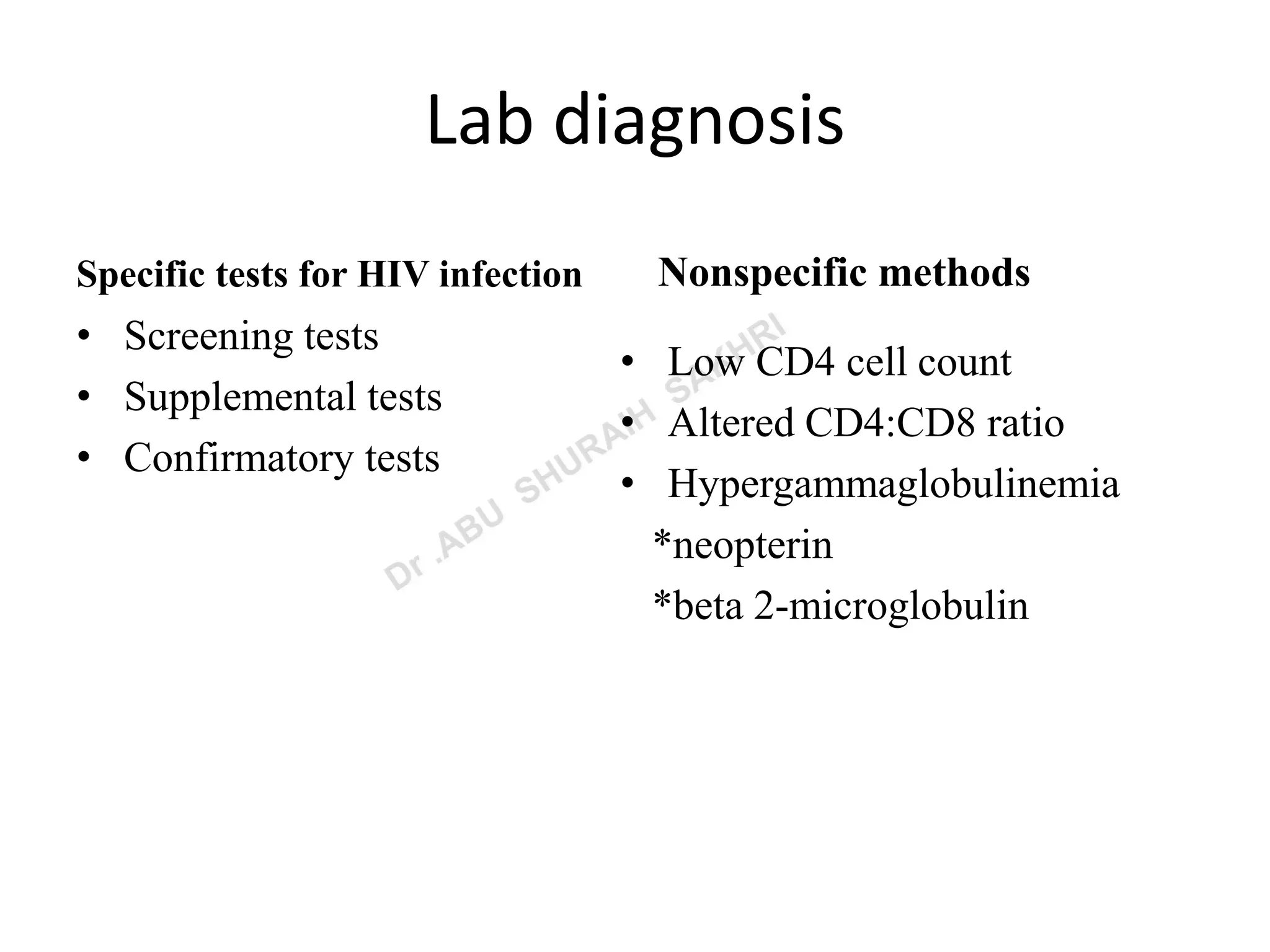
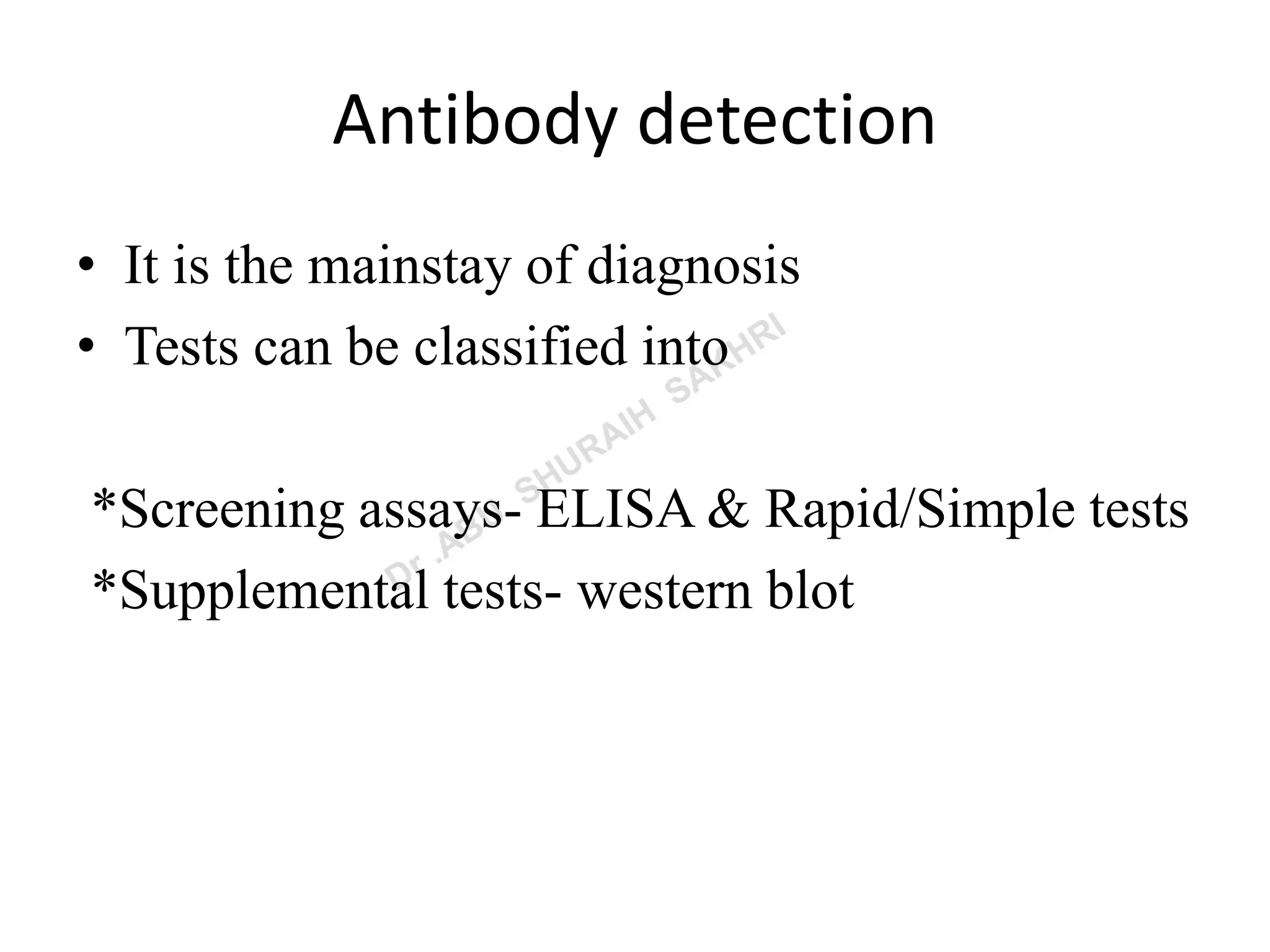
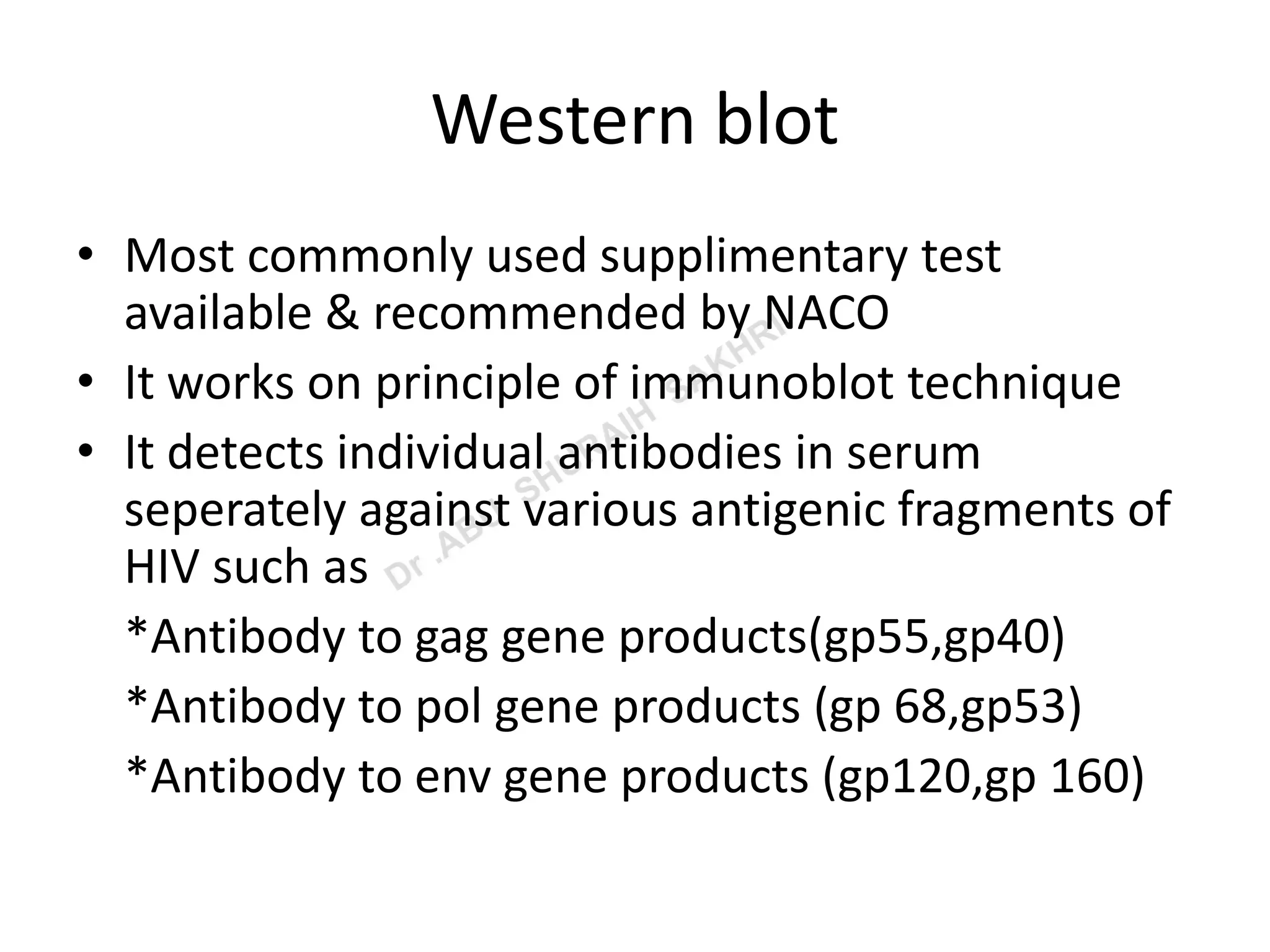
This document summarizes the various methods used to diagnose HIV infection in a laboratory setting. It discusses screening tests like ELISA and rapid tests that detect HIV antibodies, supplemental tests like Western Blot for antibody confirmation, and confirmatory tests including viral RNA detection by PCR and p24 antigen detection. It also mentions nonspecific immunological markers and stresses the importance of pre-test and post-test counseling.