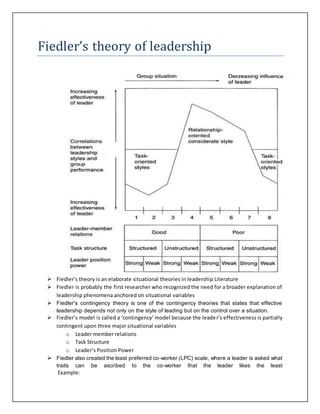
Fiedler's contingency theory states that effective leadership depends on both the leader's style and the situation. The theory assesses leadership situations based on three factors: leader-member relations, task structure, and the leader's position power. It also uses the Least Preferred Co-worker scale to determine a leader's orientation as either relationship-oriented or task-oriented. Depending on how favorable or unfavorable a situation is based on the three factors, different leader orientations will be more or less effective.