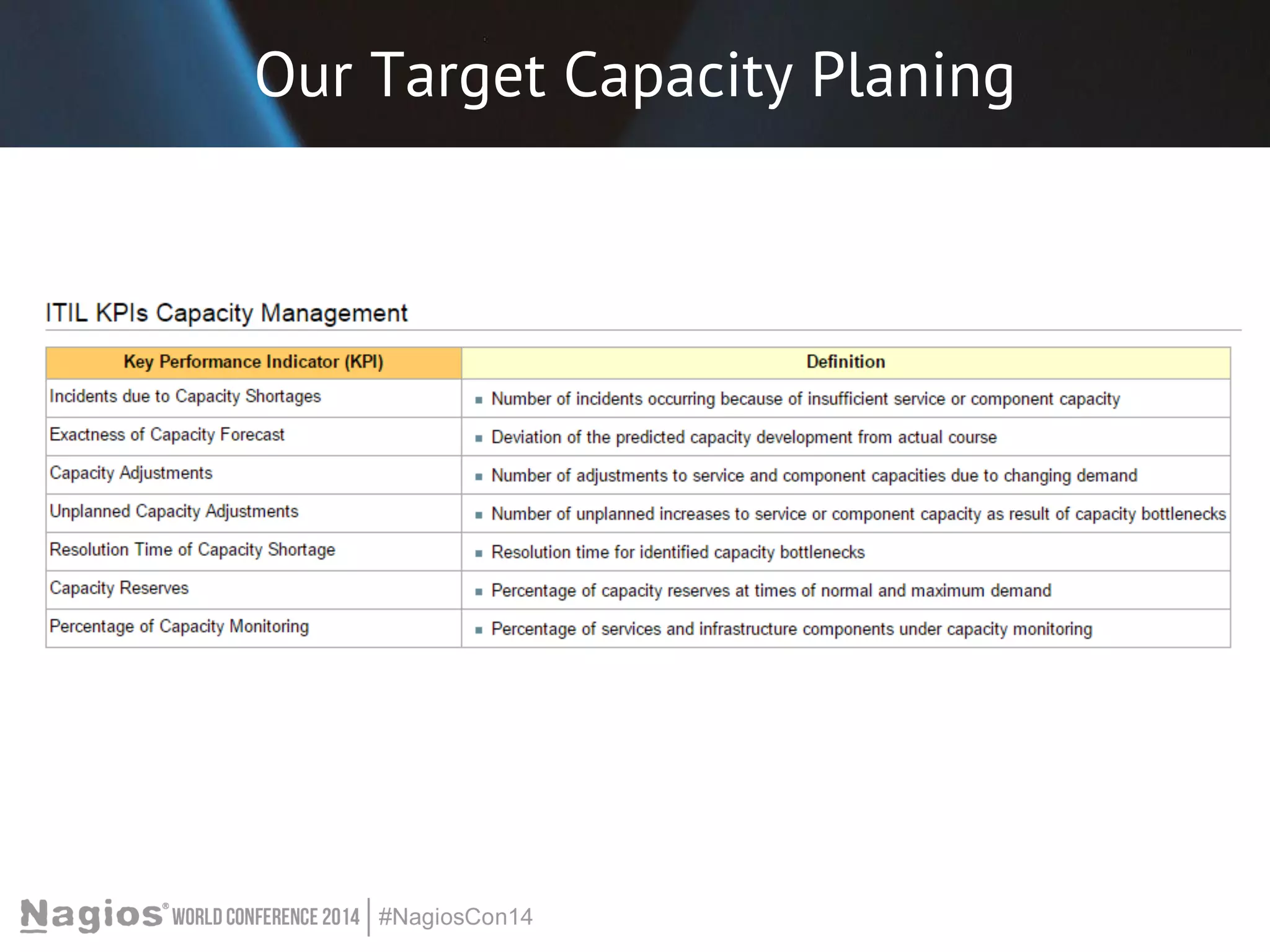
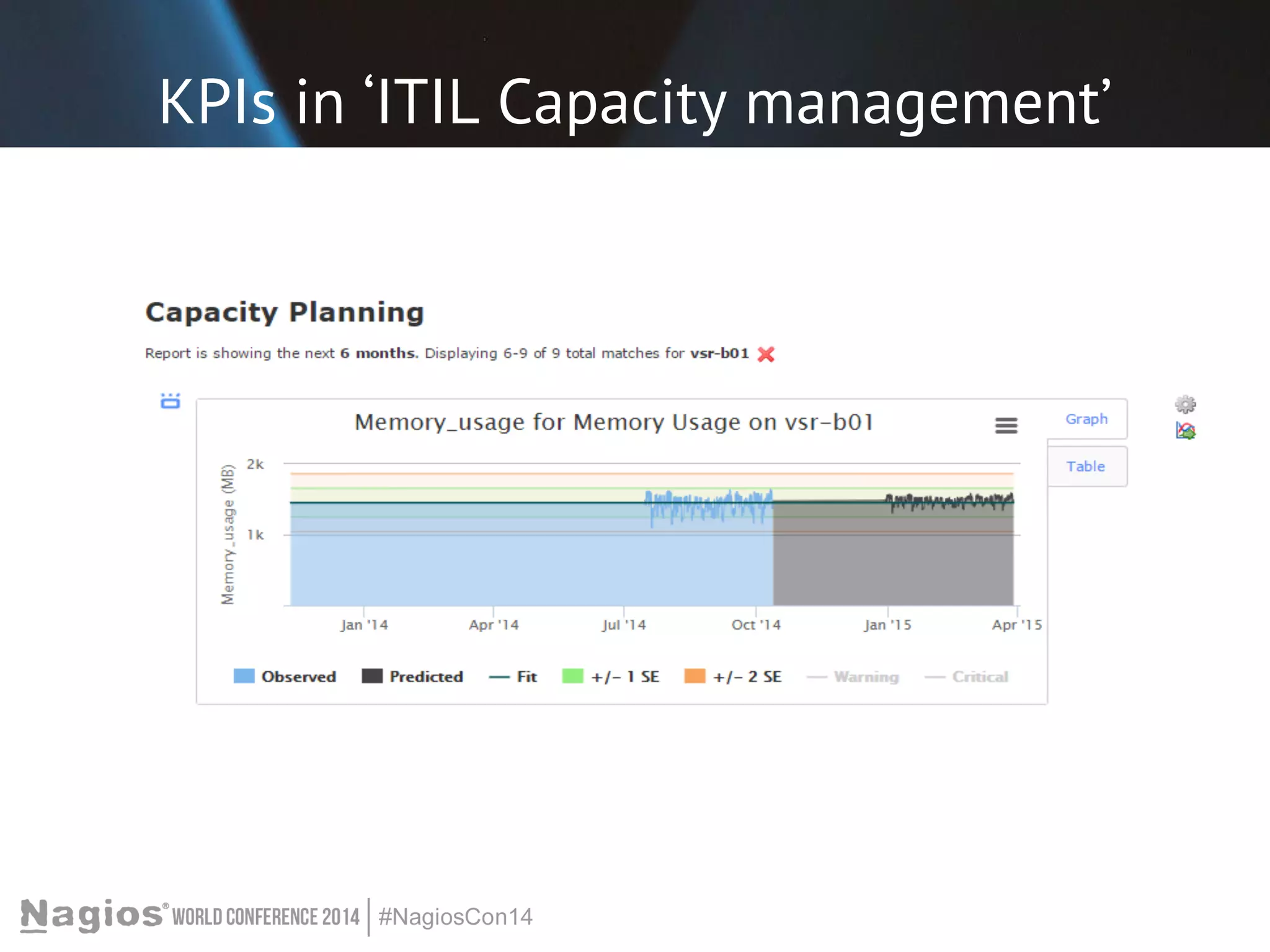
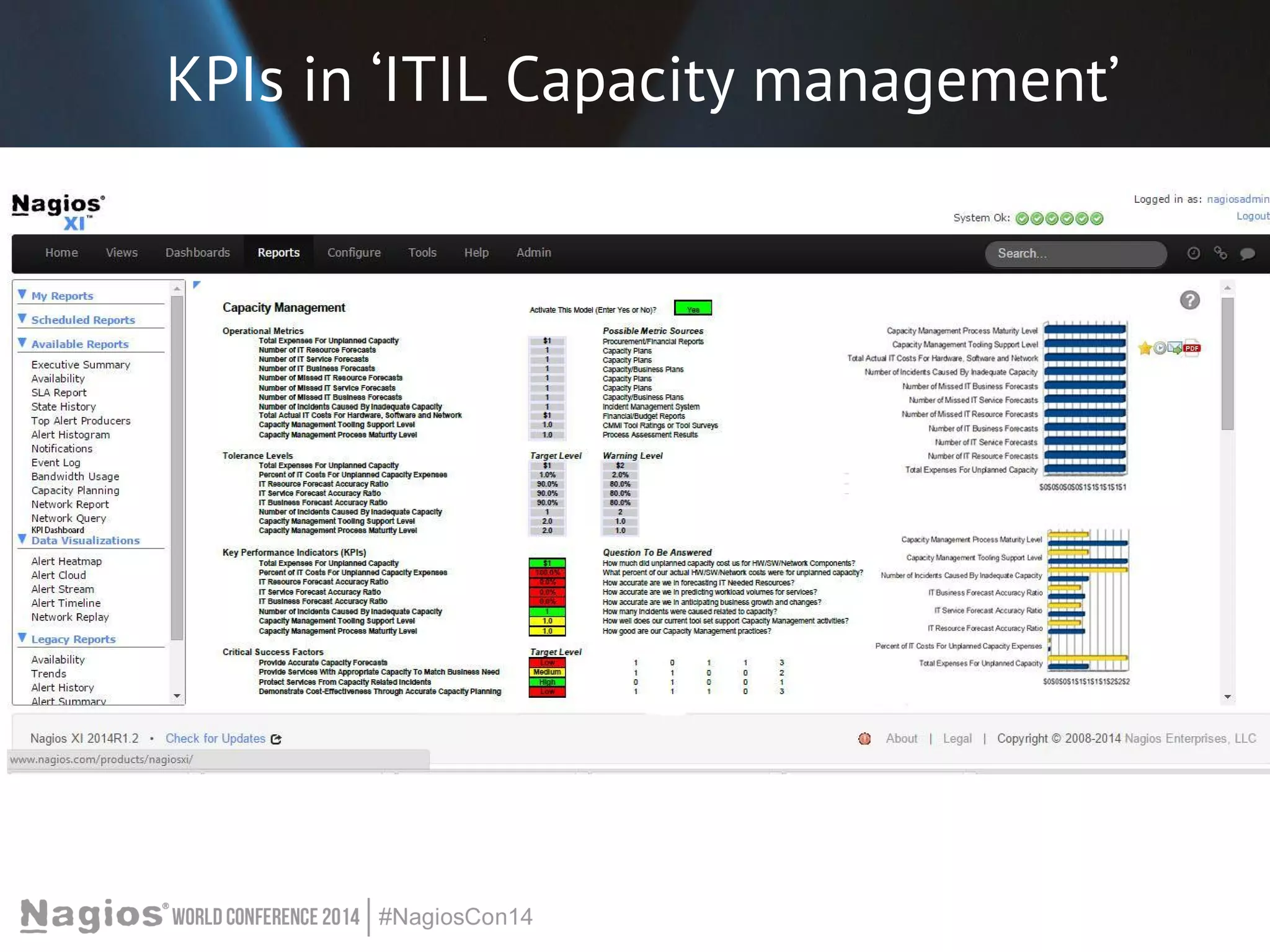
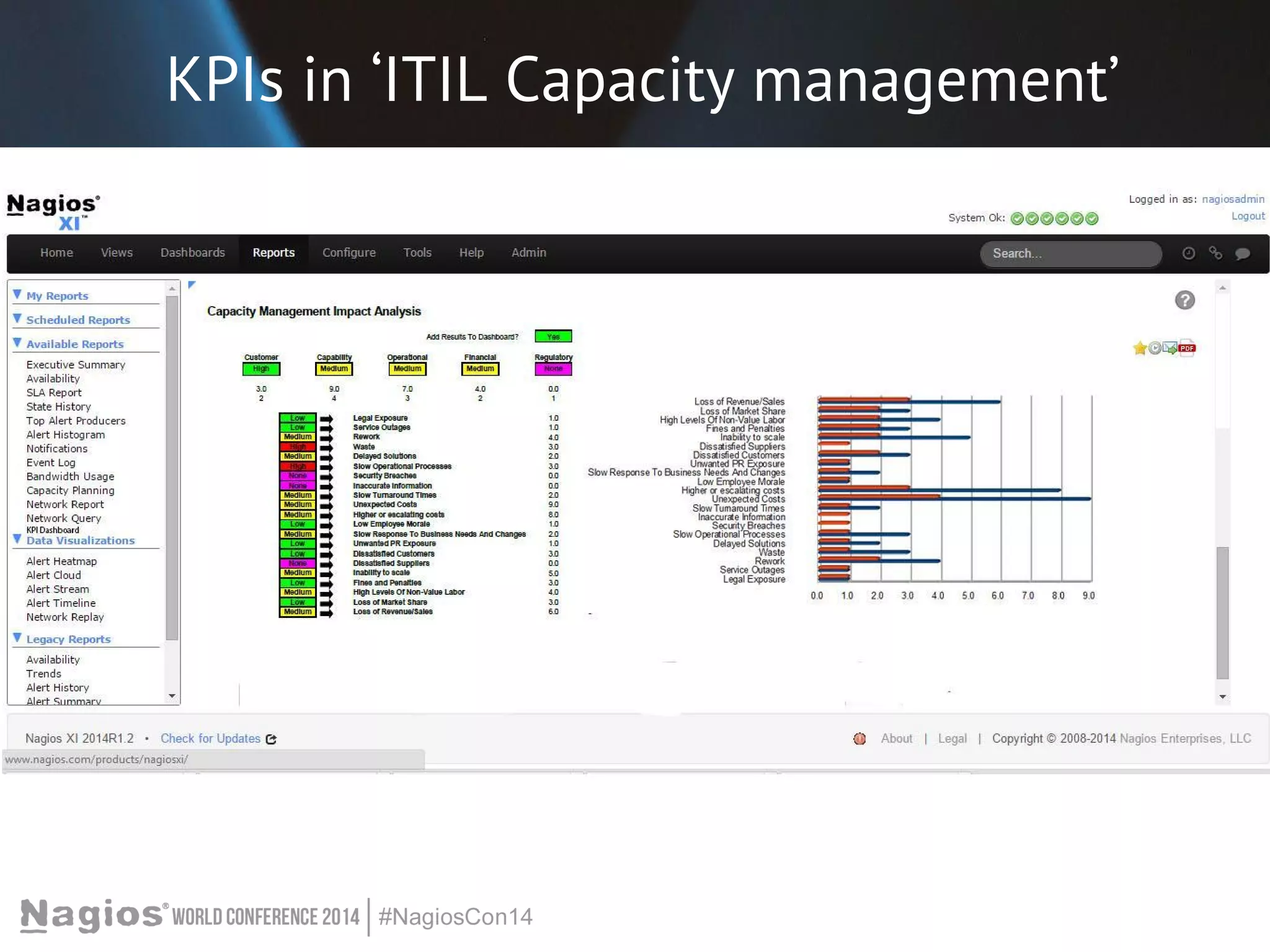
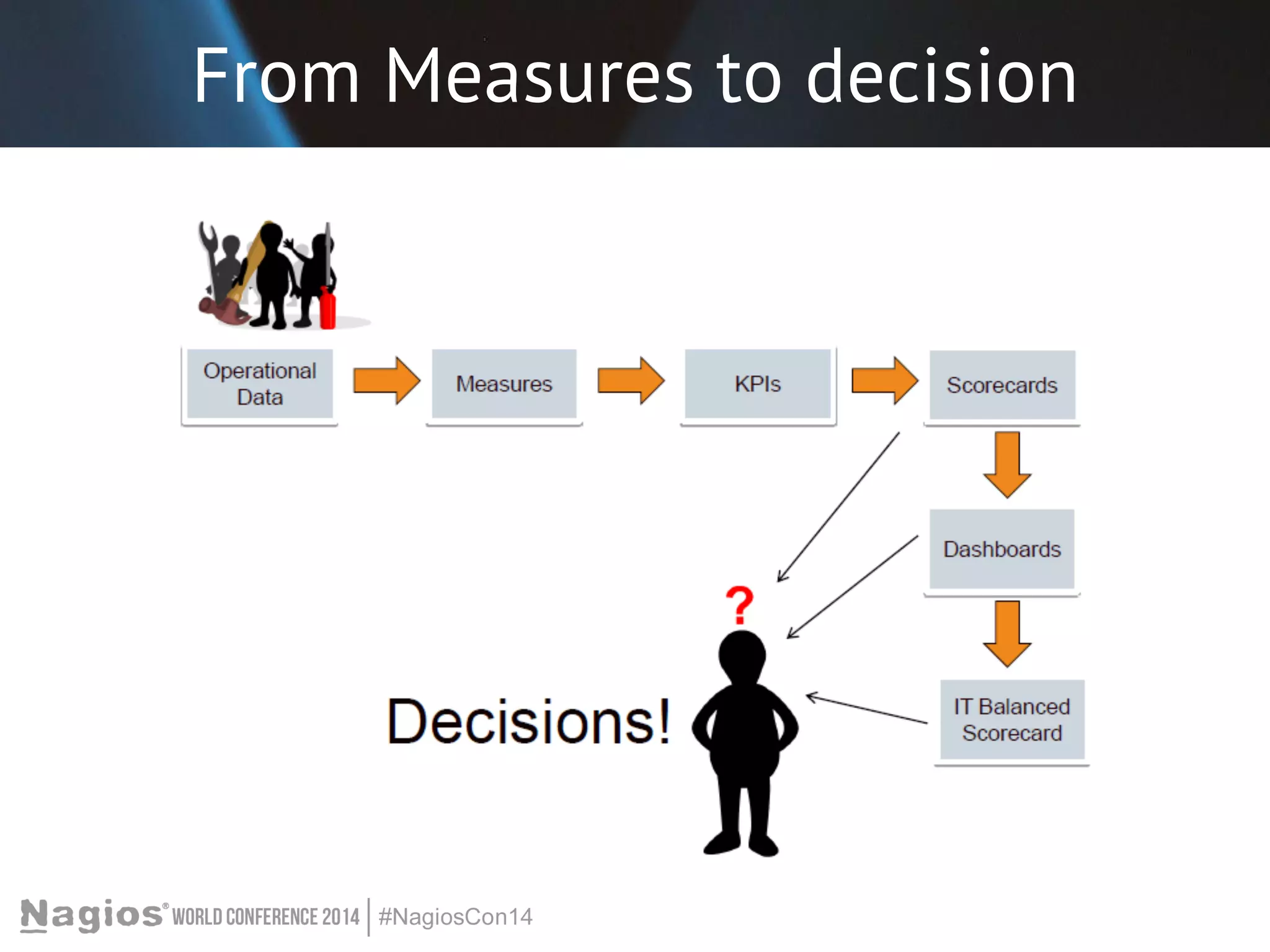
The document outlines the importance of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for measuring organizational performance, emphasizing their role in aligning with strategic goals. It discusses the creation of a KPI dashboard utilizing Nagios XI, detailing objectives for IT service management such as availability and capacity planning. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for clear objectives and metrics tailored to stakeholder requirements for effective performance management.