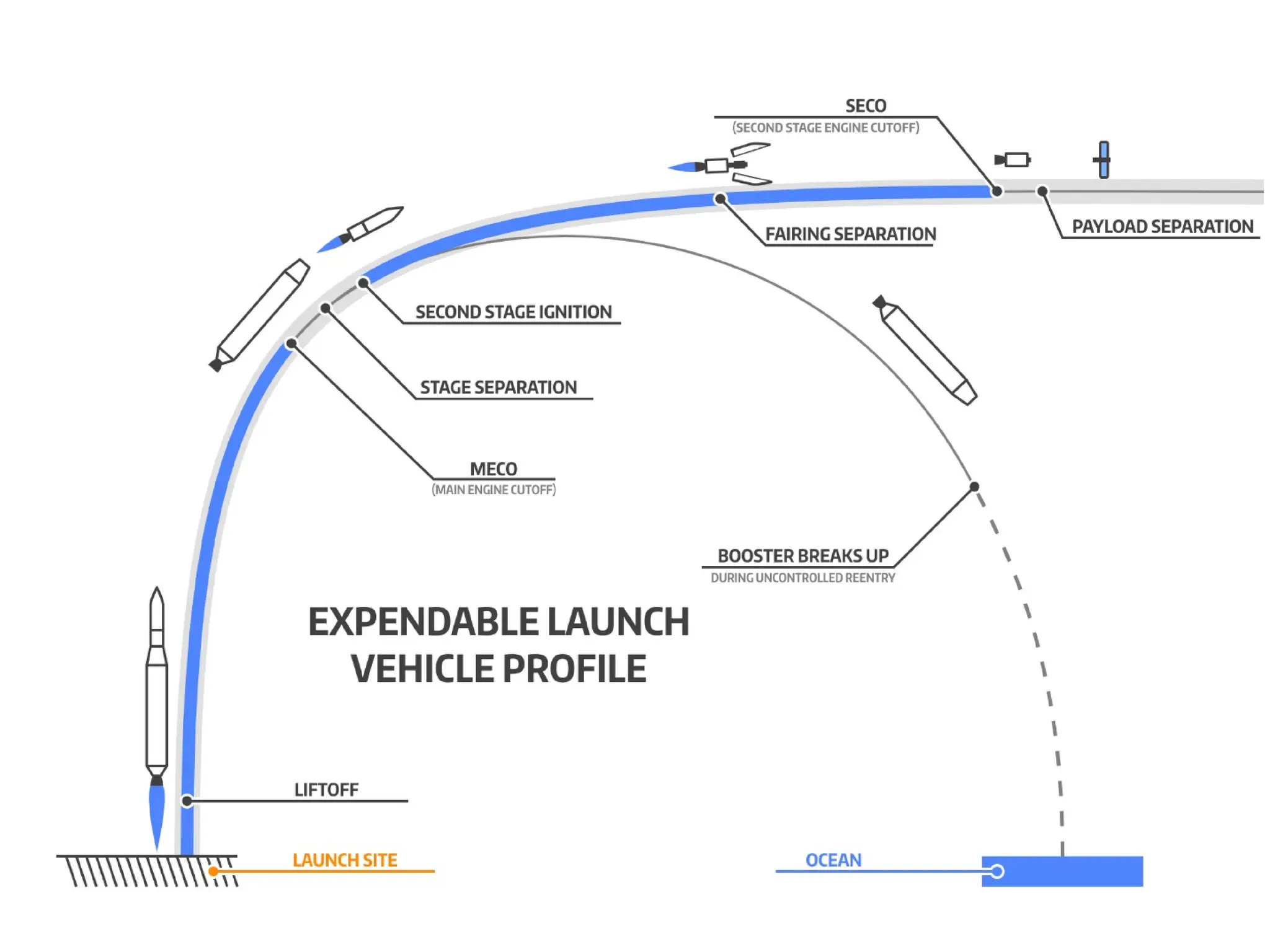
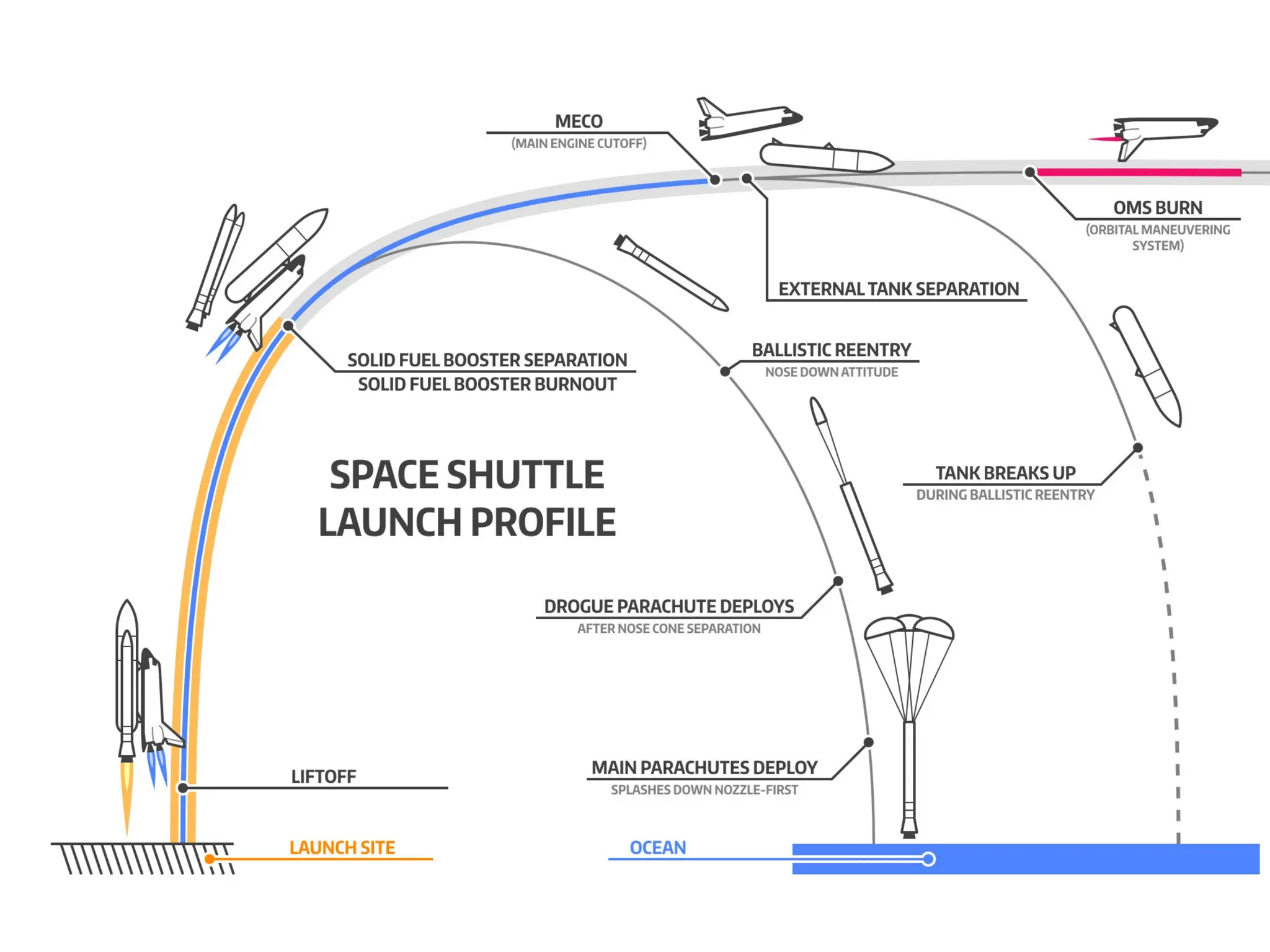
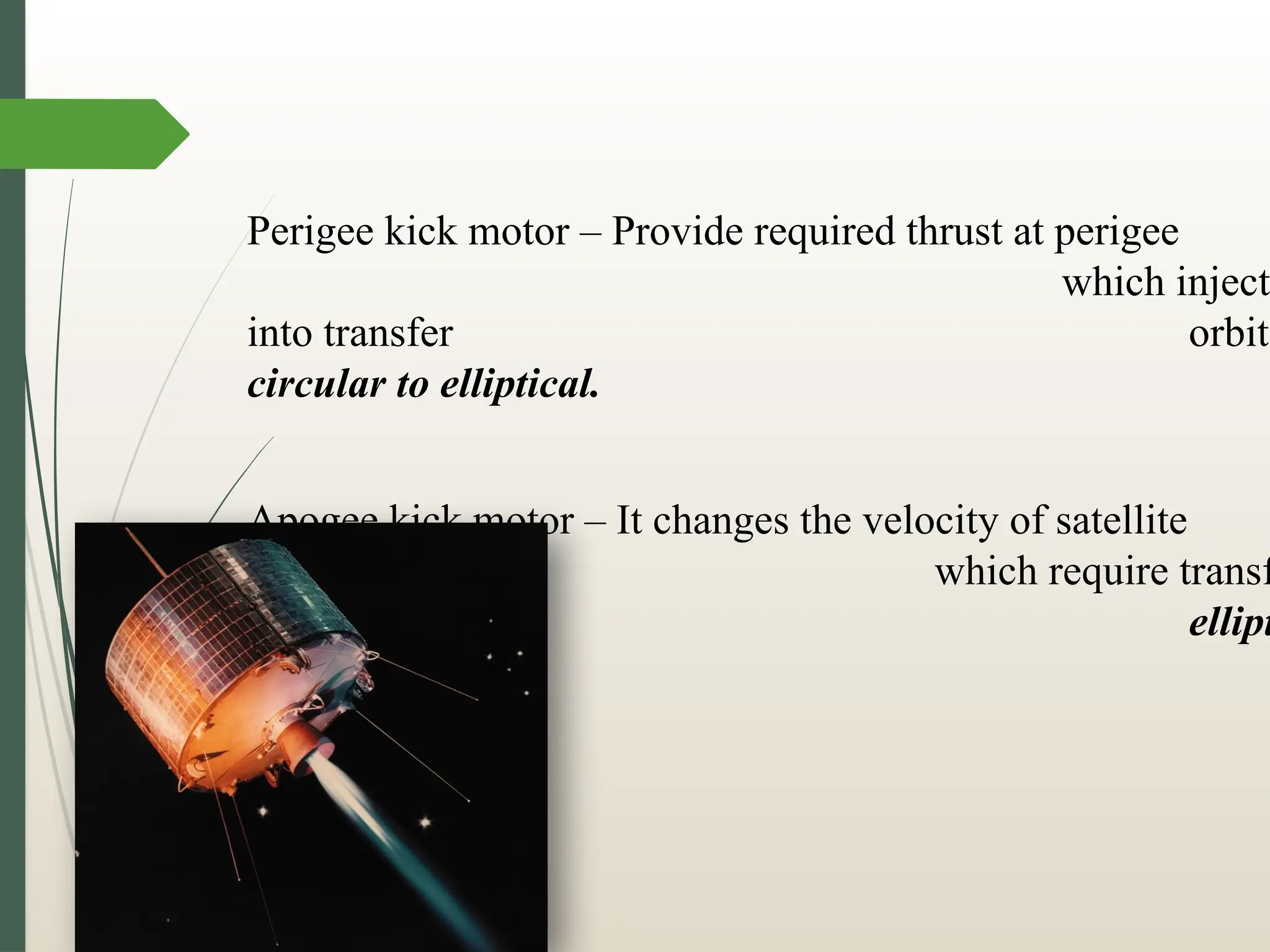
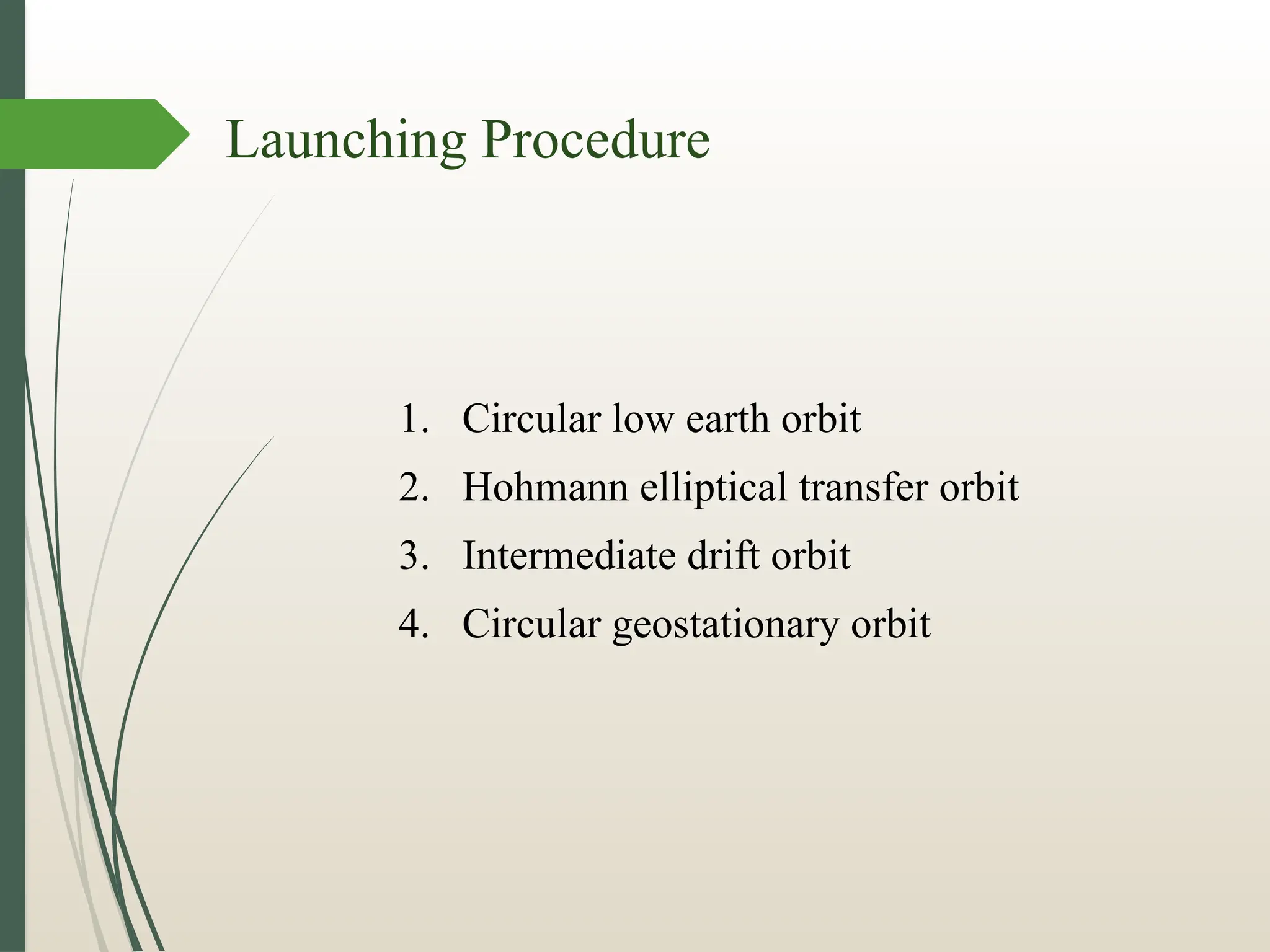
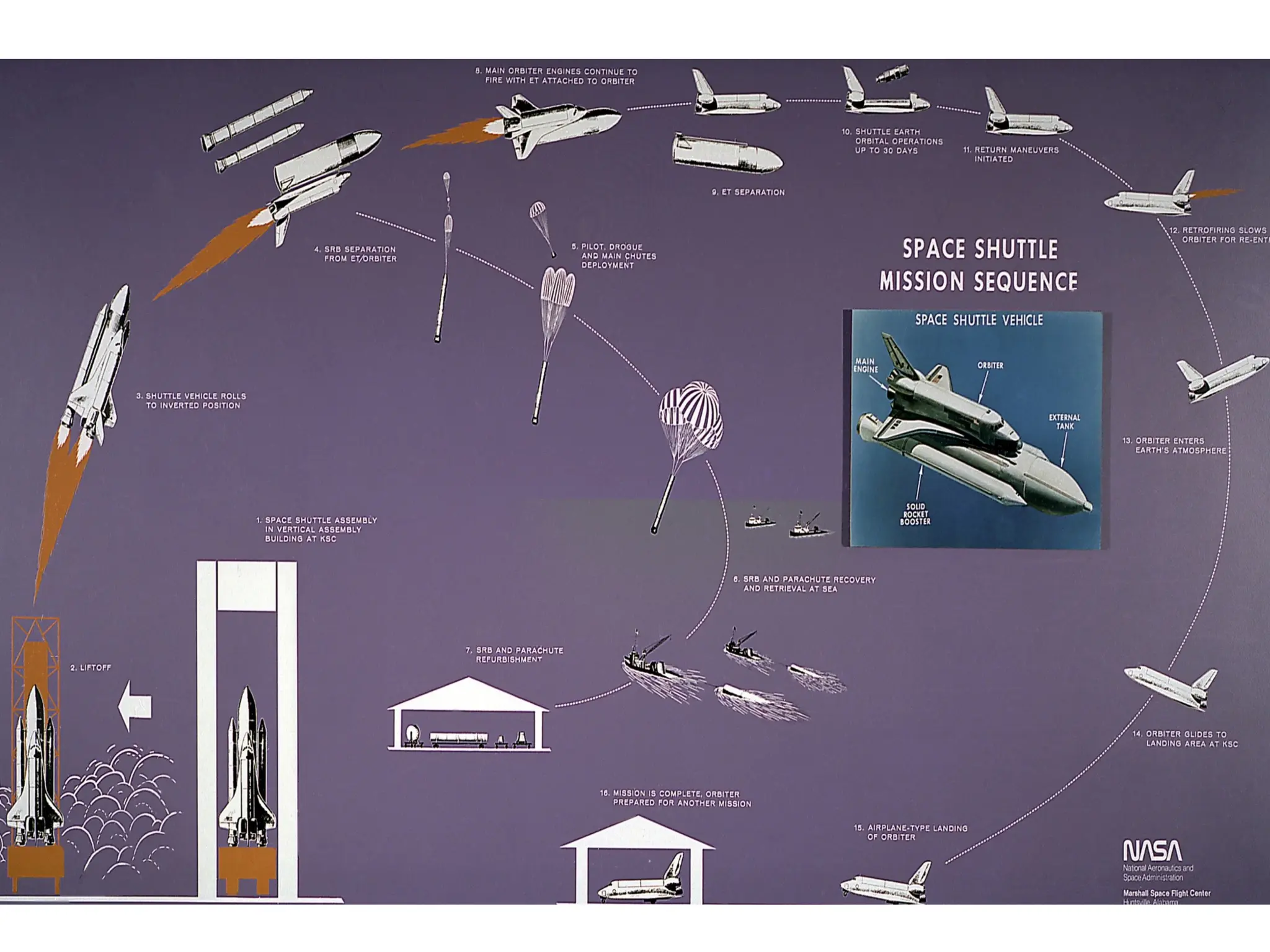
The document discusses launching procedures and types of launch vehicles used to place satellites into orbit, specifically outlining expendable and reusable launch vehicles. It explains the mechanics of satellite injection into lower Earth orbit and the use of Hohmann transfer orbits for satellites destined for higher orbits, highlighting crucial components such as perigee and apogee kick motors. Additionally, it notes challenges faced during launch, including environmental factors and technical errors.