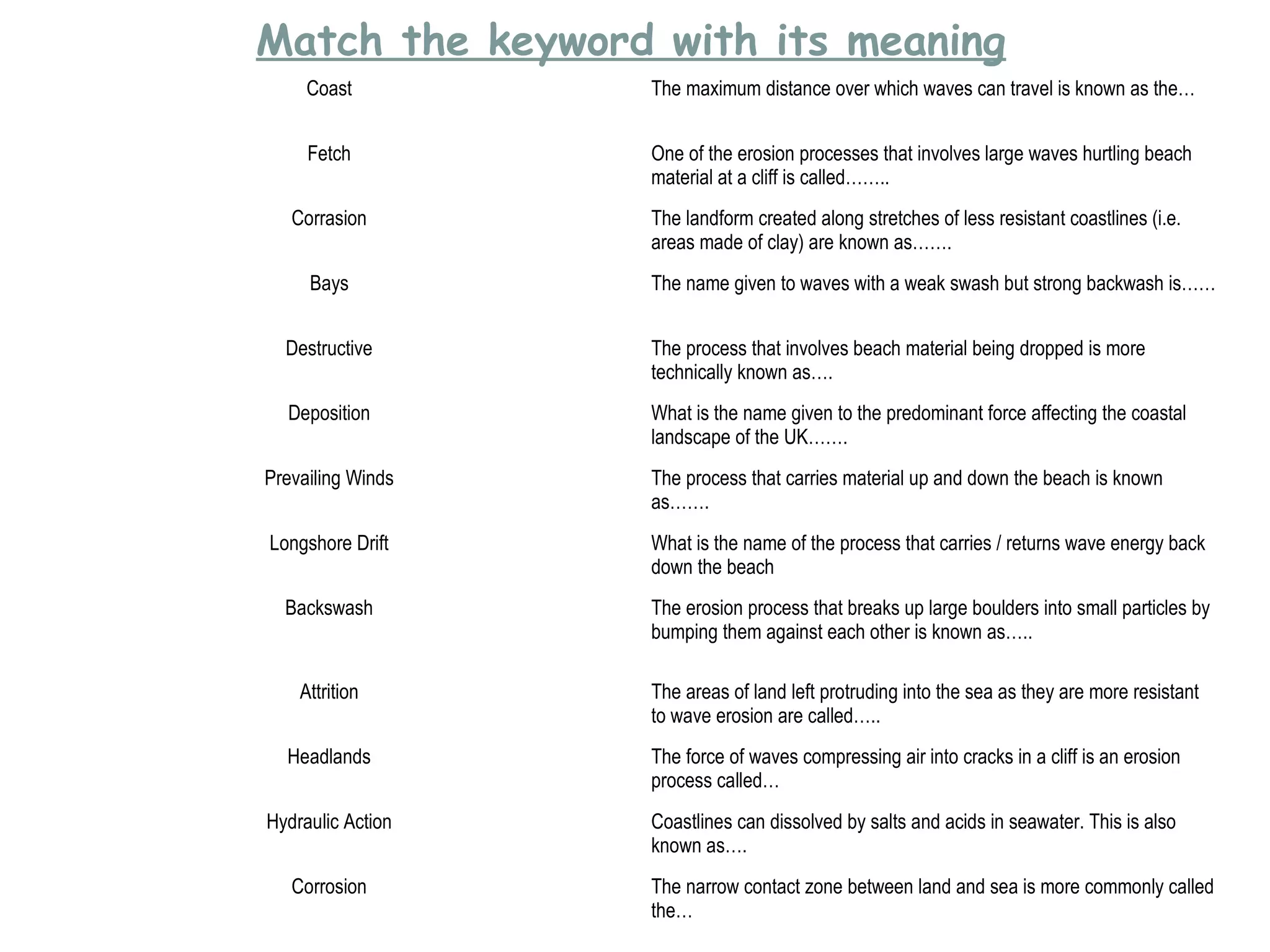
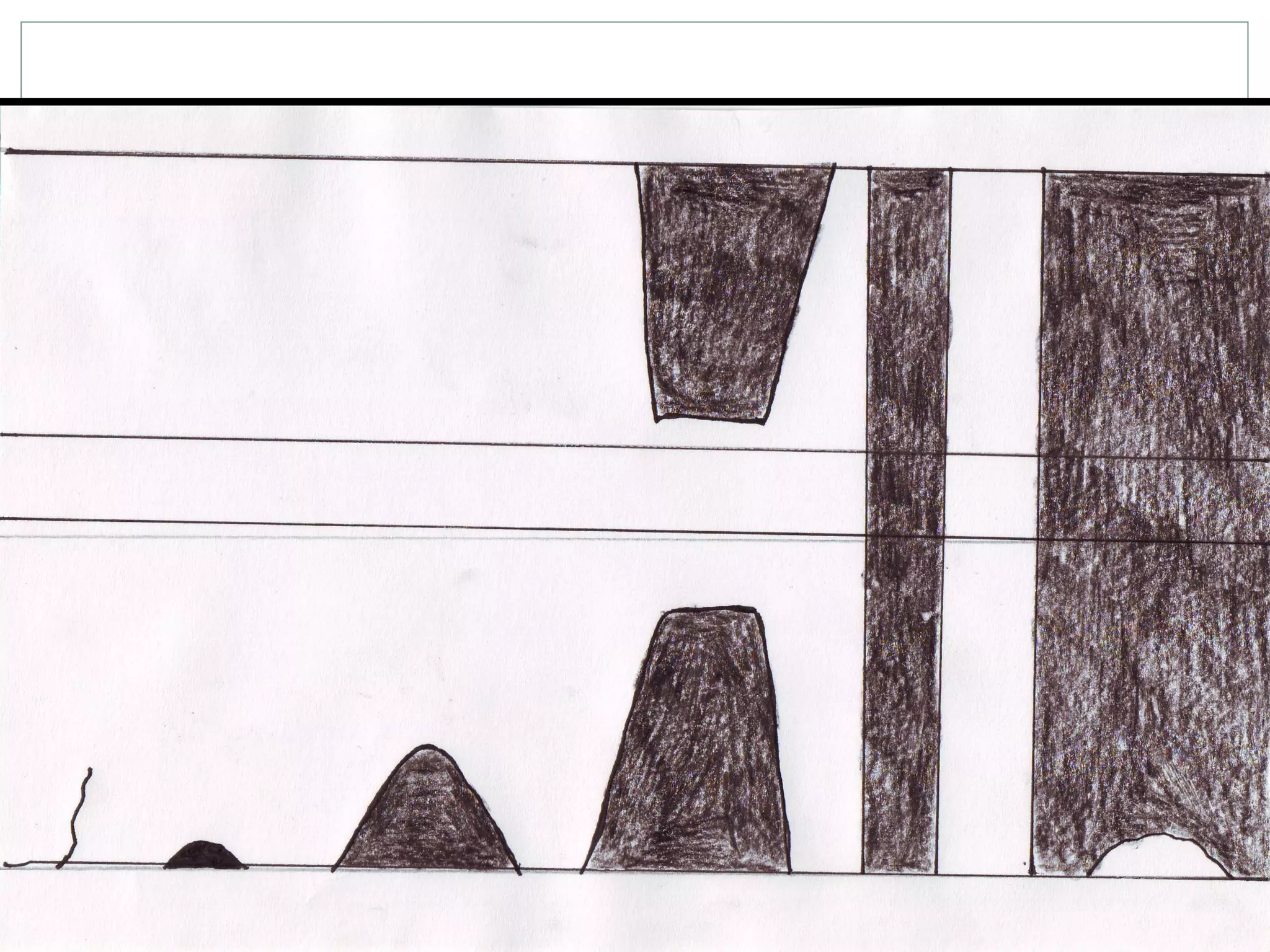
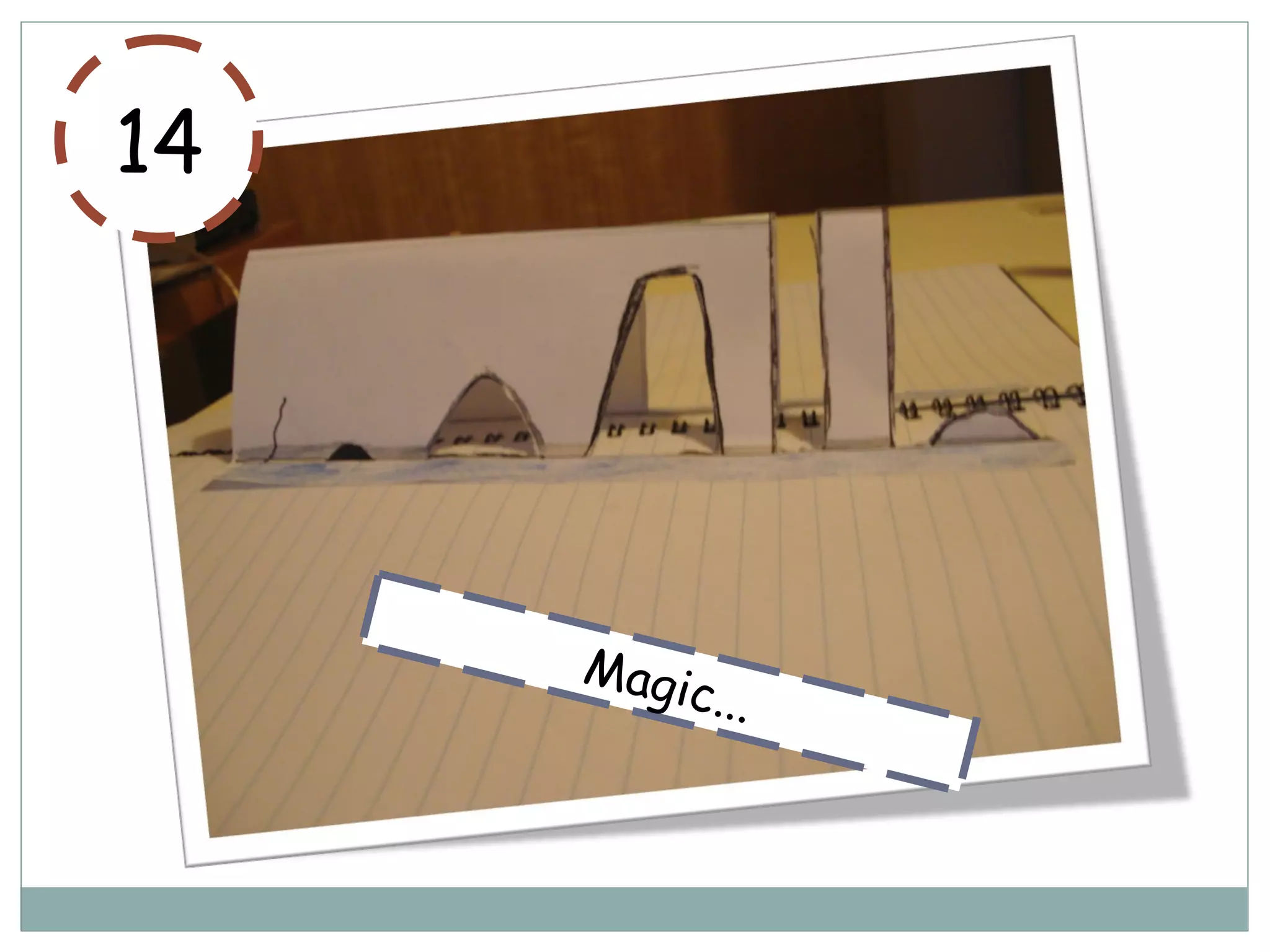
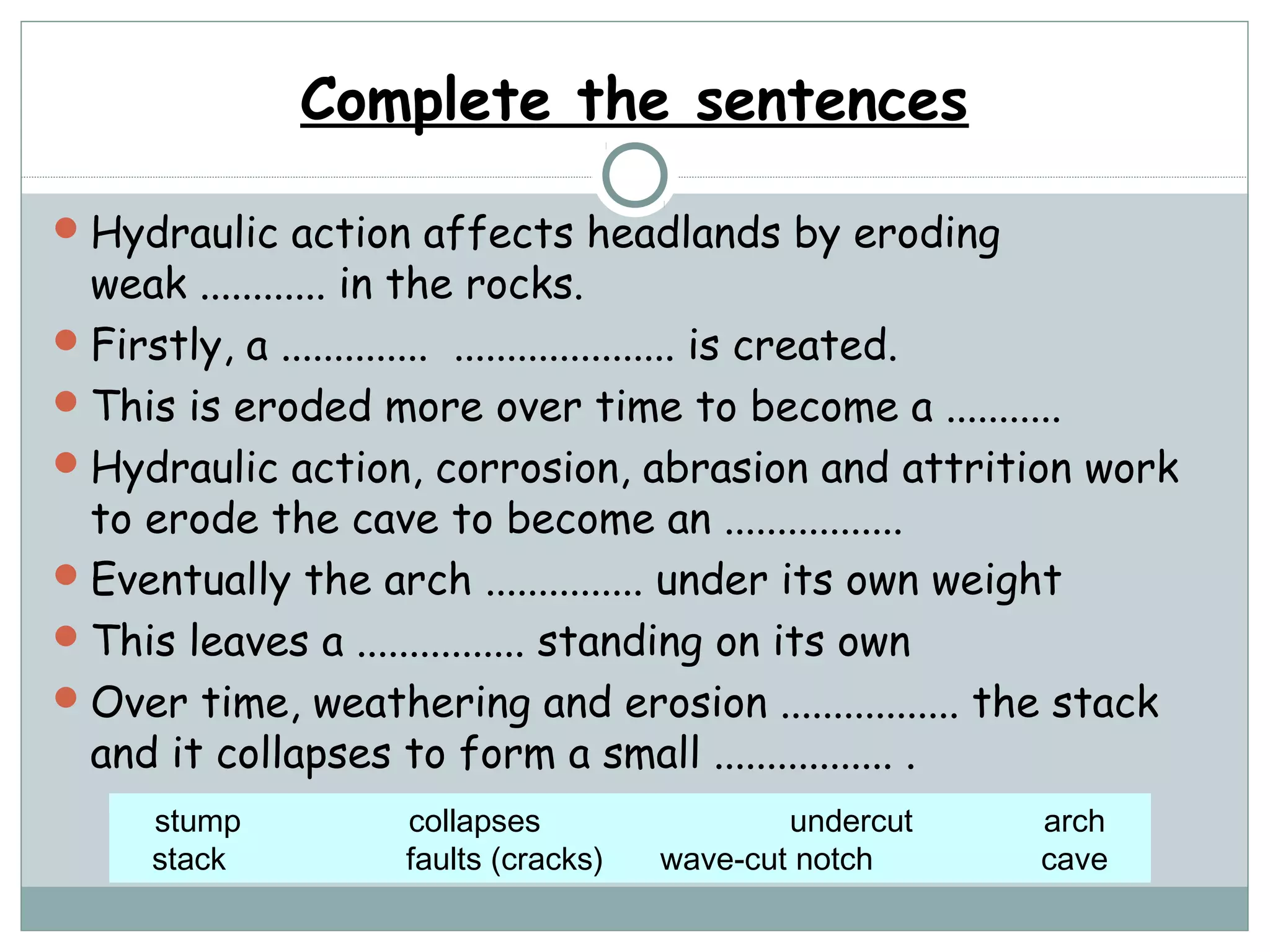
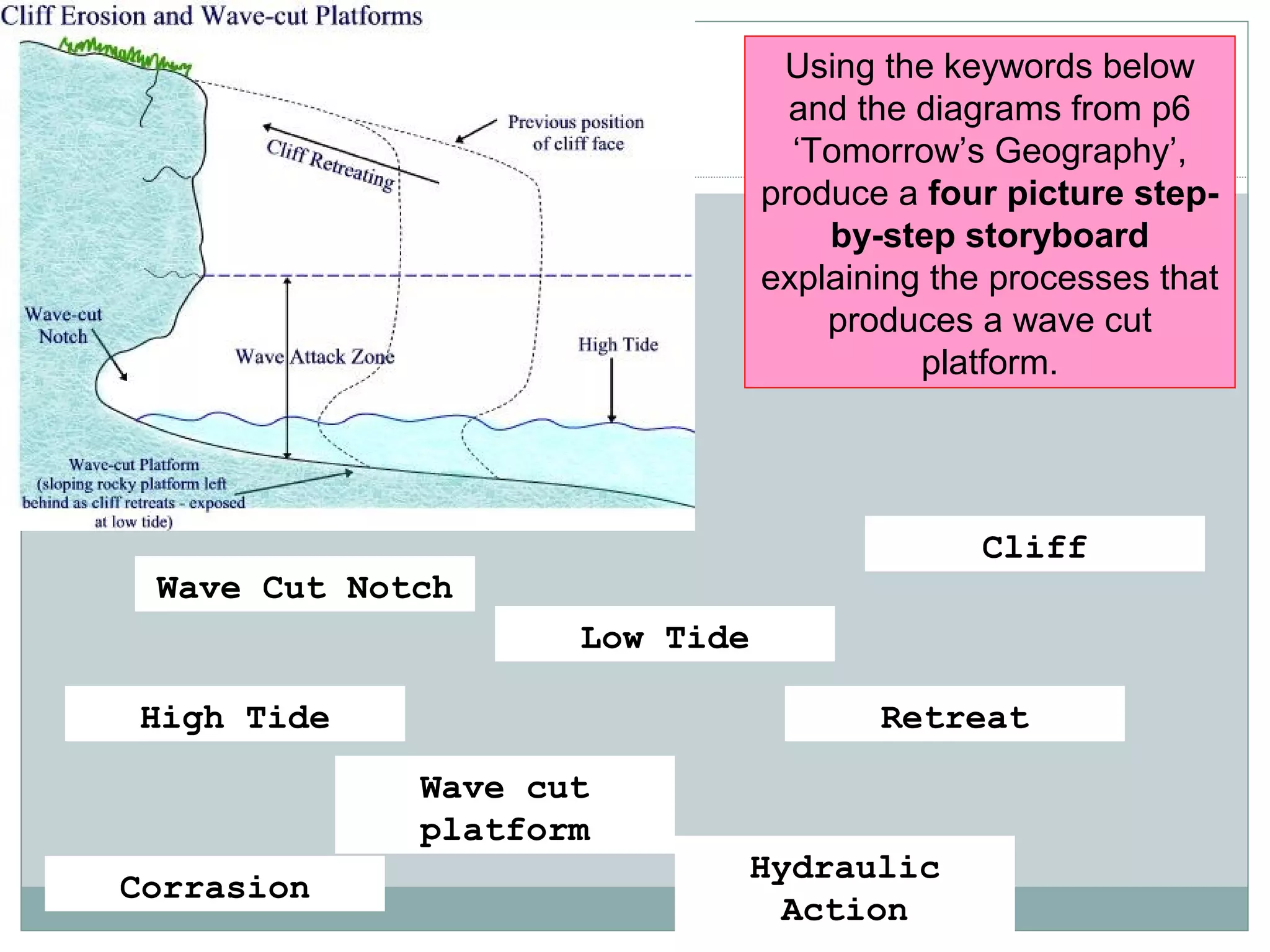
This document provides information on various coastal landforms and erosion processes. It defines key terms like headlands, bays, fetch, corrasion, deposition, longshore drift, backwash, attrition, hydraulic action, and corrosion. It also matches these terms to their meanings. The document discusses how differing rock properties lead to different coastal landform shapes. It specifically examines how headlands, cliffs, and wave-cut platforms are formed through erosion processes acting on resistant and weak rocks over time.