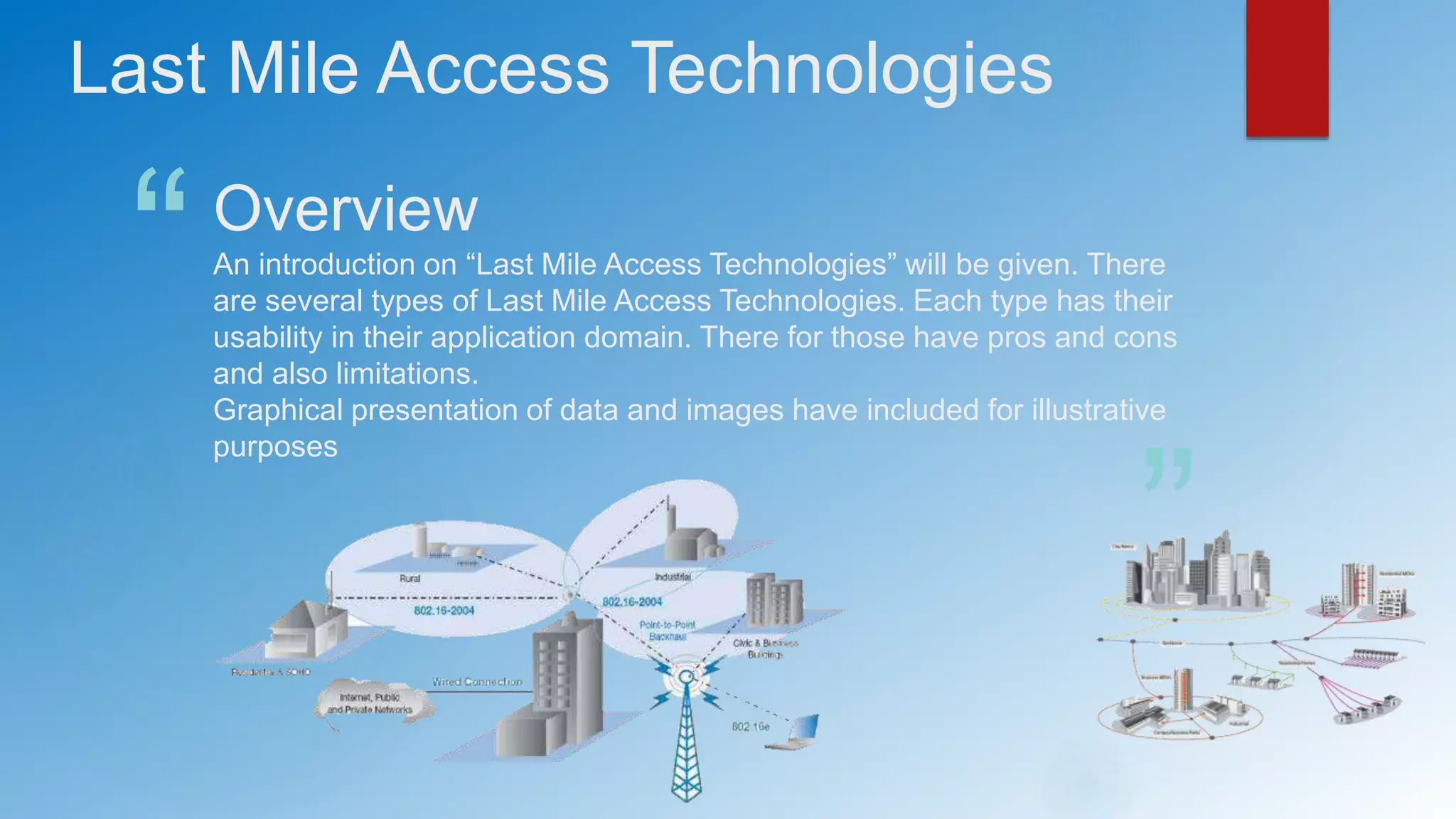
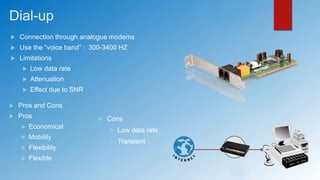
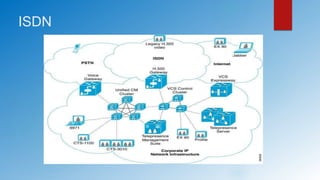
The document provides an overview of last mile access technologies, detailing various types such as copper wire-based, cable TV, wireless, and other physical access networks. Each technology has distinct pros and cons, and the trends show a movement towards more reliable methods while acknowledging the continued use of legacy systems. It emphasizes the importance of different implementation mechanisms, mobility, and the need for optimized security and performance.











![References
[1] “Last Mile”. Jan 3 2014 . Available http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Last_mile. [Accessed: May 29,
2014].
[2] “last-mile technology” . Apr 2005. [Blog entry] Rouse. Available
http://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/definition/last-mile-technology [Accessed: 29 May
2014].
[3] A.Z. Dodd, Essential guide to telecommunications, 5th ed. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 2012.
[4] “Broadband Telecommunications” . Mar 7 2012. [Blog entry] Jchan. Available
http://jonapchan.blogspot.com/ [Accessed: 29 May 2014].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lastmileaccesstechnologies-150203084145-conversion-gate01/85/Last-Mile-Access-Technologies-15-320.jpg)