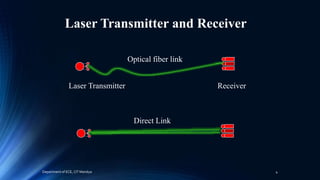
The document presents a technical seminar on laser communication systems, detailing their functioning, components such as transmitters and receivers, modulation techniques, and application areas. It highlights the advantages, including ease of deployment and immunity to electromagnetic interference, while also addressing limitations like atmospheric absorption and interference from background light. The conclusion emphasizes laser communication as a viable alternative to RF communications, particularly for high-performance inter-satellite links.