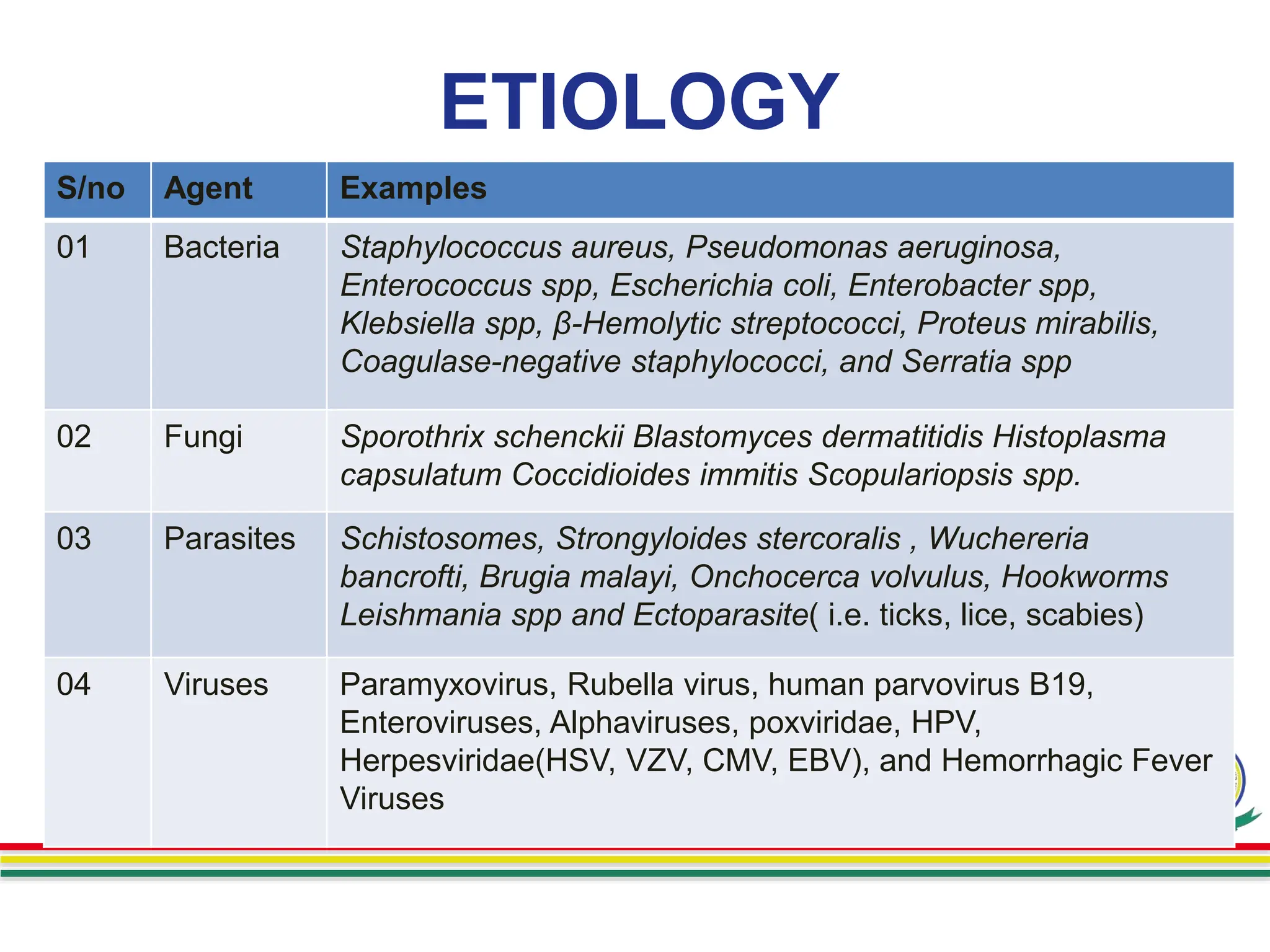
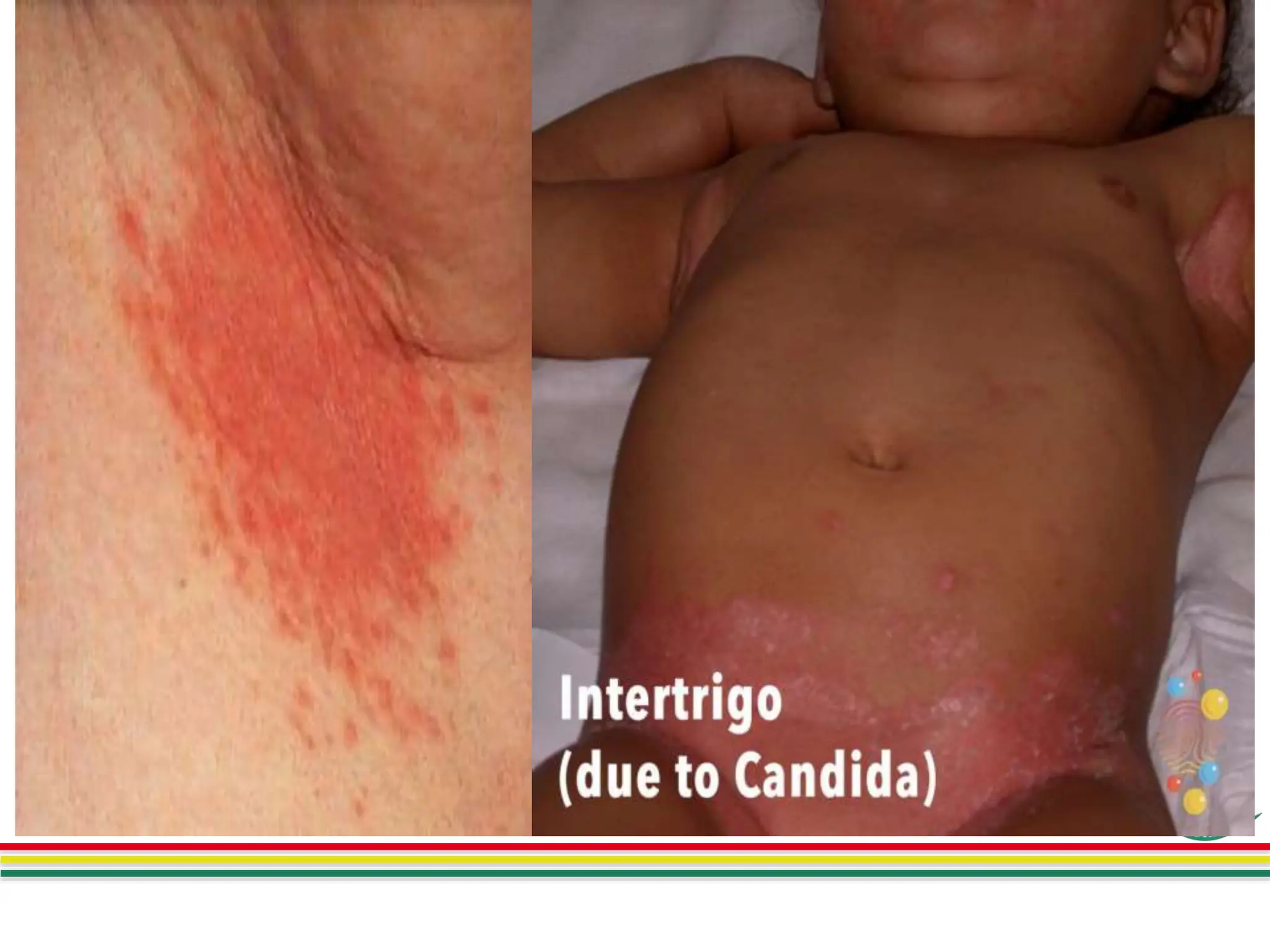
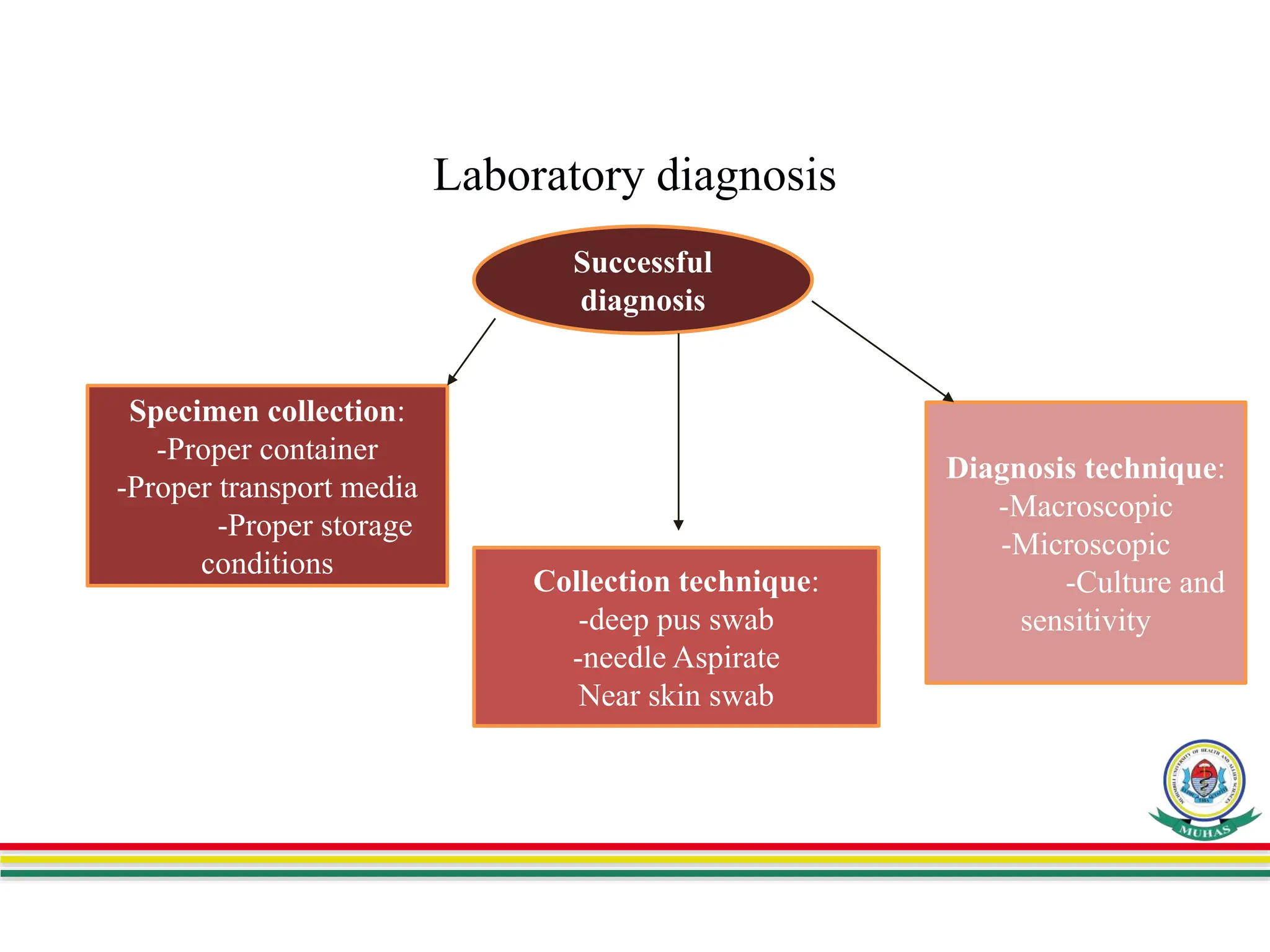
This document summarizes a presentation on skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs). SSTIs can be caused by bacteria, fungi, parasites, or viruses. They range from mild to life-threatening. Risk factors include hospitalization, skin injuries, surgery, skin conditions like eczema, obesity, diabetes, and immunosuppression. Classification is based on lesion type, causative agent, and pathogenesis. Clinical manifestations vary and include dermatitis, erythrasma, ringworm, pyoderma, impetigo, and necrotizing infections. Diagnosis involves specimen collection and testing like microscopy, culture, identification and antimicrobial susceptibility. Treatment is guided by test results and prevention focuses on hygiene,