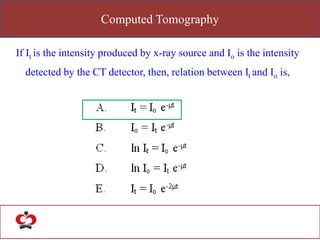
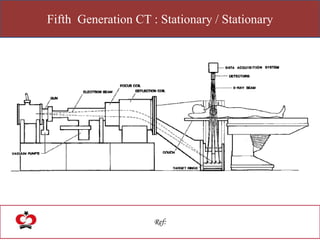
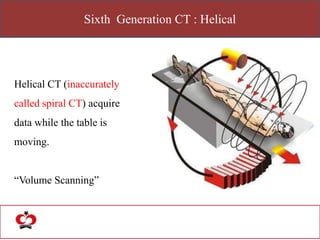
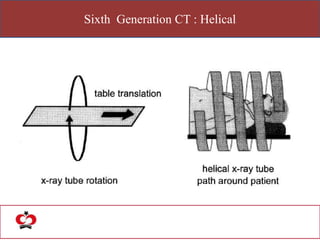
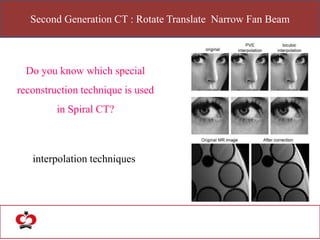
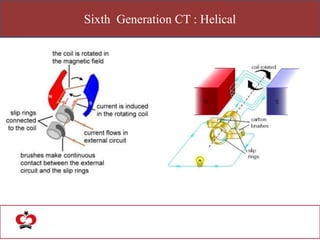
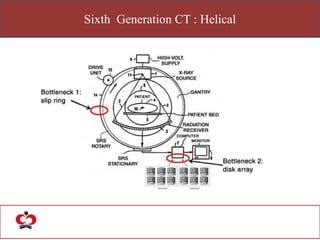
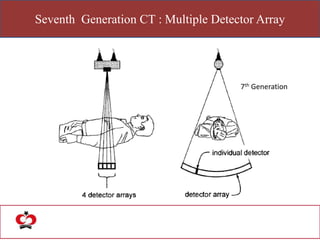
The document outlines the evolution of computed tomography (CT) technology through different generations, detailing the characteristics and innovations associated with each. It discusses various beam geometries used in CT scanners and the advantages of helical scanning over traditional methods, including faster scan times and improved image quality. Key terms such as projections, detector geometry, and special reconstruction techniques are highlighted throughout the lecture content.