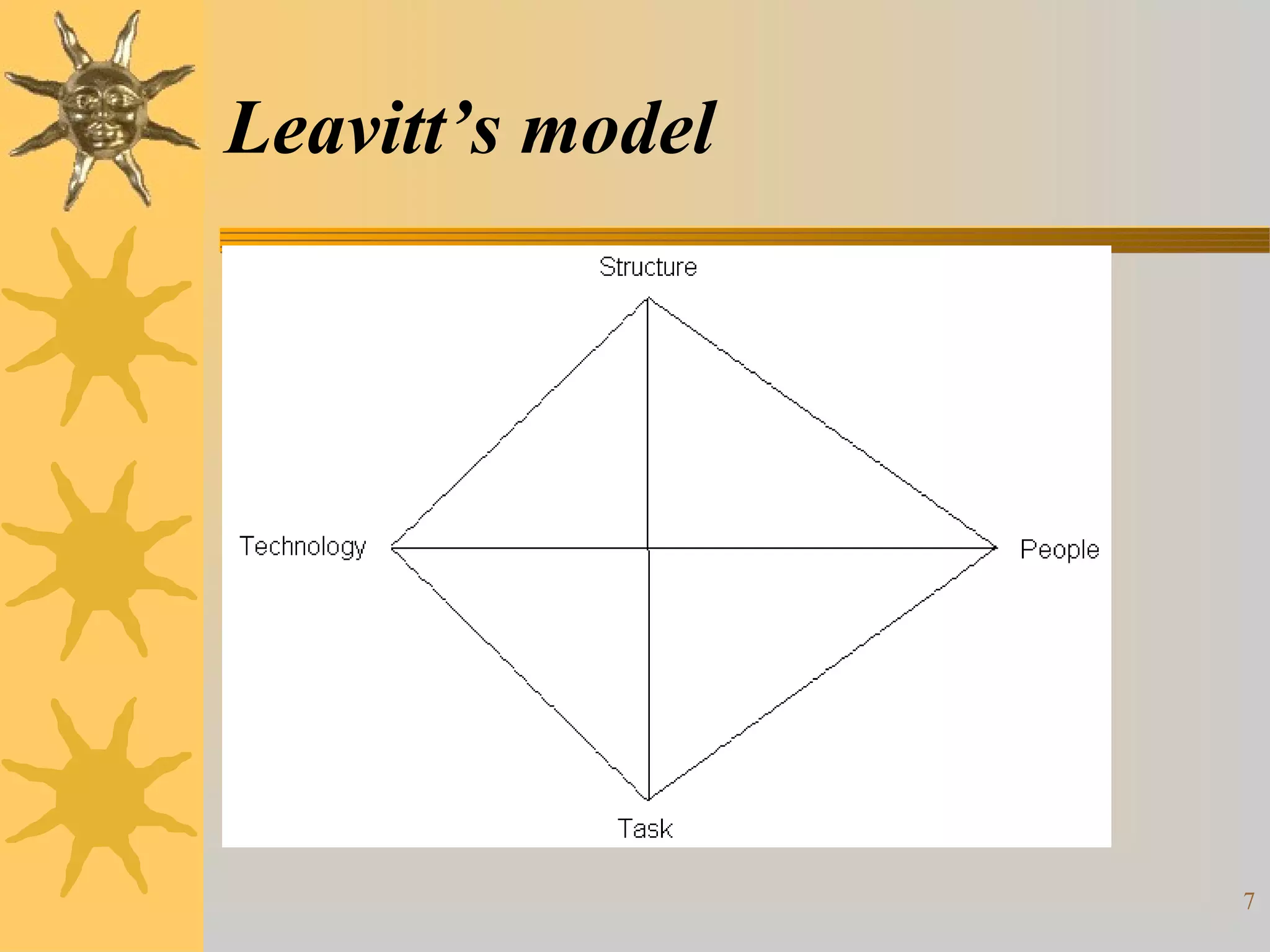
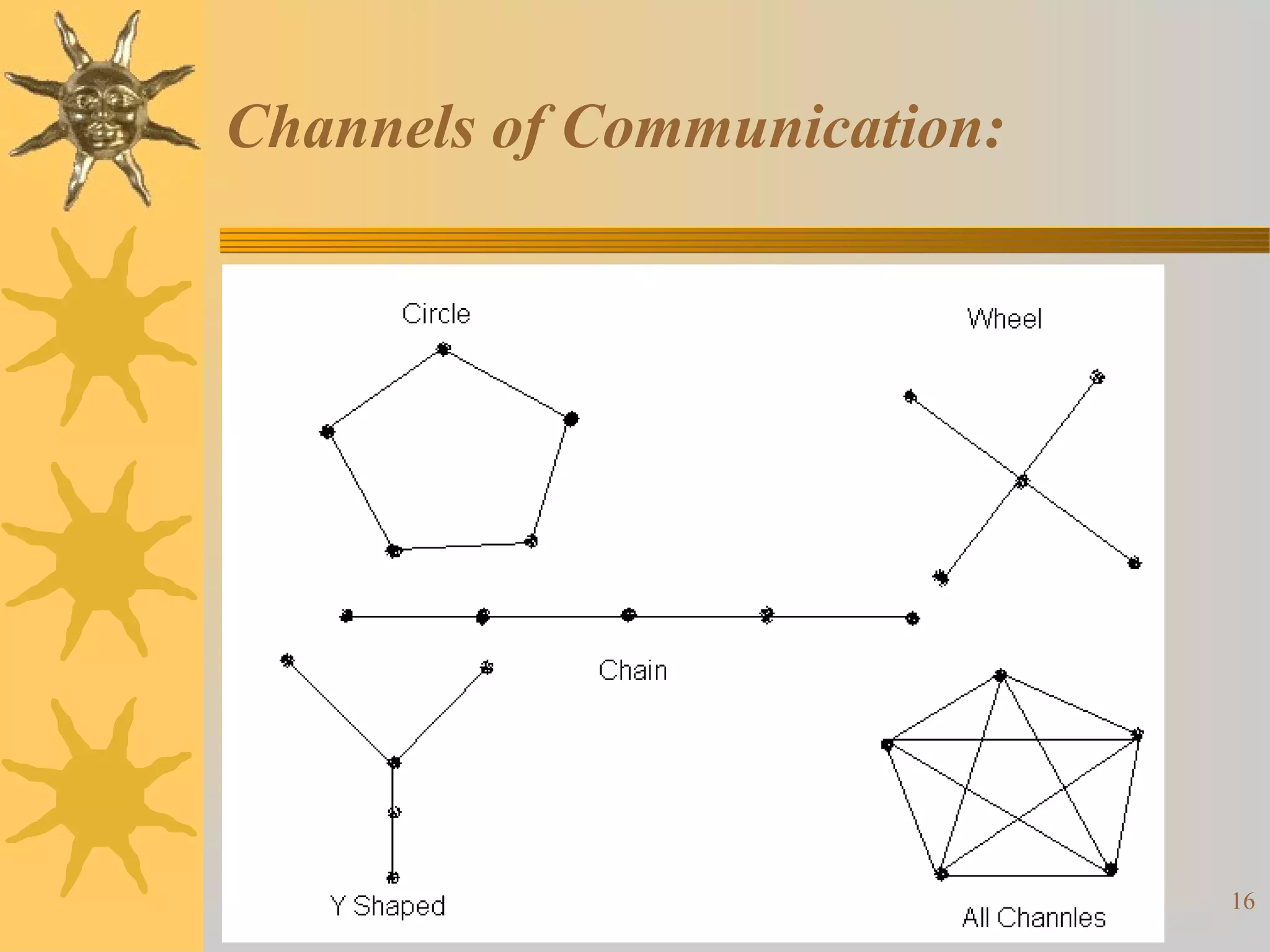
This document discusses organizational development (OD). It defines OD as a systematic, integrated approach to improve organizational effectiveness by solving problems at all levels. The key objectives of OD include improving performance, adaptability, problem-solving skills, and internal behaviors. OD uses models like Lewin's change model and is based on theories of individual and organizational behavior. Interventions can be individual-focused, like training, or organization-focused, like surveys or team building. Factors like applicability and acceptability influence the choice of interventions. Effective communication is also important for OD.