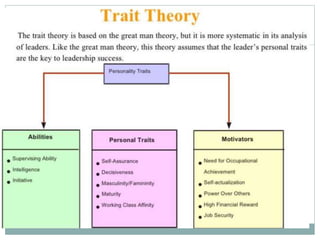
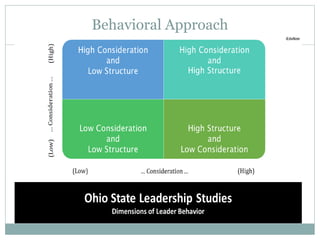
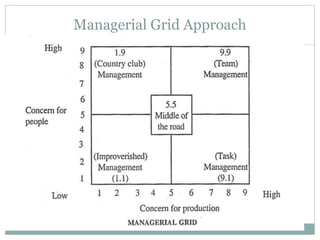
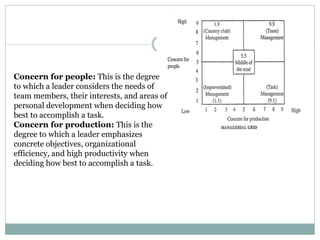
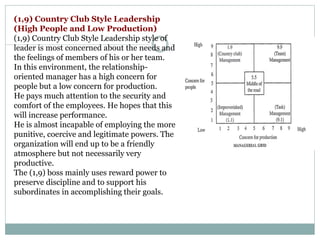
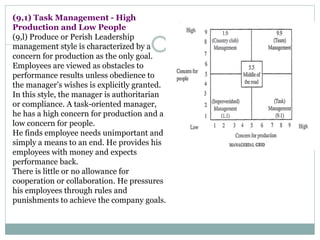
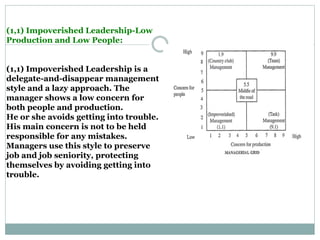
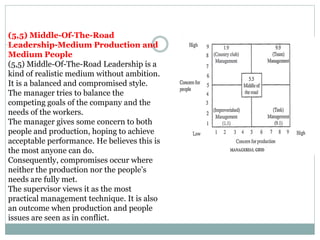
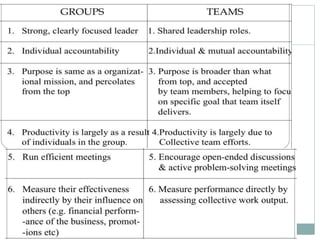
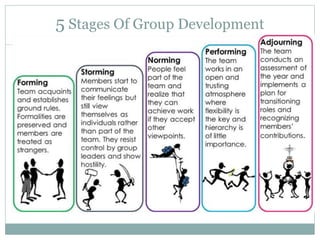
The document discusses leadership, motivation, groups, and teams. It covers key concepts such as different leadership styles (autocratic, democratic, laissez-faire), approaches to leadership (trait, behavioral, transformational), stages of group development (forming, storming, norming, performing), and differences between groups and teams. The document provides definitions and characteristics of these various management-related concepts to help understand leadership functions and group dynamics within organizations.