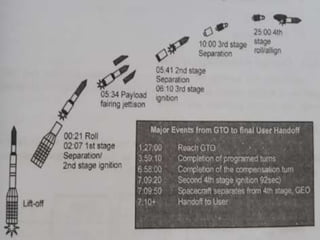
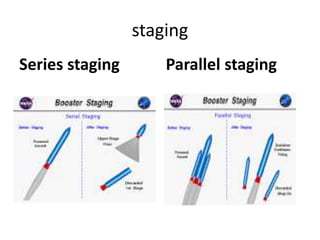
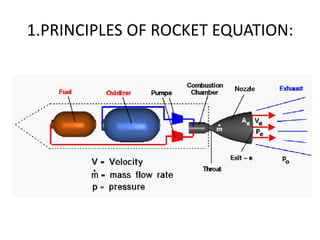
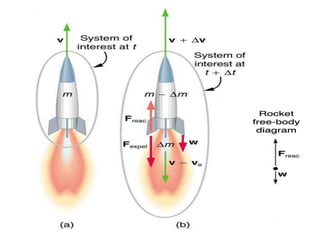
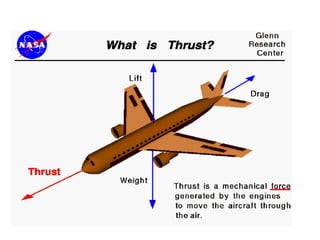
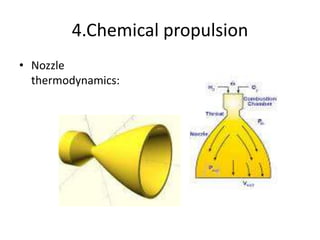
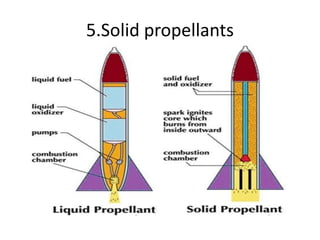
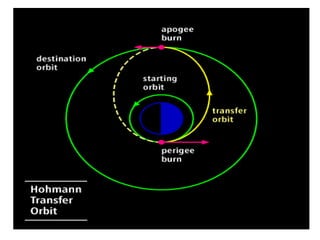
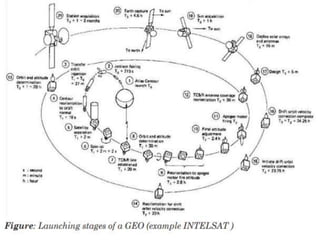
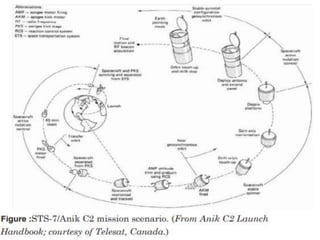
Launch vehicles use multi-stage configurations and rocket propulsion to inject payloads into specific orbital trajectories based on velocity and altitude, with chemical propulsion being the most common but ion engines providing higher exhaust velocities. Satellites are launched on expendable or reusable vehicles depending on their design from sites around the world, with factors like Earth's rotation sometimes providing an assist through sling effect to reduce launch costs. Over 2500 satellites currently orbit Earth for purposes including communication, and careful orbital placement prevents collisions despite increasing congestion.