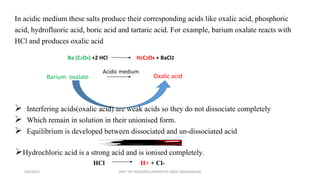
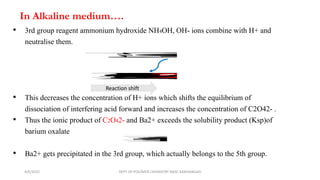
Certain anions like oxalate, tartrate, fluoride, borate, phosphate, and chromate can interfere with the qualitative analysis of cations if not removed. They are eliminated through processes like dry ignition (oxalate), treatment with hydrochloric acid (fluoride, borate), precipitation with zirconyl nitrate (phosphate), and evaporation with hydrochloric acid (chromate). Arsenate is first reduced to arsenite using ammonium iodide before both are eliminated by precipitation with hydrogen sulfide. The order of elimination is oxalate, tartrate, fluoride, borate, phosphate, and arsenate/arsenite to ensure accurate analysis of metal cations.