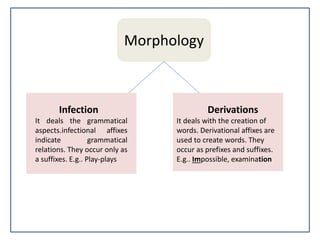
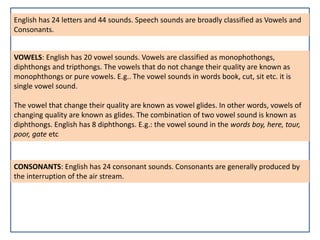
The document discusses the relationship between language and culture. It states that language is the most important component of culture, and that language and culture are intertwined. Culture determines how people communicate through language by influencing message encoding and imposing social norms. The document also discusses the role of family and community in language development for children, with parents and interaction with others being important factors. Finally, it examines how culture can shape perspectives and the way linguistic concepts are categorized.