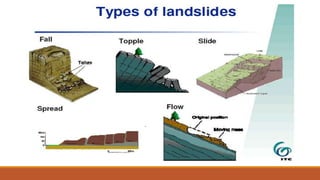
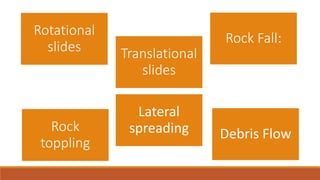
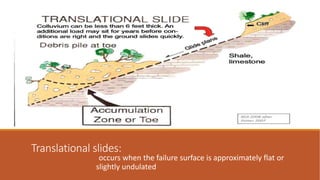
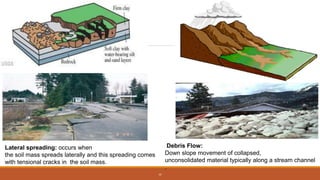
The document discusses landslides, including different types (rotational, translational, lateral spreading, debris flow, rock fall, rock toppling), main causes (gravity, geology, rainfall, earthquakes, forest fires, volcanoes, development, deforestation, drainage), and safety measures. It also describes a specific landslide lake that formed in Pakistan in 2010 due to a large landslide that blocked the Hunza River, causing flooding and secondary landslides. Prevention methods include passive intervention, active prevention, proper land use, and structural and non-structural safety measures.