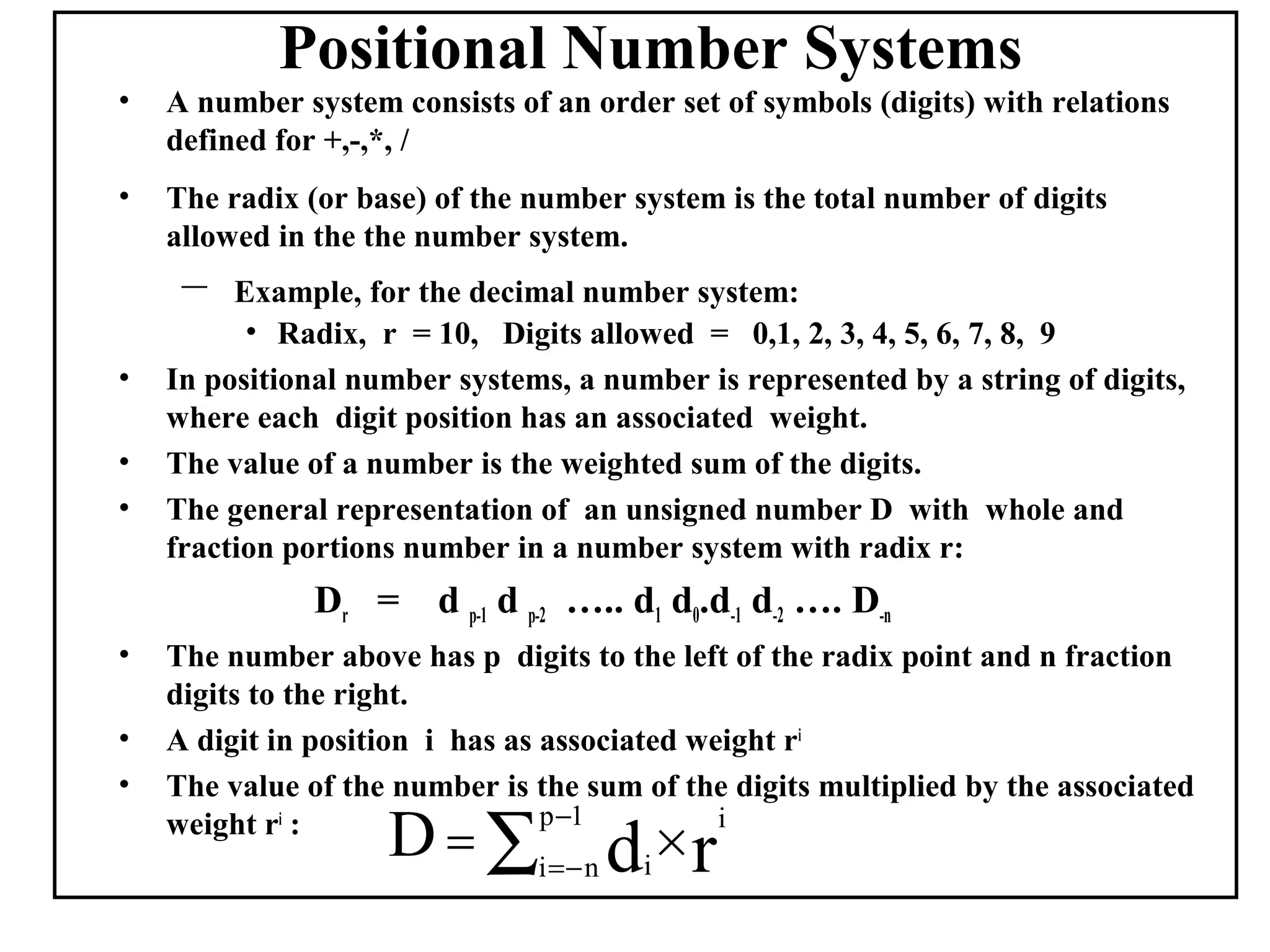
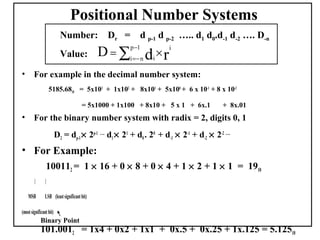
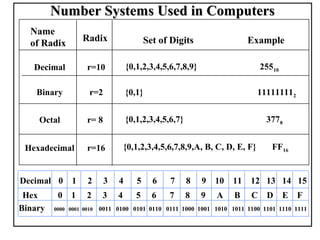
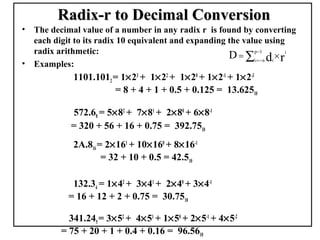
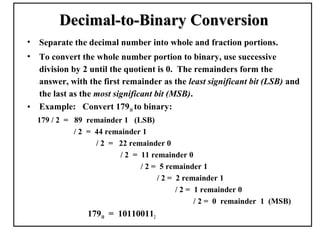
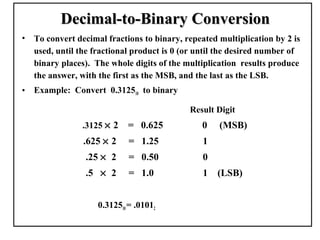
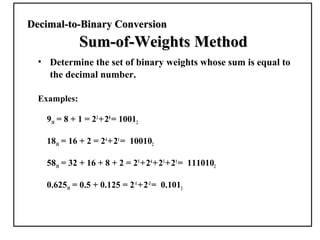
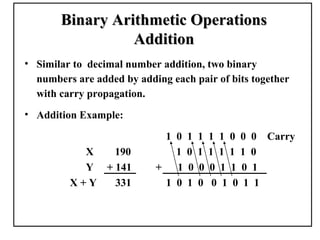
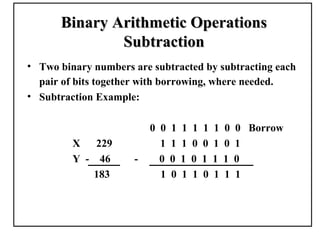
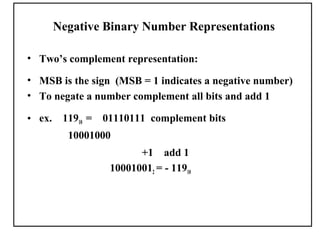
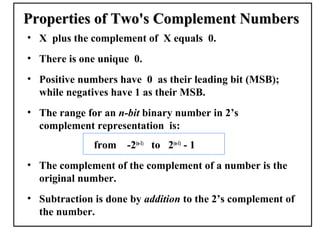
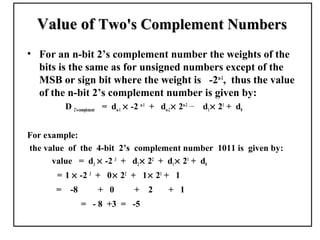
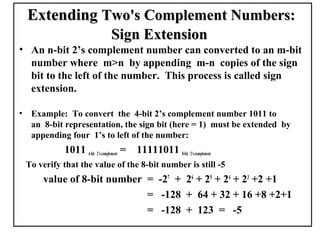
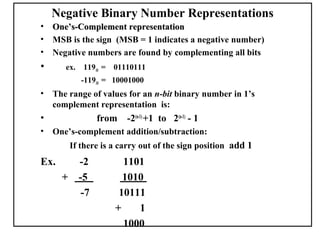
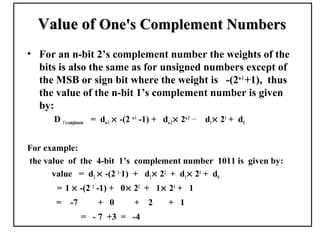
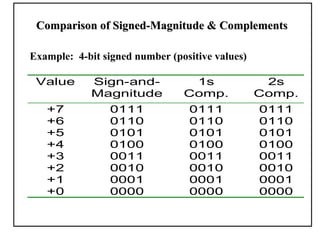
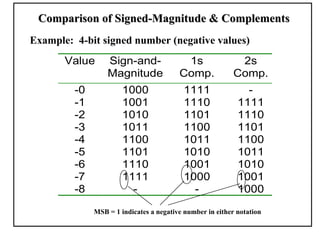
Positional number systems represent numbers as a sequence of digits with each digit position having an associated weight. In positional systems, the value of a number is the sum of the digit values multiplied by their weights. Common positional systems include decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal. Converting between these systems involves grouping digits and mapping groups to new bases. Negative numbers are represented using sign-magnitude or two's complement systems.