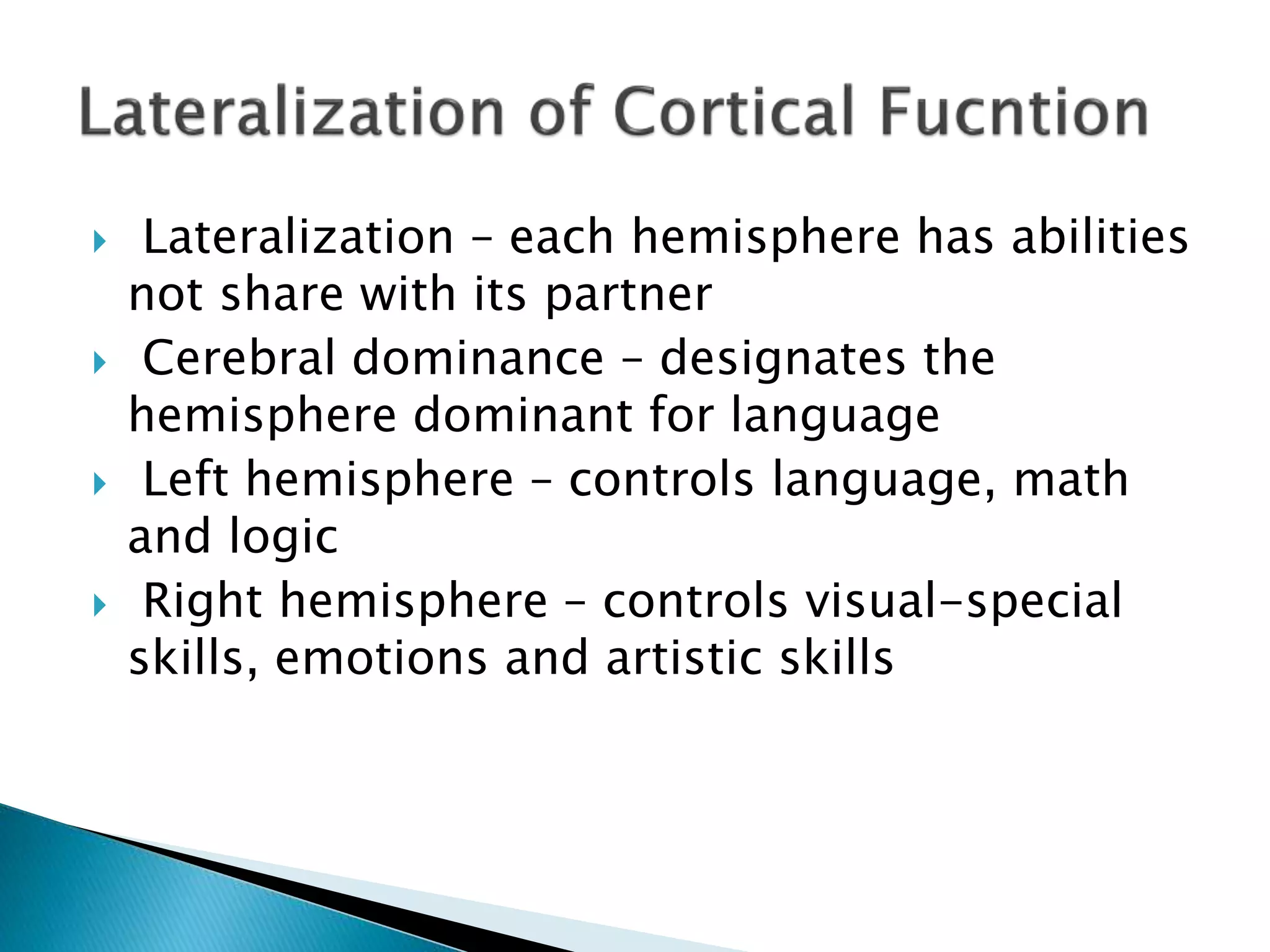
The document discusses several key points about lateralization of brain function:
- The brain is divided into two hemispheres, the left and right, which each specialize in different functions. The left hemisphere typically controls language and logical thinking while the right controls visual-spatial skills and emotions.
- Lateralization refers to this functional specialization of the two hemispheres, with some neural processes localized to one side or the other. The two hemispheres are connected by the corpus callosum.