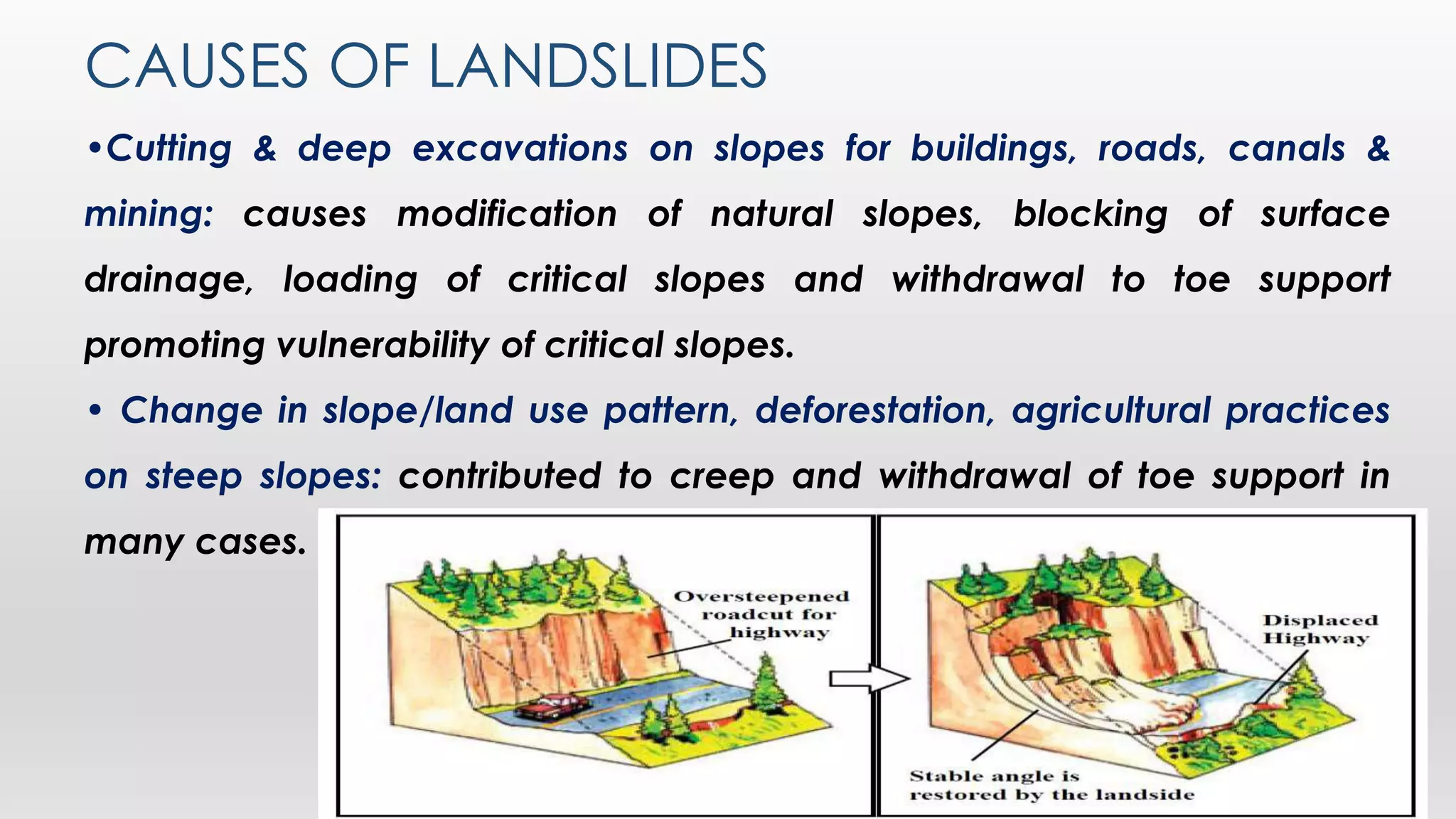
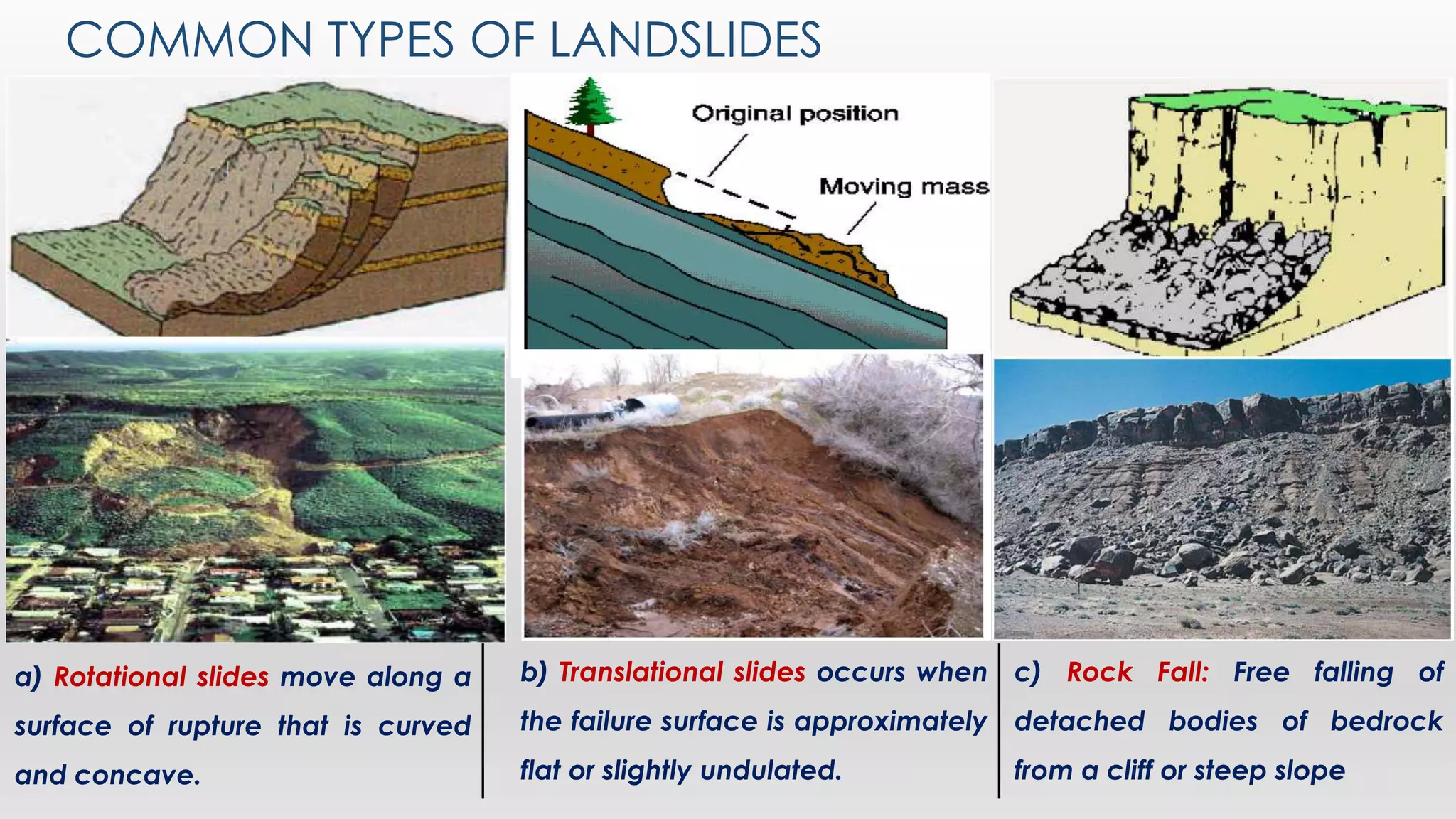
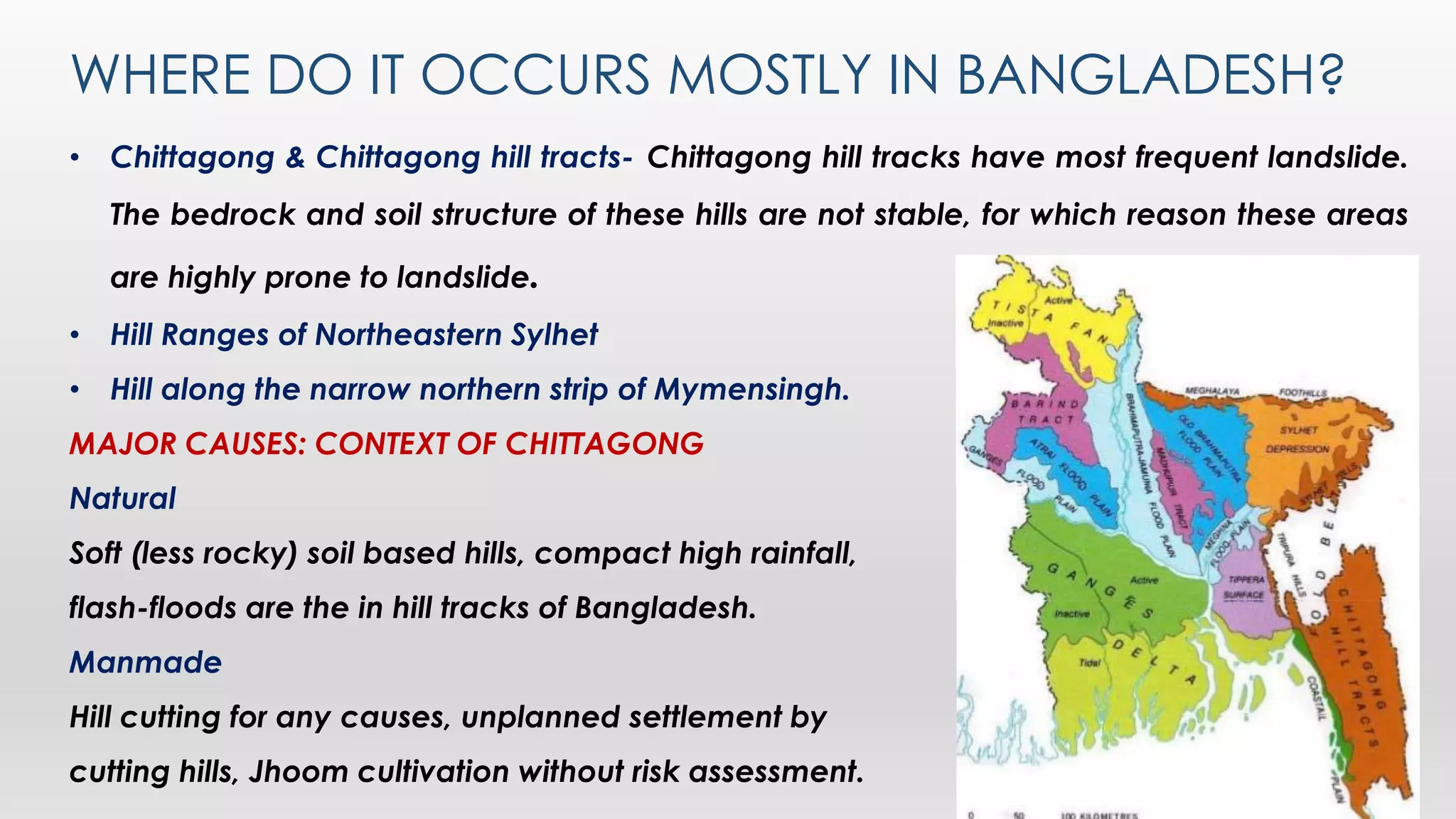
This document discusses landslides, including their causes and types. It defines a landslide as the downward or outward movement of soil, rock, or vegetation under the influence of gravity. Landslides are caused by both natural factors like heavy rainfall, earthquakes, and geological conditions, as well as human factors like deforestation and construction activities. The main types of landslides described are rotational, translational, rock falls, rock toppling, and debris flows. Strategies for mitigating landslides include hazard mapping, controlling surface drainage, using retaining walls, and increasing vegetation cover. Chittagong and the Chittagong Hill Tracts in Bangladesh experience the most landslides due to soft soil, high rainfall, and