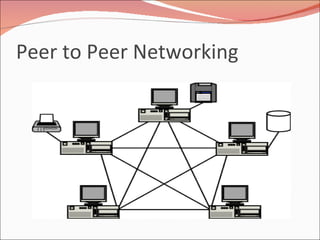
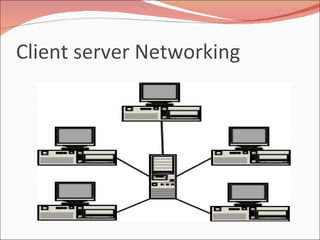
The document provides information about networking including:
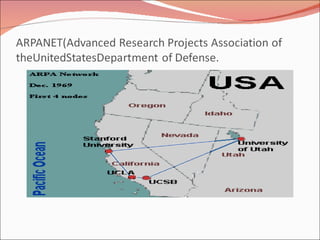
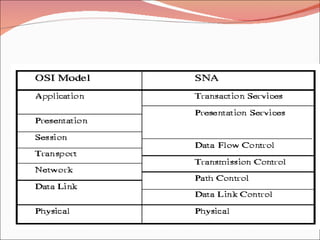
1. It defines what a network is and discusses the early origins and development of networking beginning in the 1960s for military purposes.
2. It outlines the key exams, certifications, and topics covered in the CCNP certification for networking professionals.
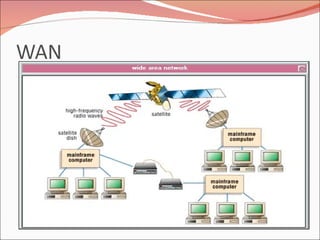
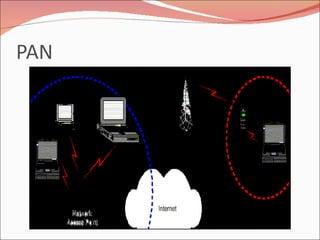
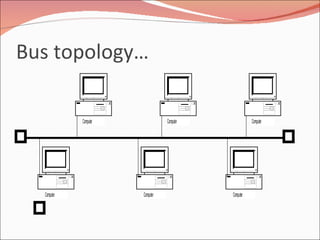
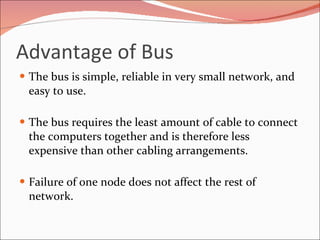
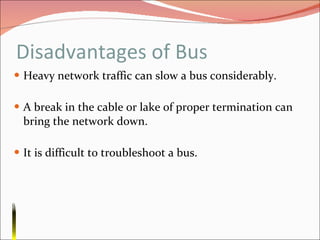
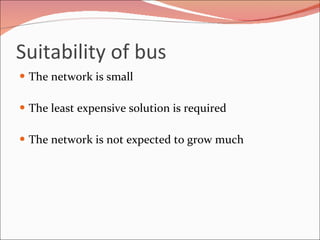
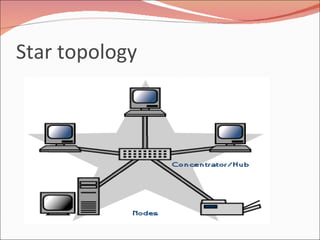
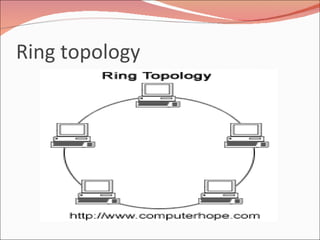
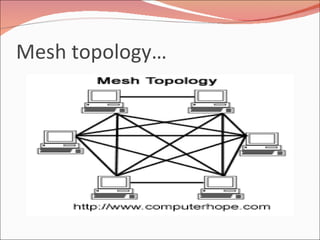
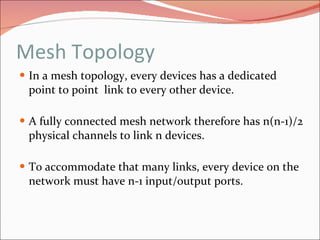
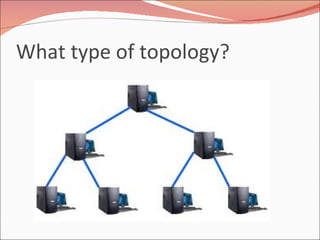
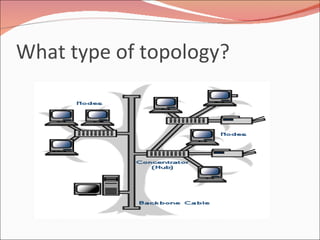
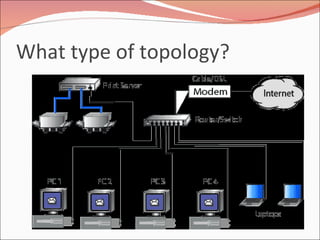
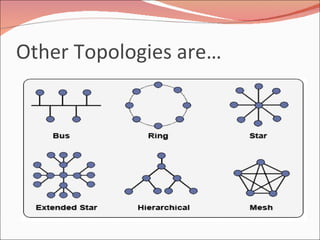
3. It discusses different types of network topologies including bus, star, ring, and mesh, and compares their advantages and disadvantages for different networking situations and needs.