Embed presentation
Downloaded 26 times


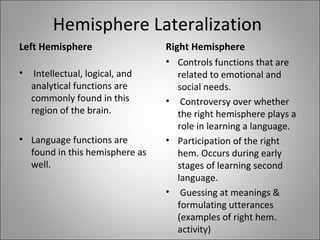
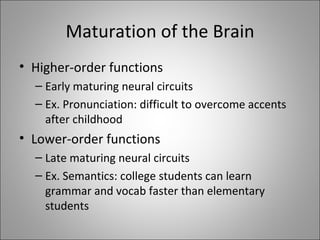


The document discusses several factors related to second language learning and the brain. It covers the critical period hypothesis, brain lateralization, brain maturation, and the role of social and cultural factors in language acquisition. Specifically, it notes that the young brain is more plastic and able to recover from trauma. Both hemispheres contribute to language learning, but different functions are specialized in each. Higher-order language skills mature earlier than lower-order skills. Finally, social and cultural influences beyond just the brain also impact second language learning.





