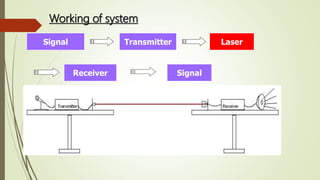
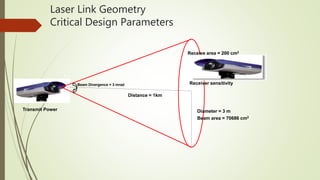
Laser communication uses laser beams to transmit data through free space. It works similarly to fiber optic communication but through the atmosphere instead of cables. The system consists of a transmitter section that converts signals into a laser beam and a receiver section that receives the beam and extracts the data signals. Laser communication has advantages over radio including higher bandwidth and more secure communication. Its applications include satellite communication and tactical networks. Challenges include atmospheric effects like absorption, fog, and rain that can disrupt the laser beam.