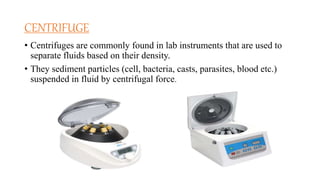
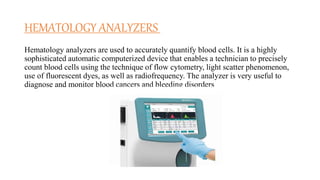
Laboratory instruments discussed include microscopes, centrifuges, analytical balances, refrigerators, hot air ovens, water baths, incubators, colorimeters/photometers, desiccators, pH meters, hematology analyzers, blood gas analyzers, haemoglobinometers, autoclaves, and biochemical analyzers. Microscopes are used to view micro-sized objects, centrifuges separate fluids by density, and analytical balances provide precision for reagent preparation. Other instruments like refrigerators, ovens, water baths, and incubators are used to control environmental conditions important for reagents and experiments. Additional tools measure various blood components and chemical properties.