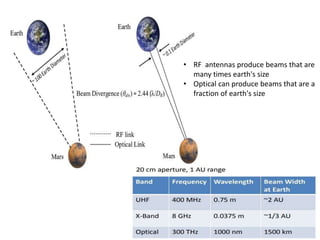
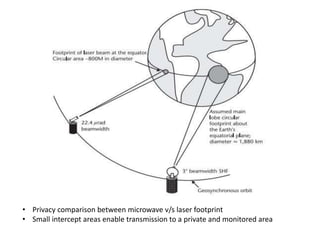
The document presents an overview of laser communication, detailing its functioning, components such as transmitters and receivers, and comparing it to RF and fiber optics. It highlights the advantages of laser communication, including high data rates and security, while also discussing its limitations such as atmospheric interference. Specific applications and a notable NASA demonstration are also mentioned, emphasizing the potential of laser communication for enhanced data transmission.