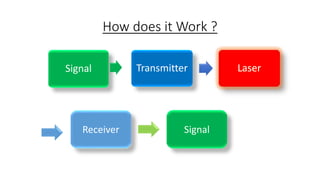
Laser communication systems transmit information via laser beams through the atmosphere, providing a wireless alternative to fiber optic cables. They involve laser transmitters that emit laser signals, and receivers with telescopes and detectors that receive the signals. Modulation techniques like amplitude modulation are used to encode data onto the laser beams. Applications include long distance communication between planets or satellites, as was demonstrated by the LADEE mission which achieved a record breaking 622 Mbps data transmission between the Moon and Earth using laser communication.