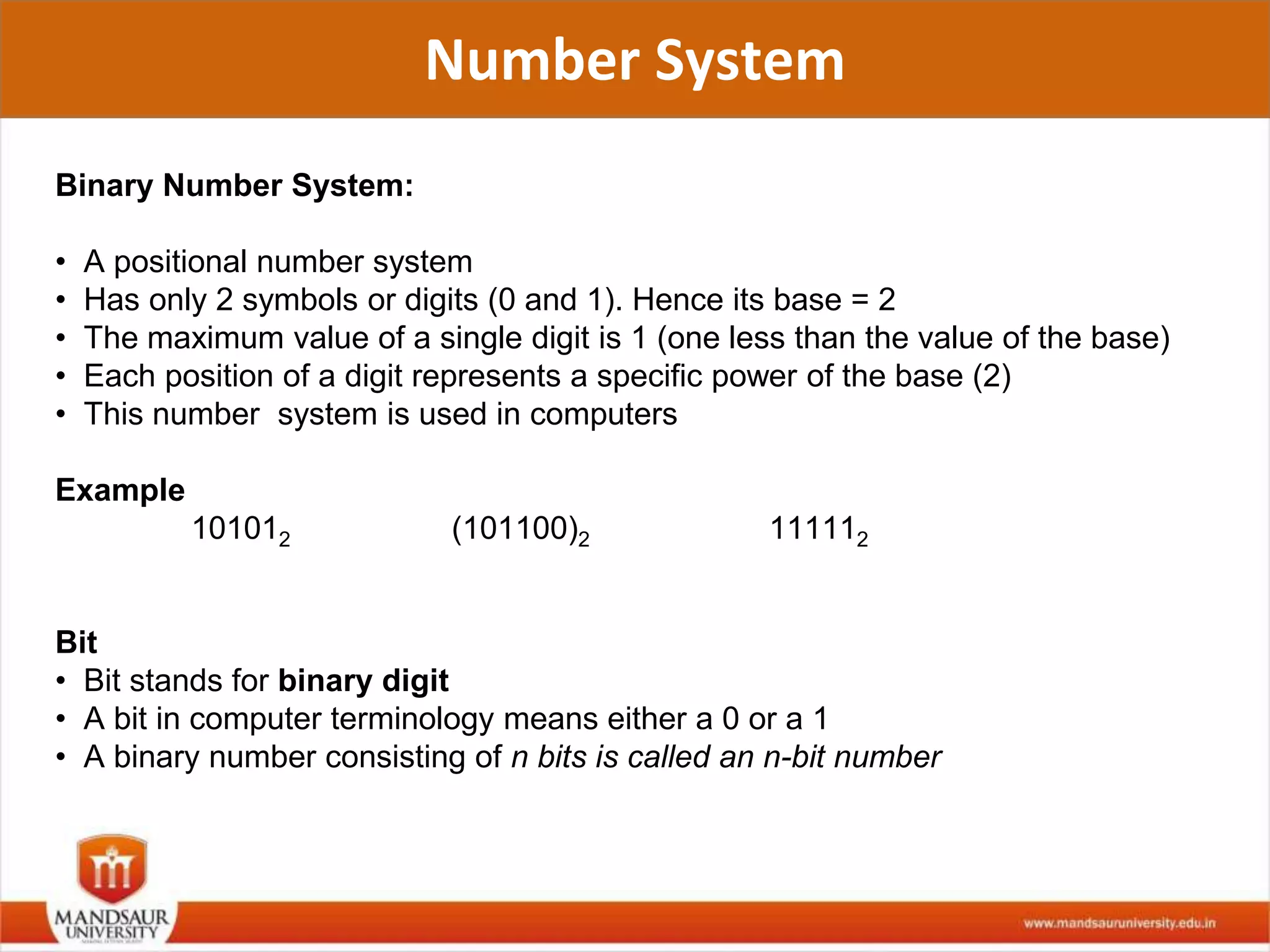
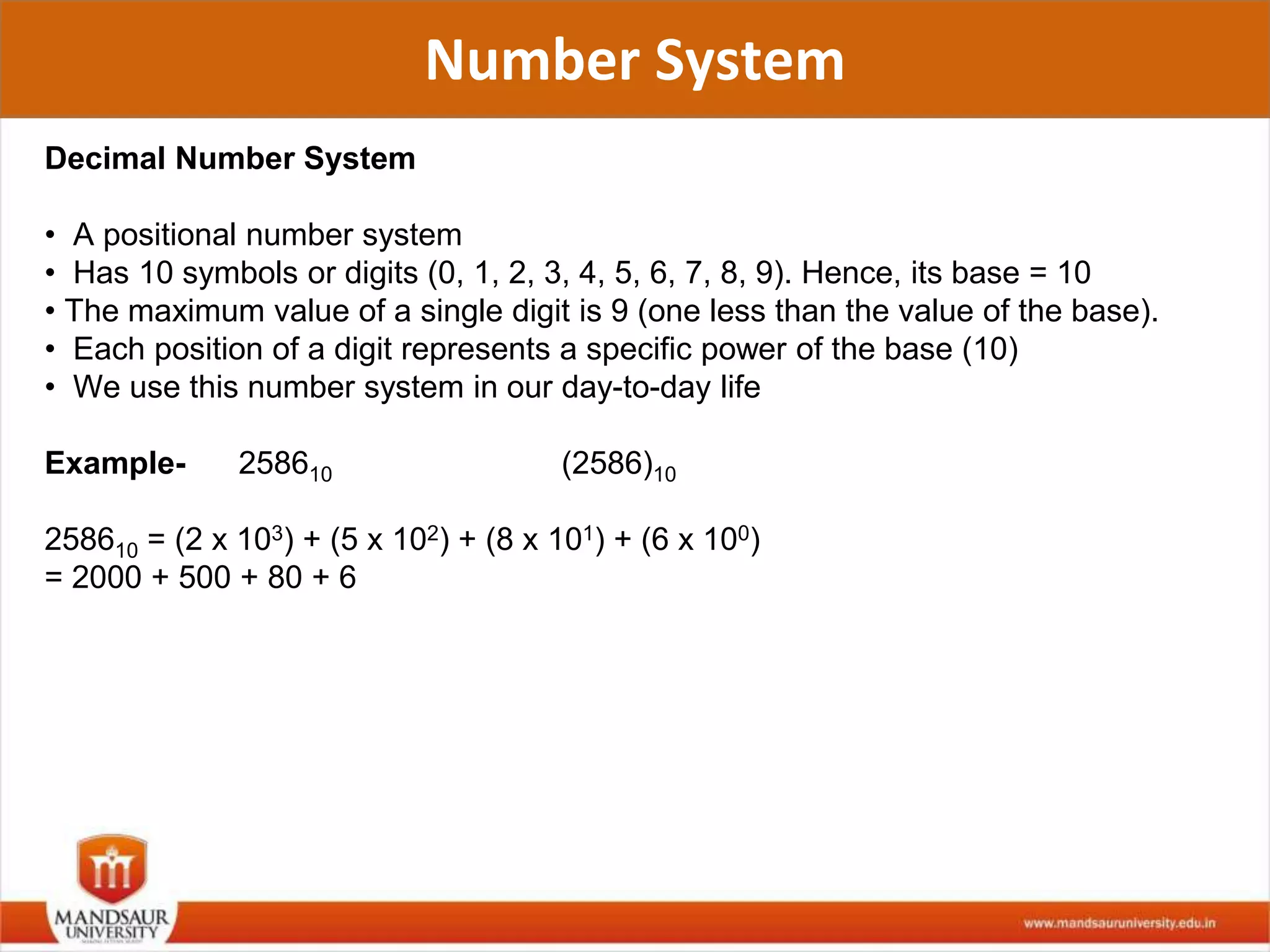
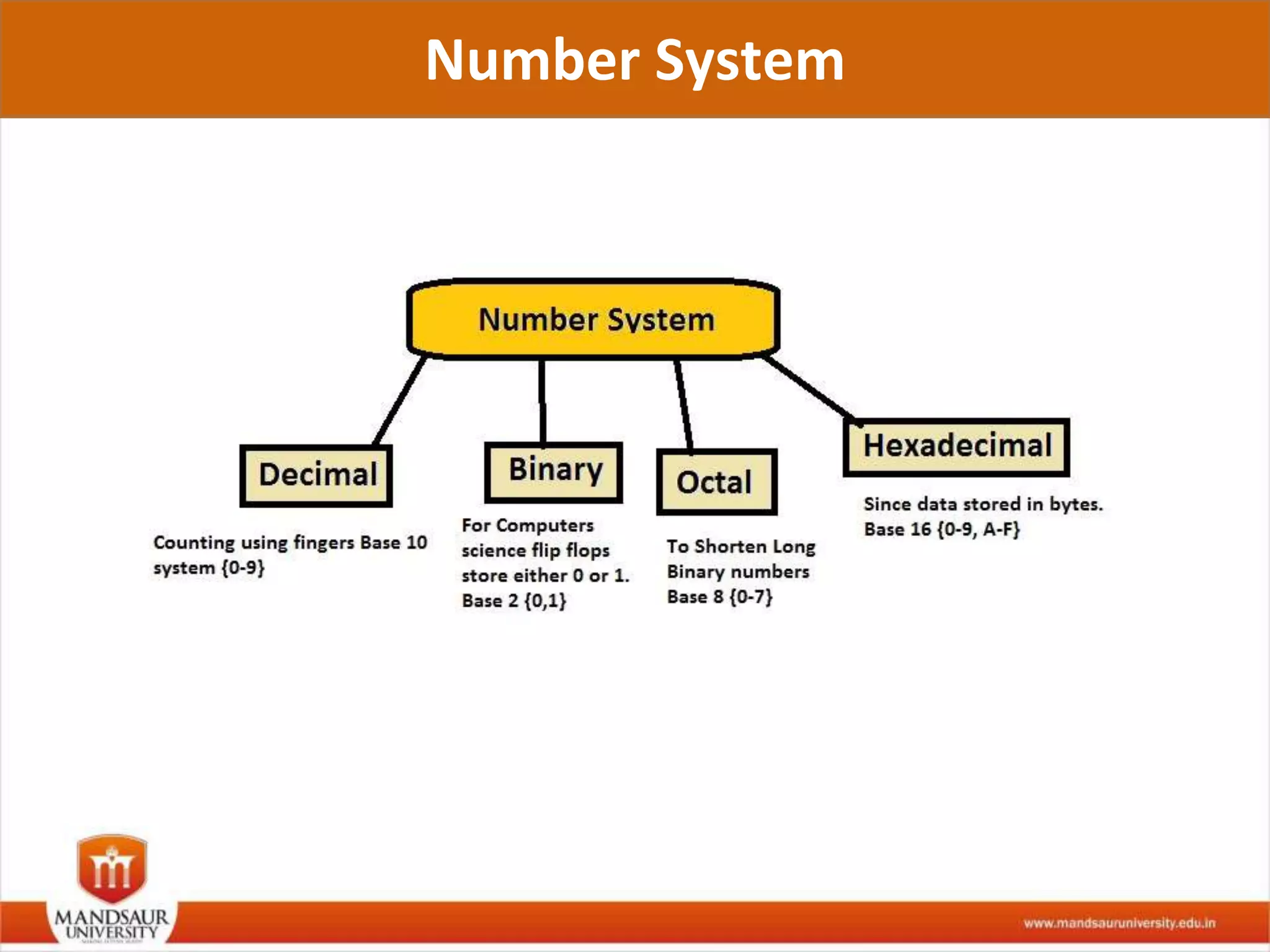
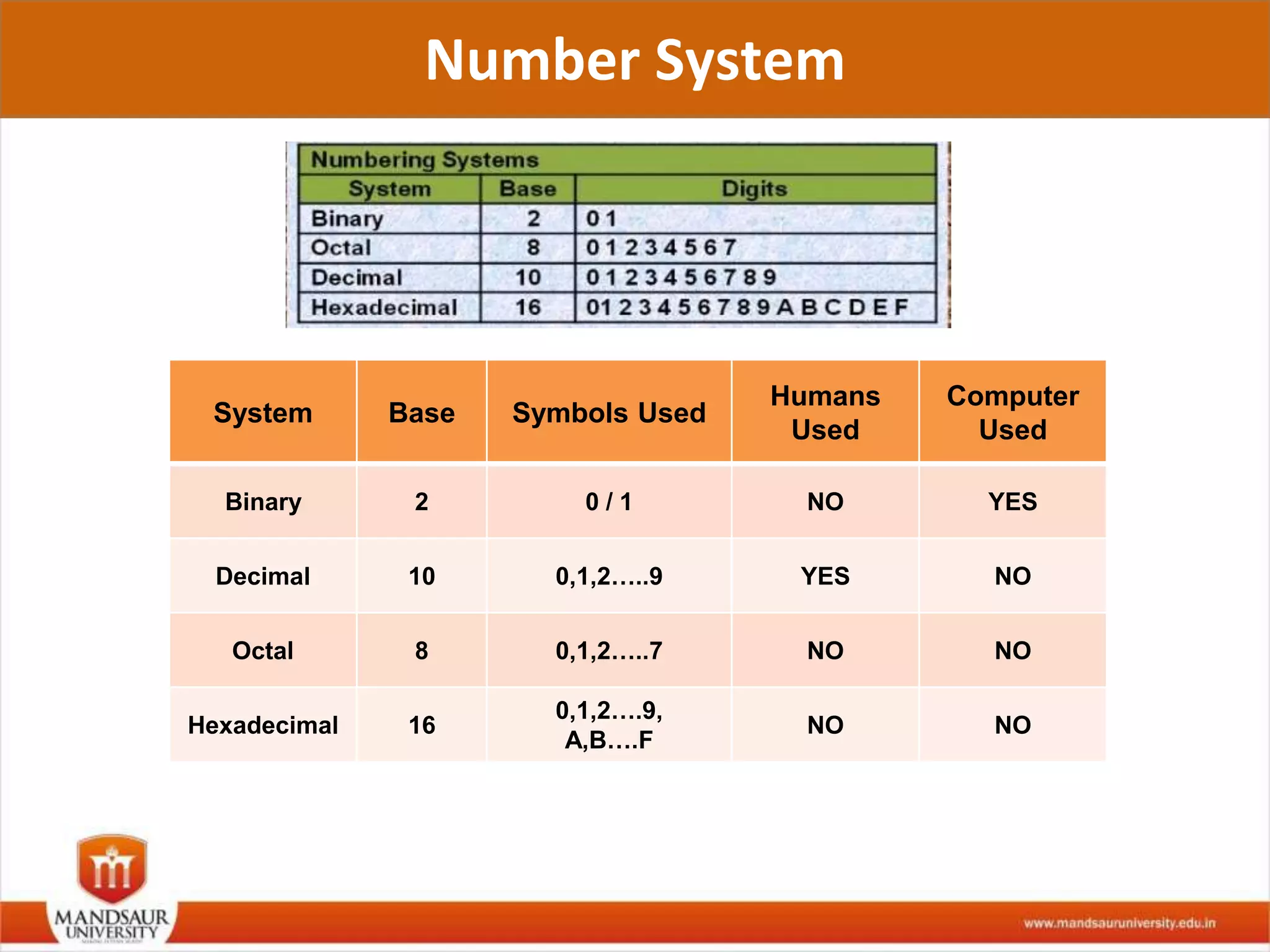
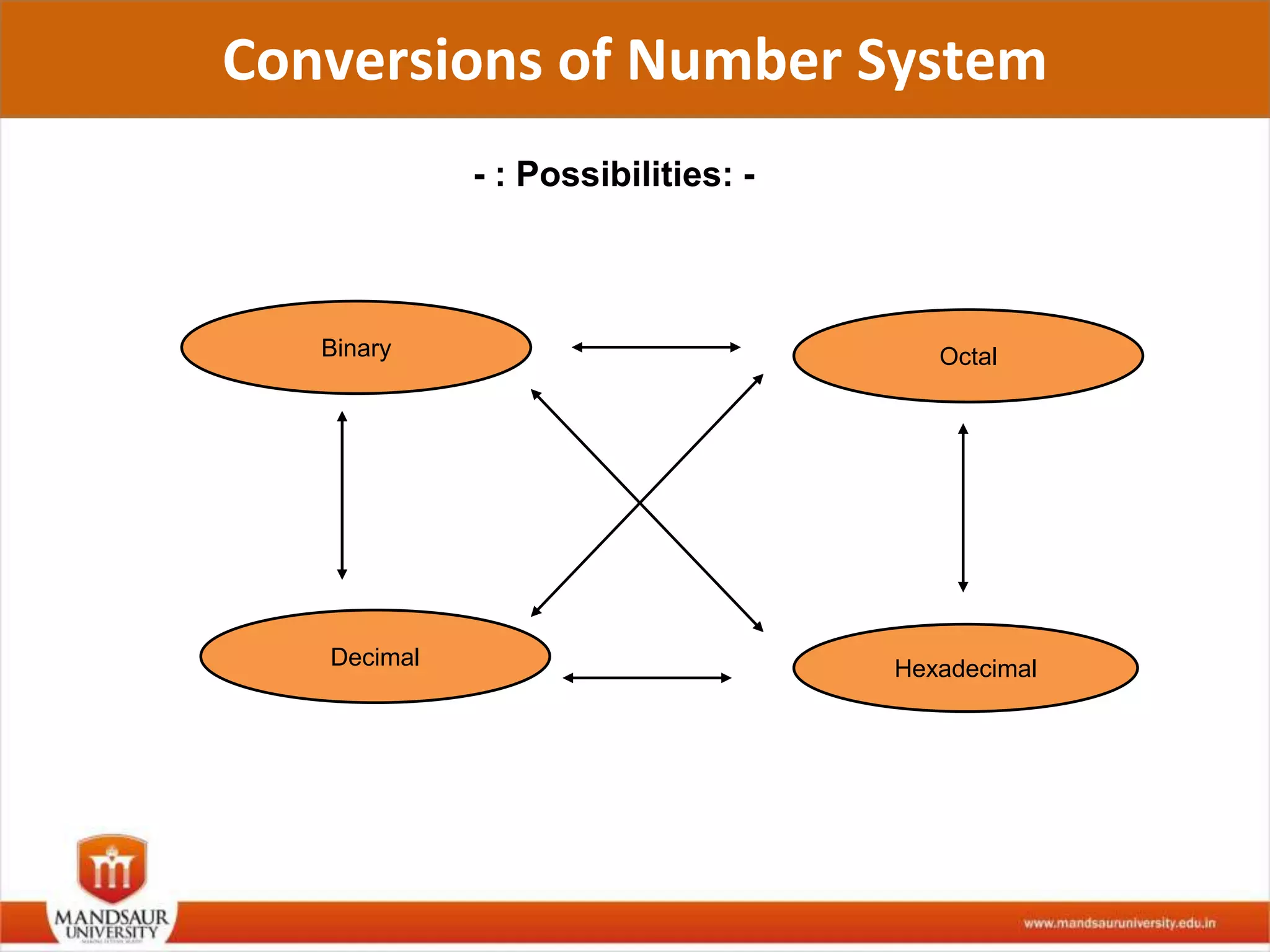
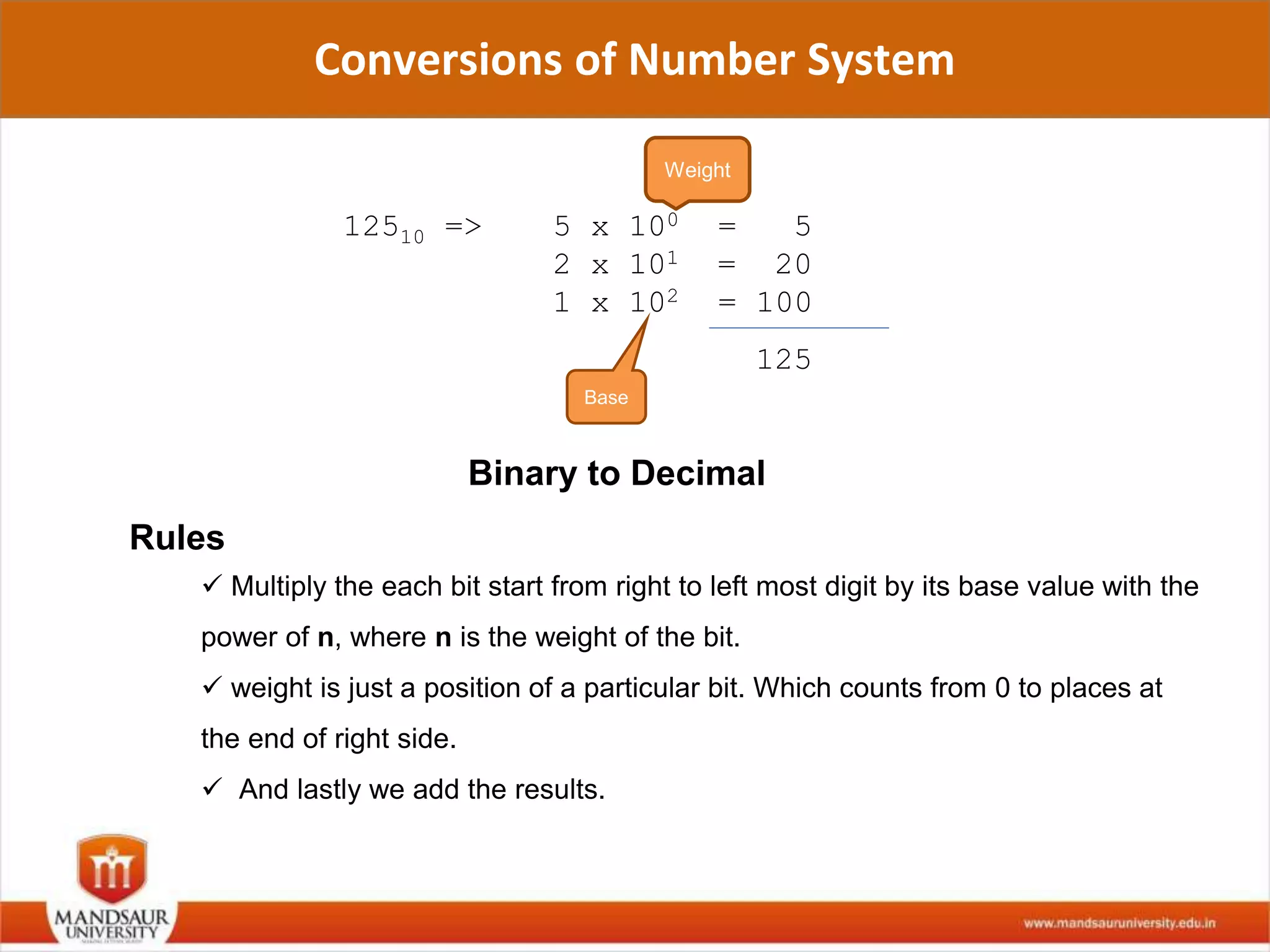
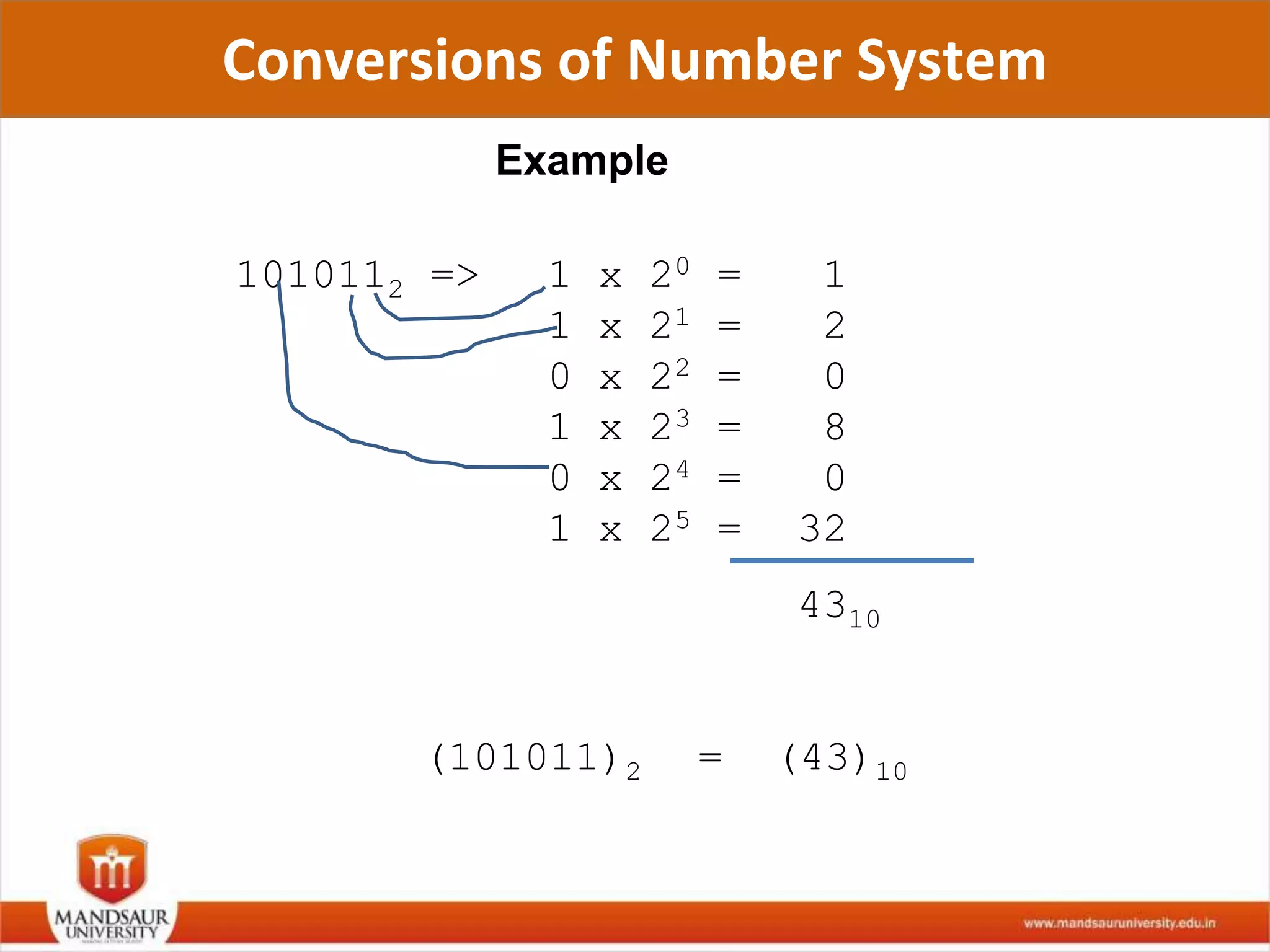
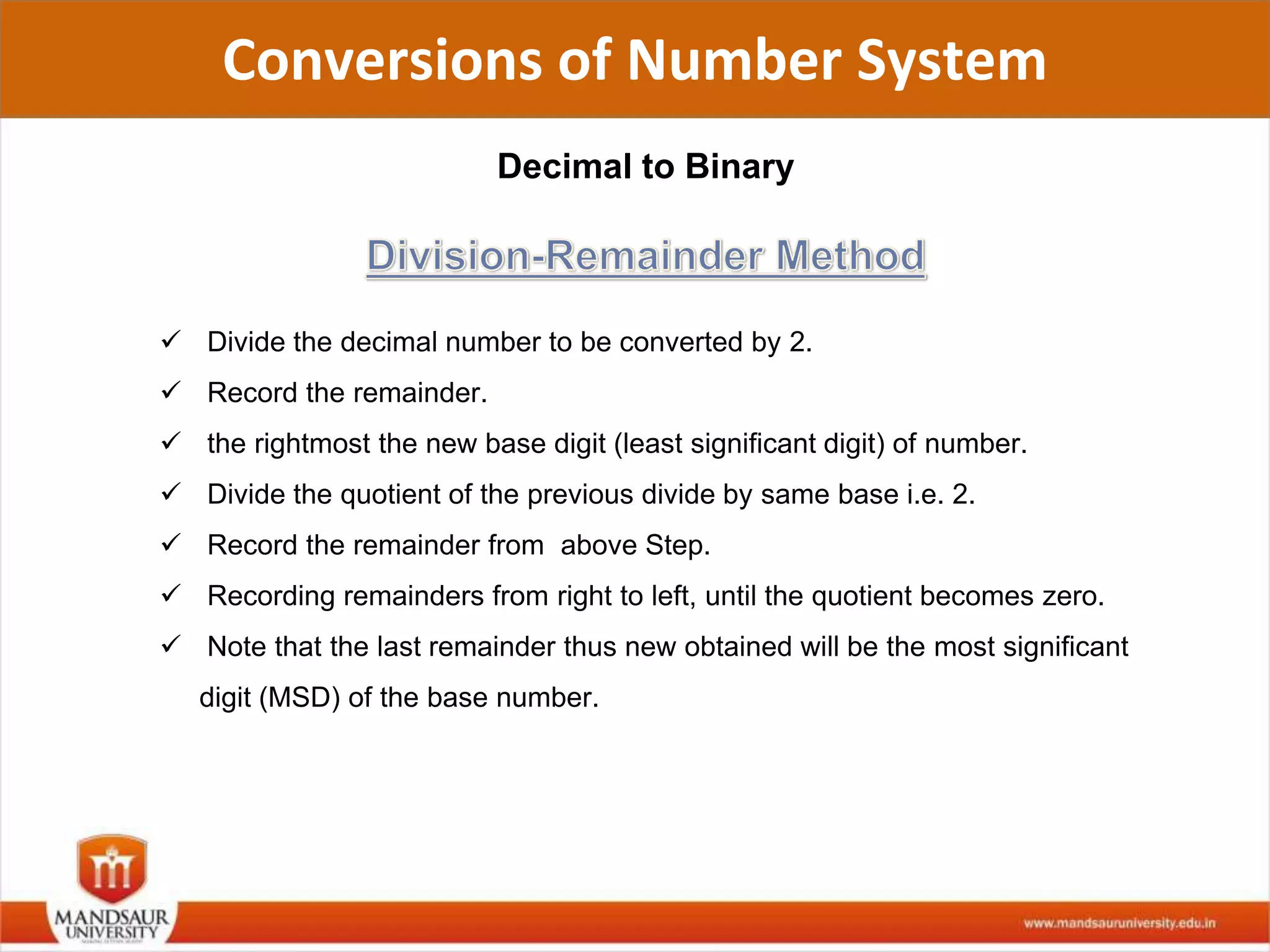
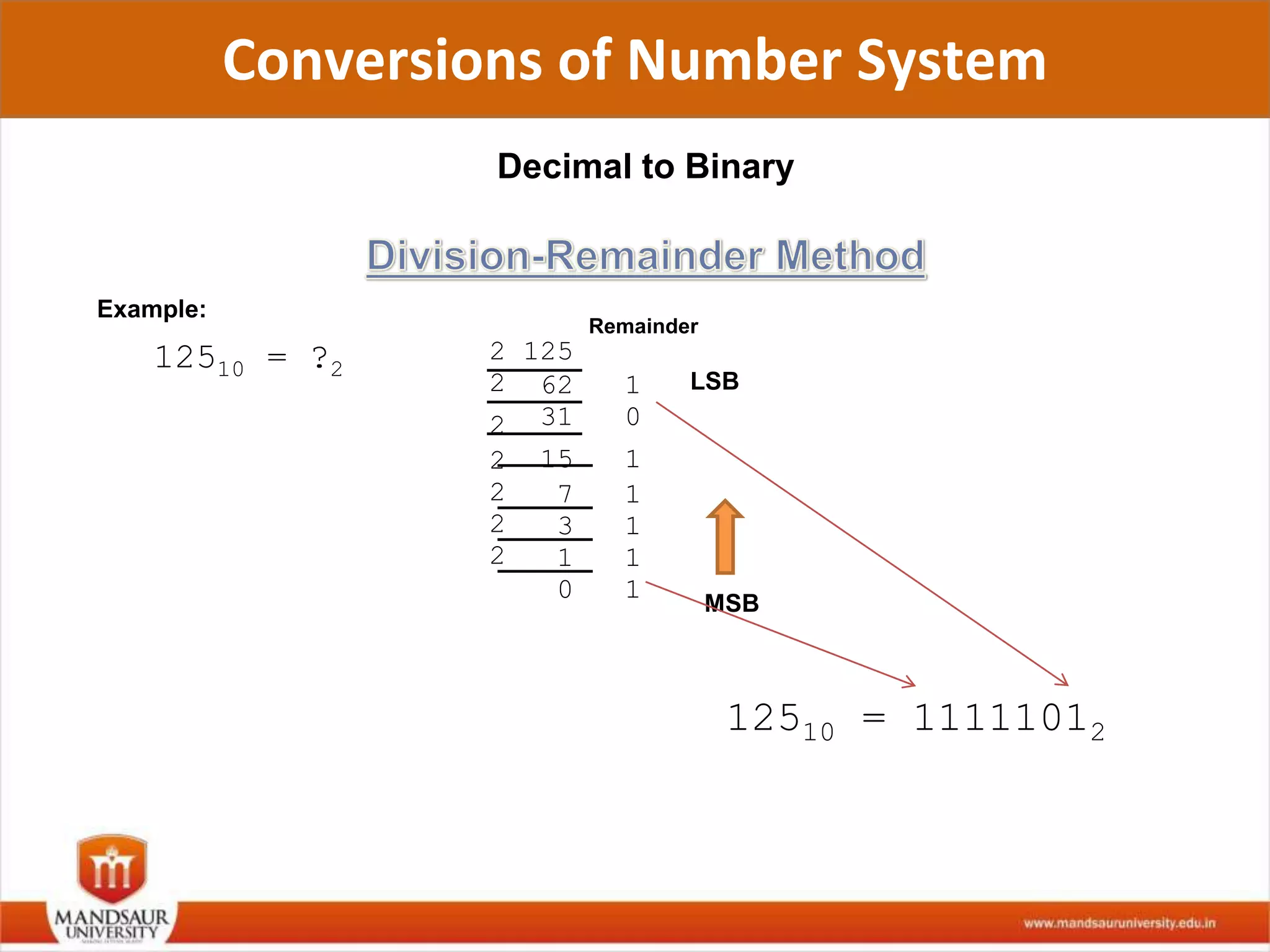
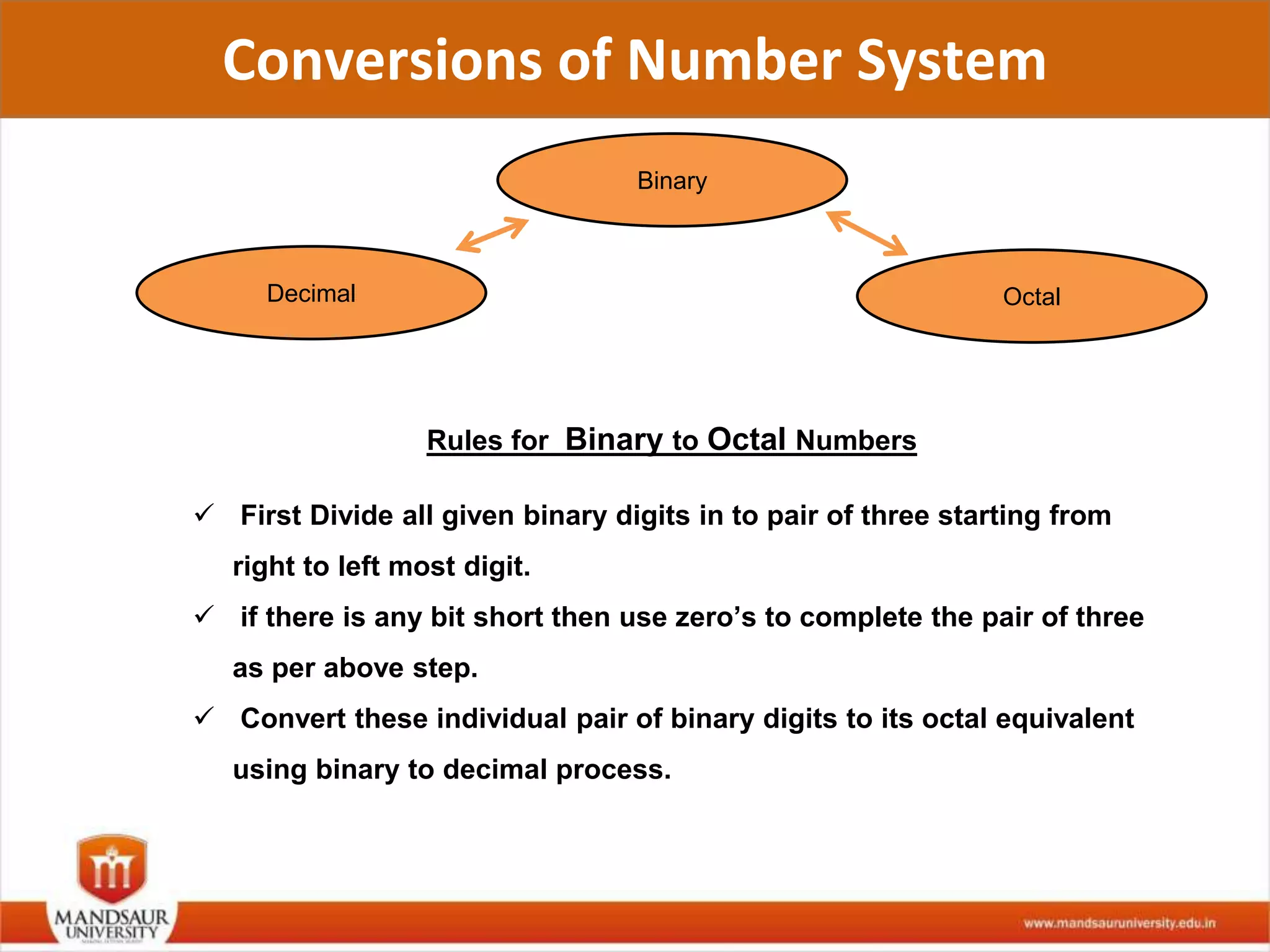
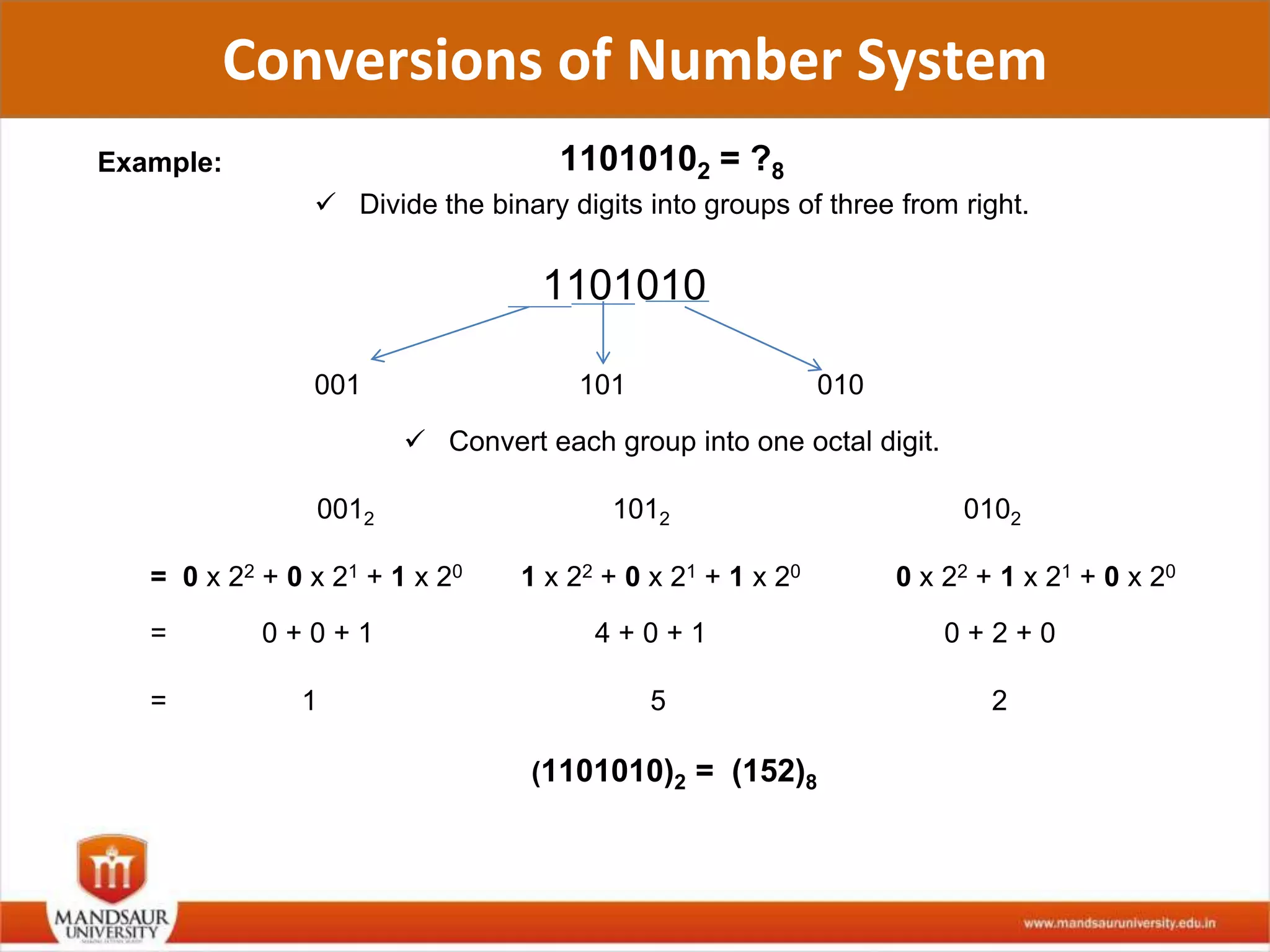
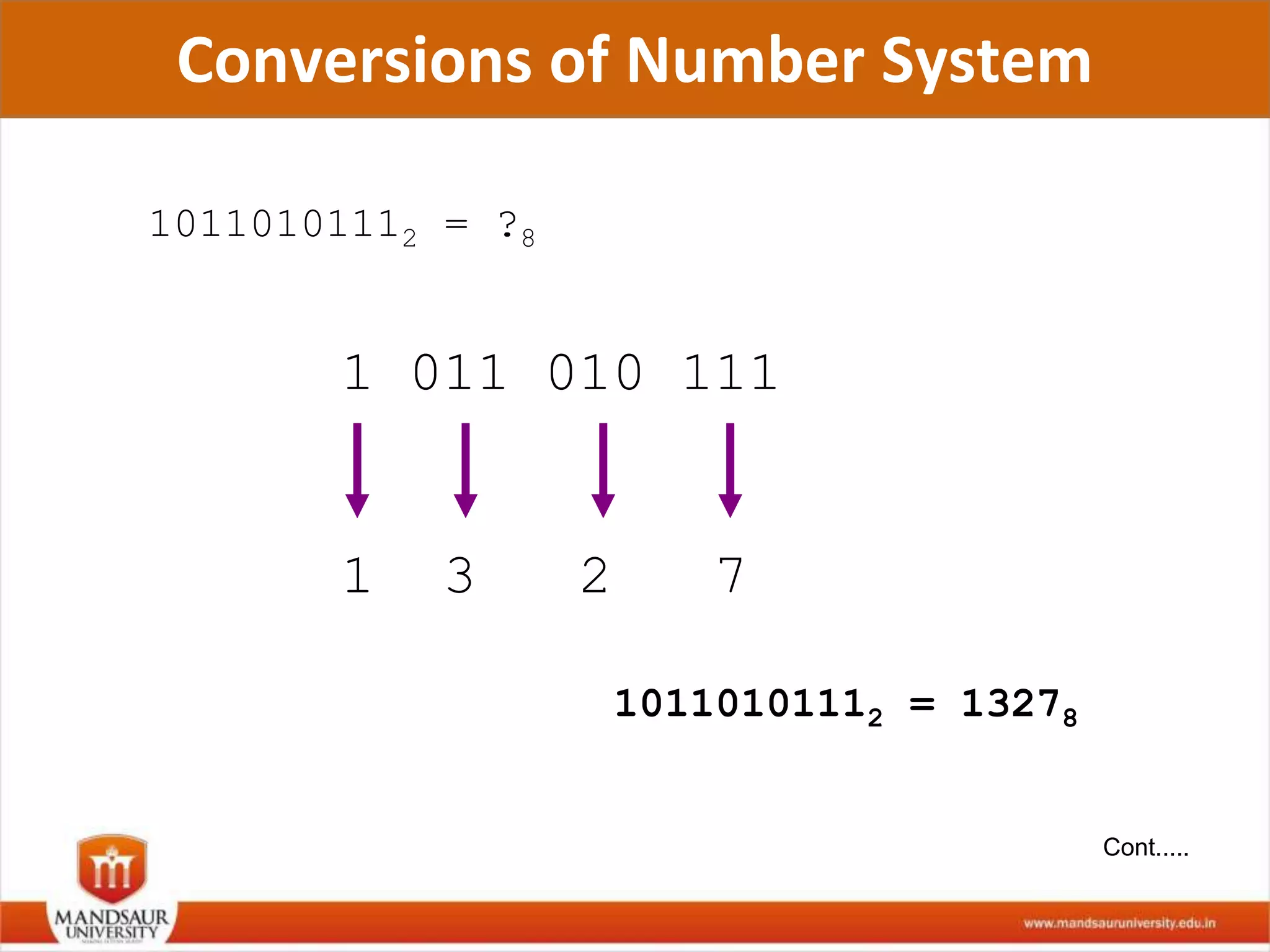
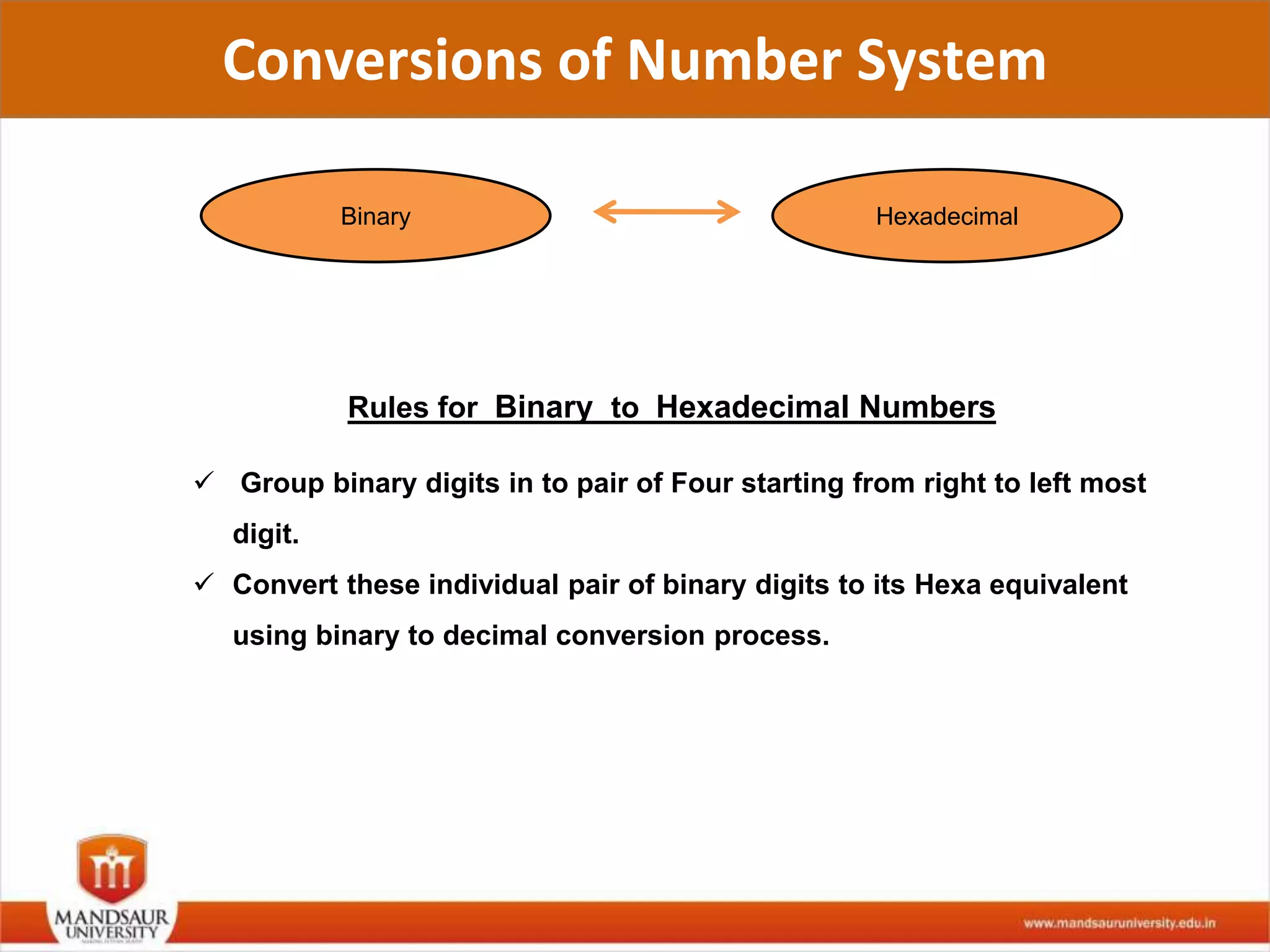
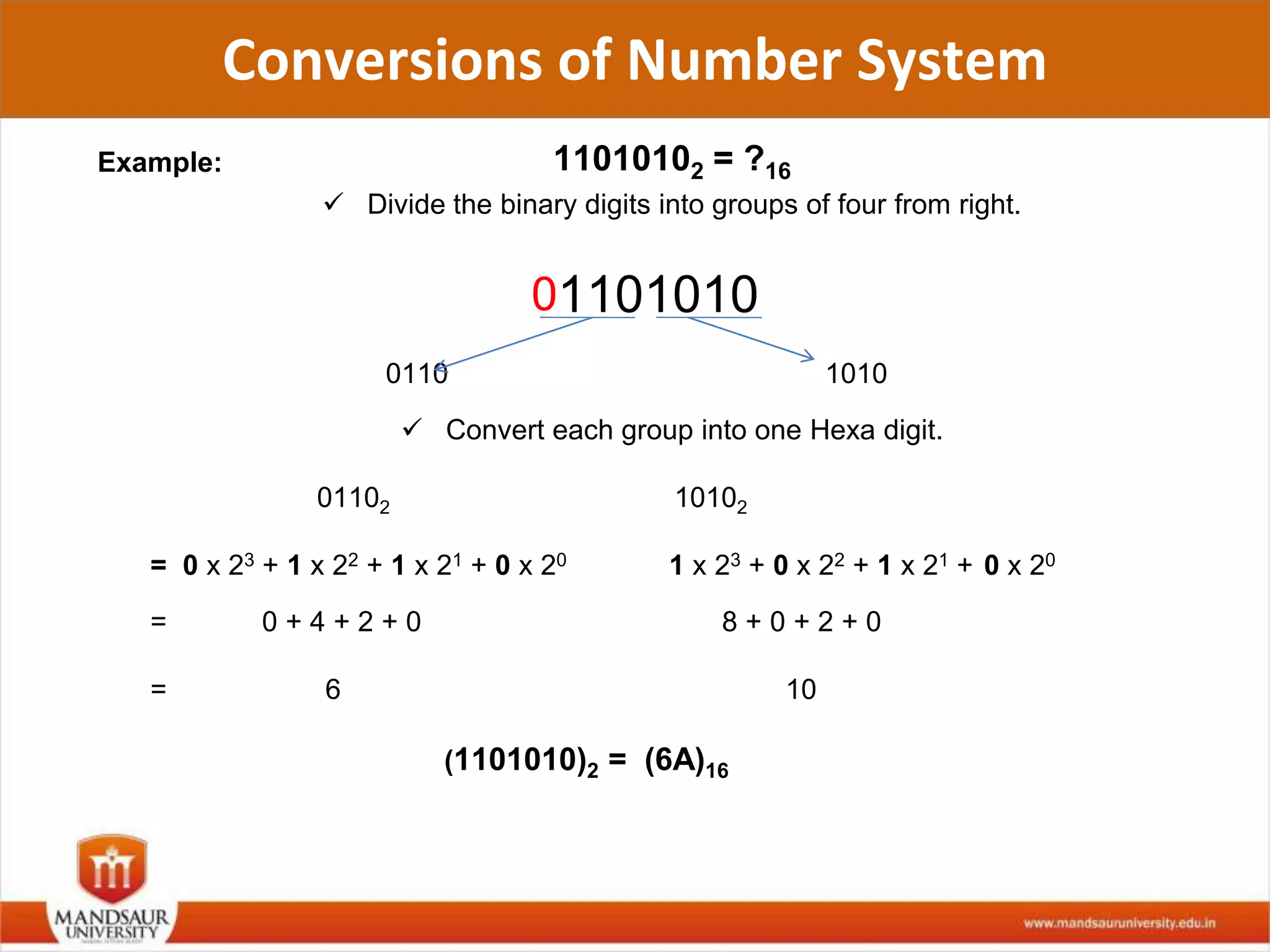
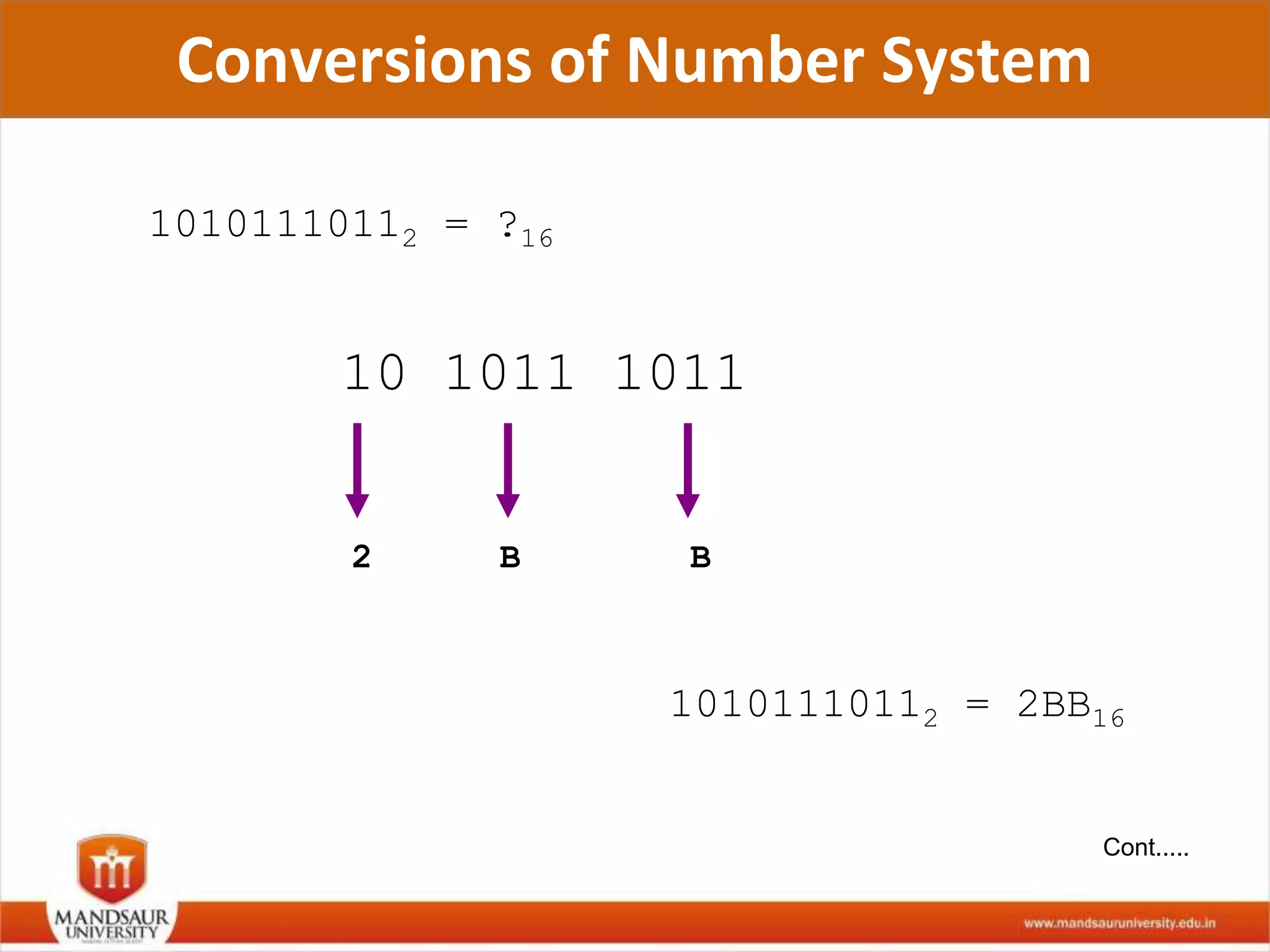
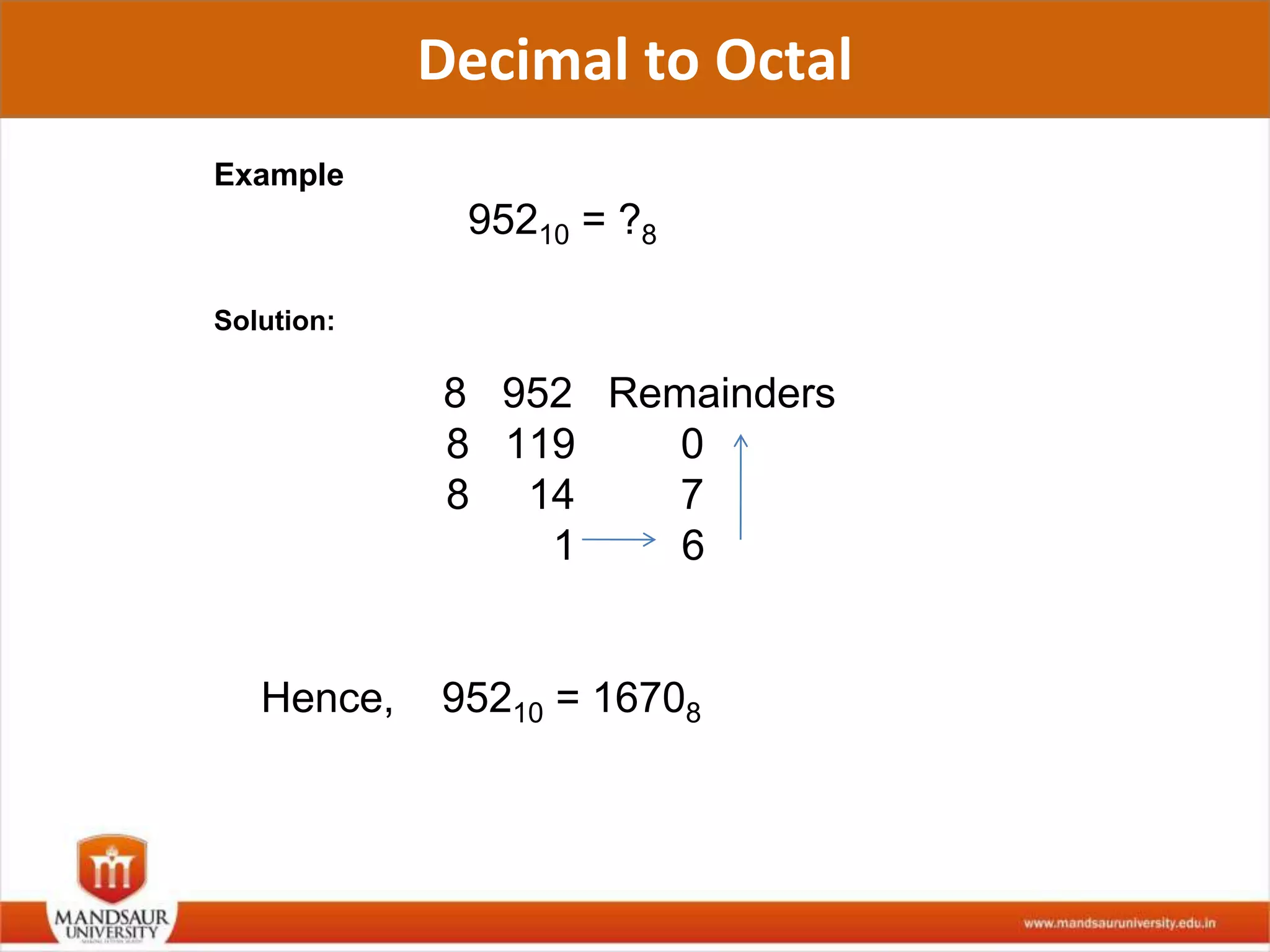
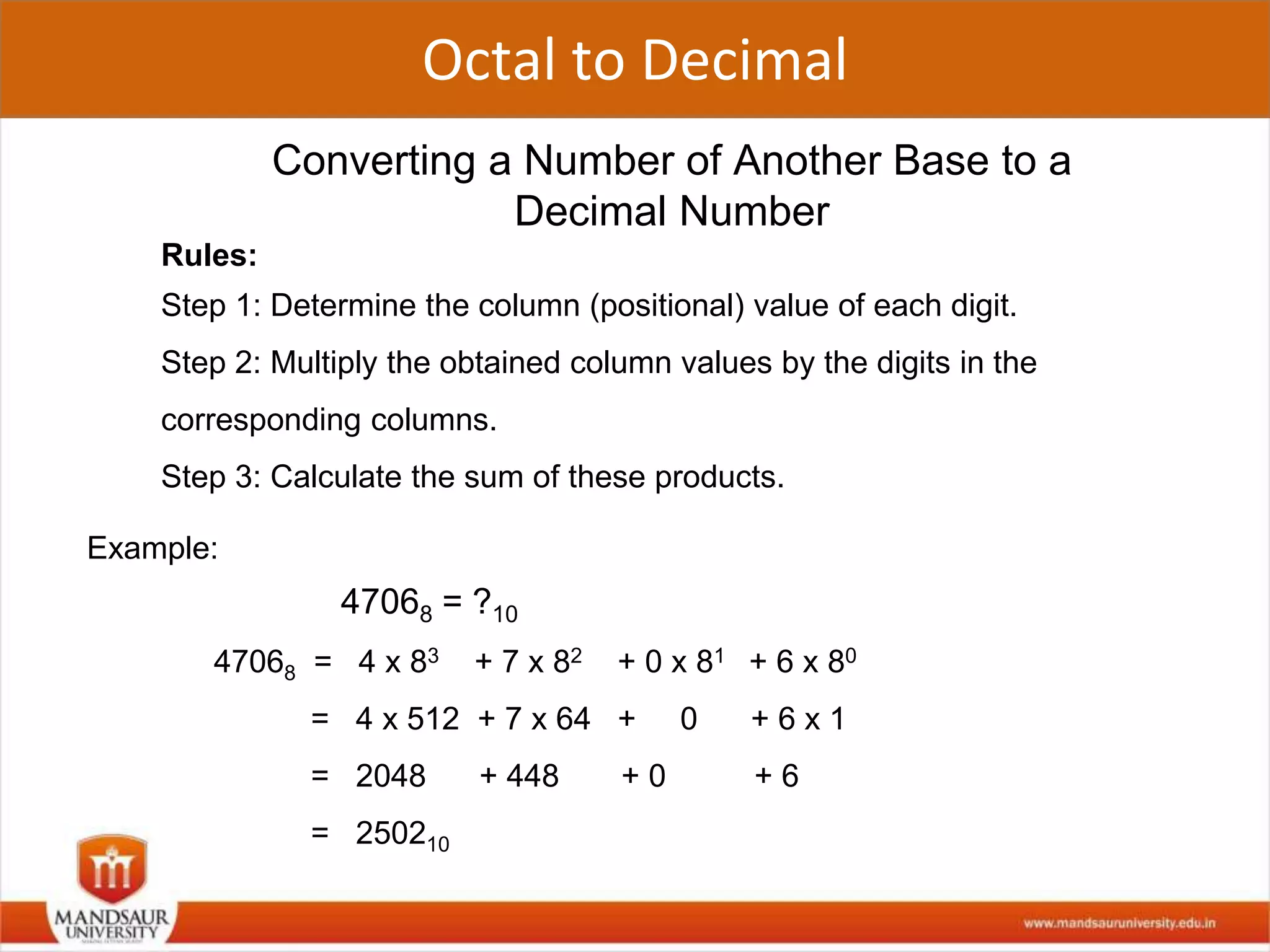
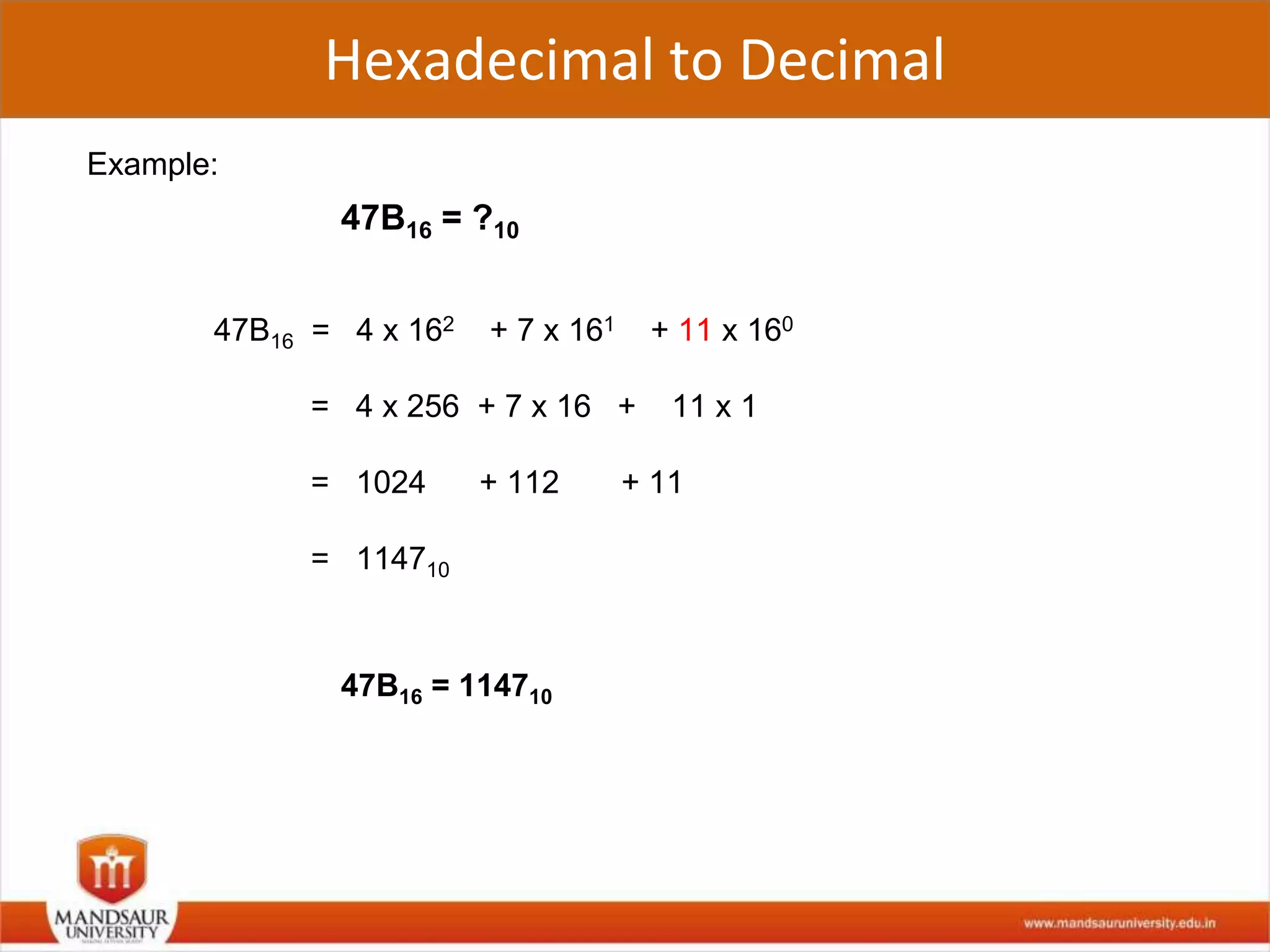
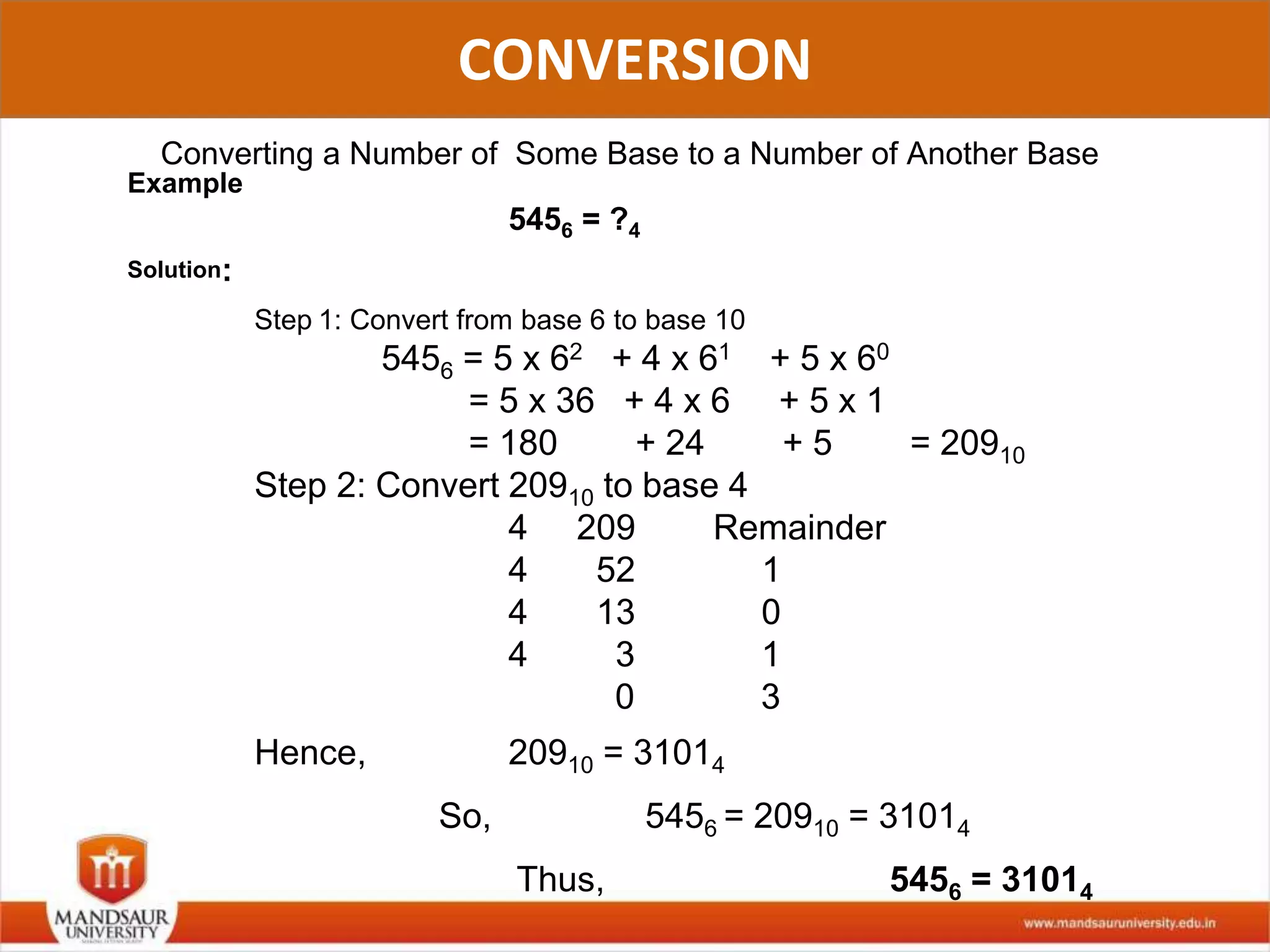
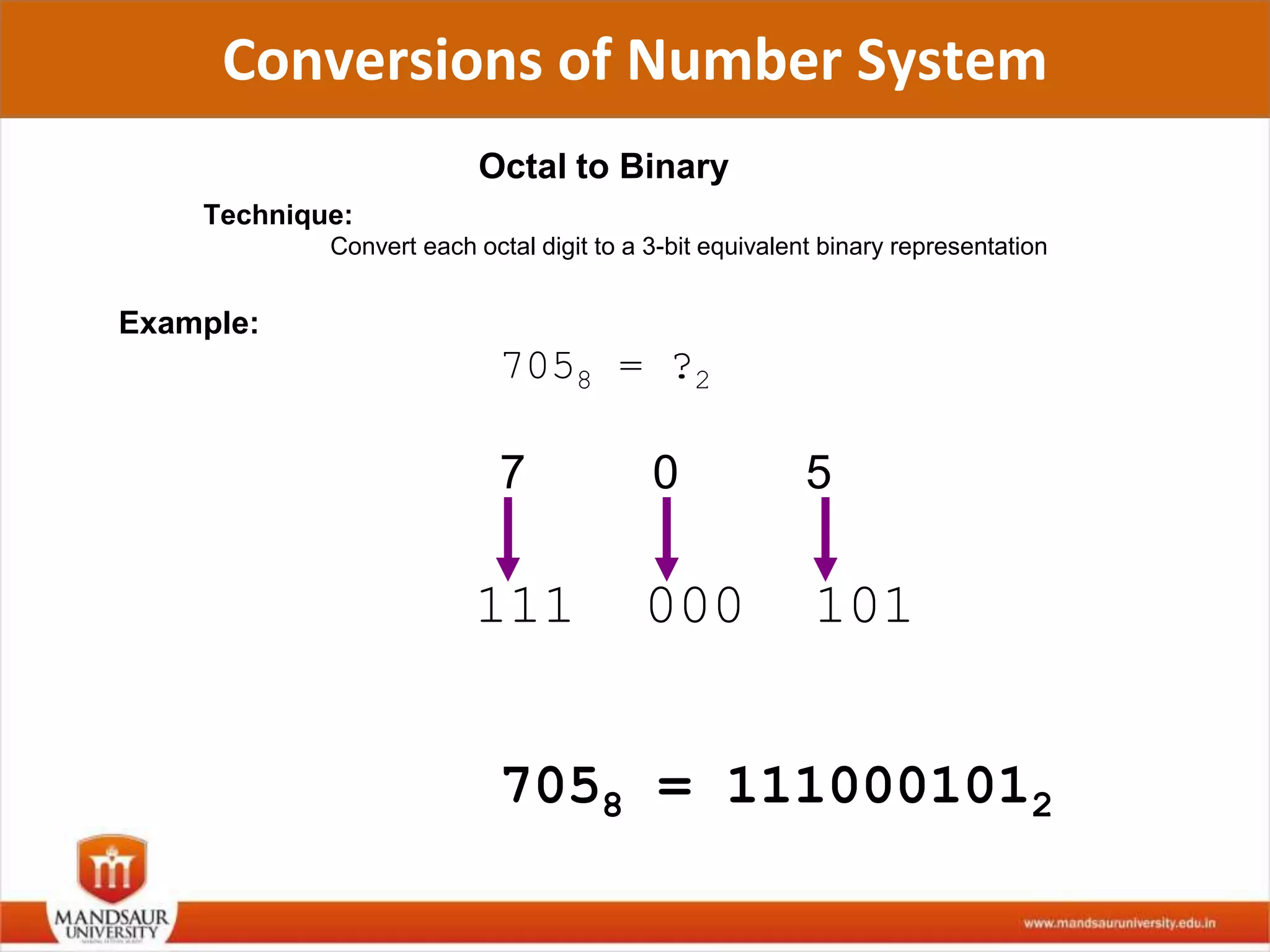
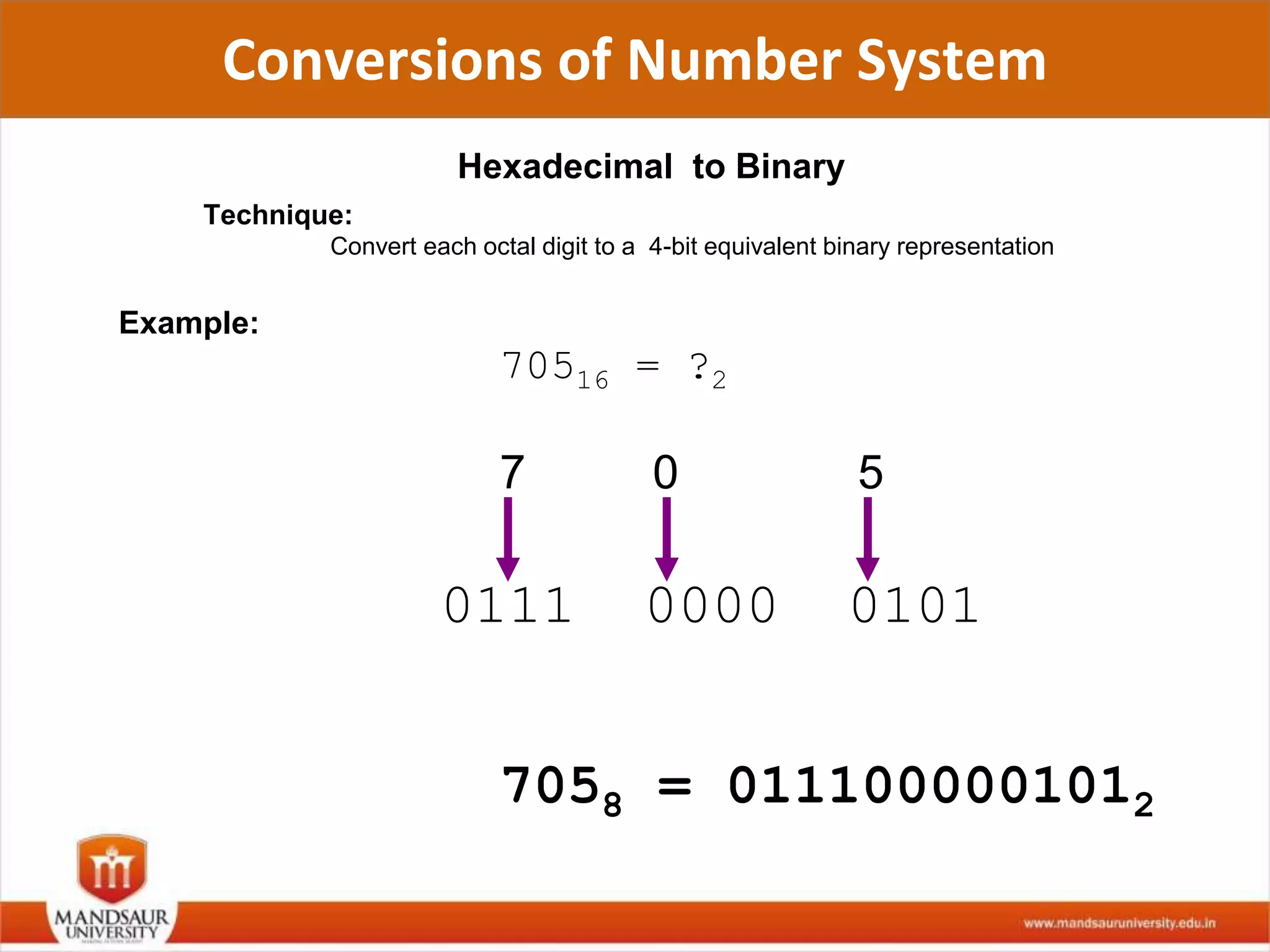
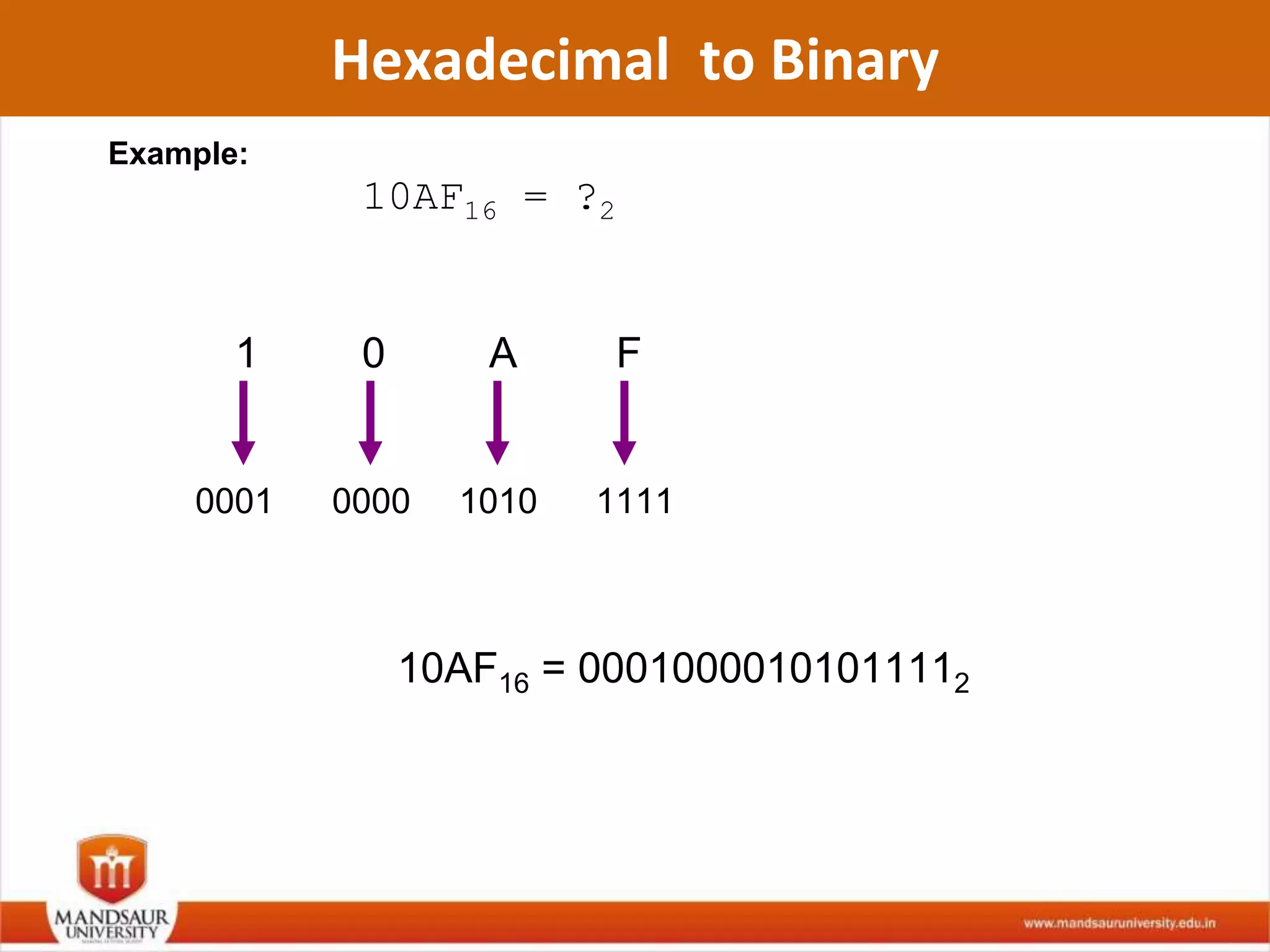
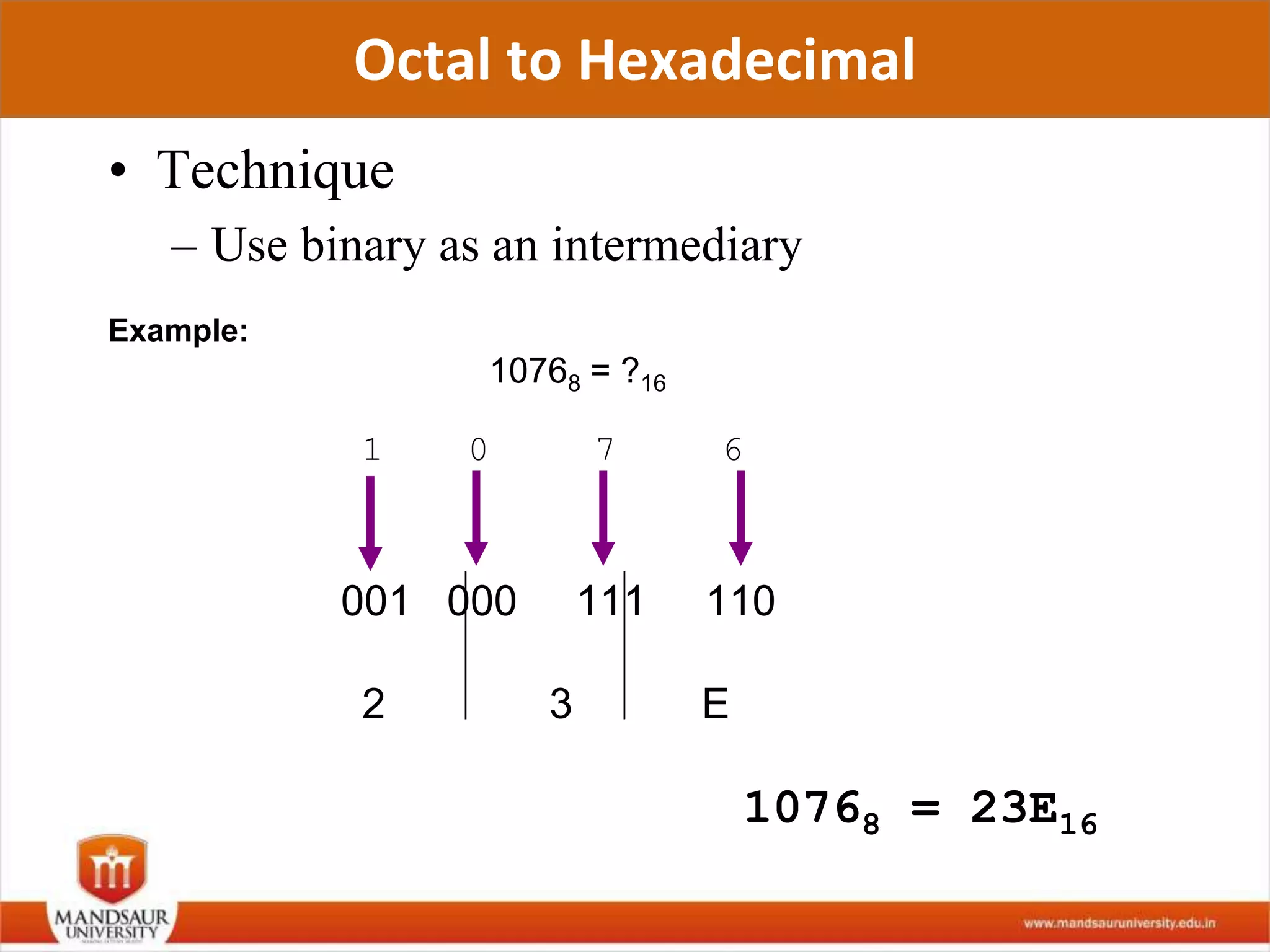
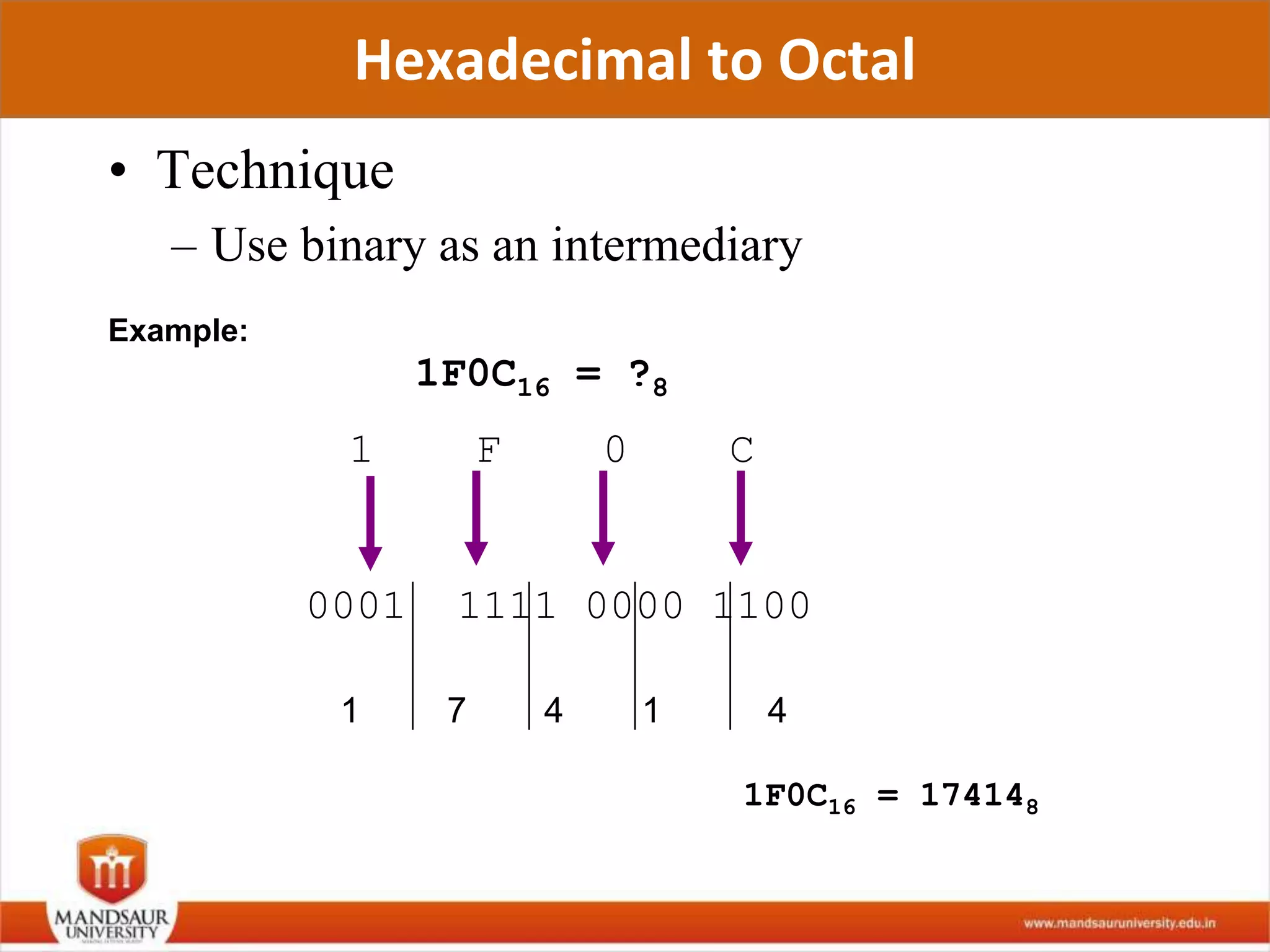
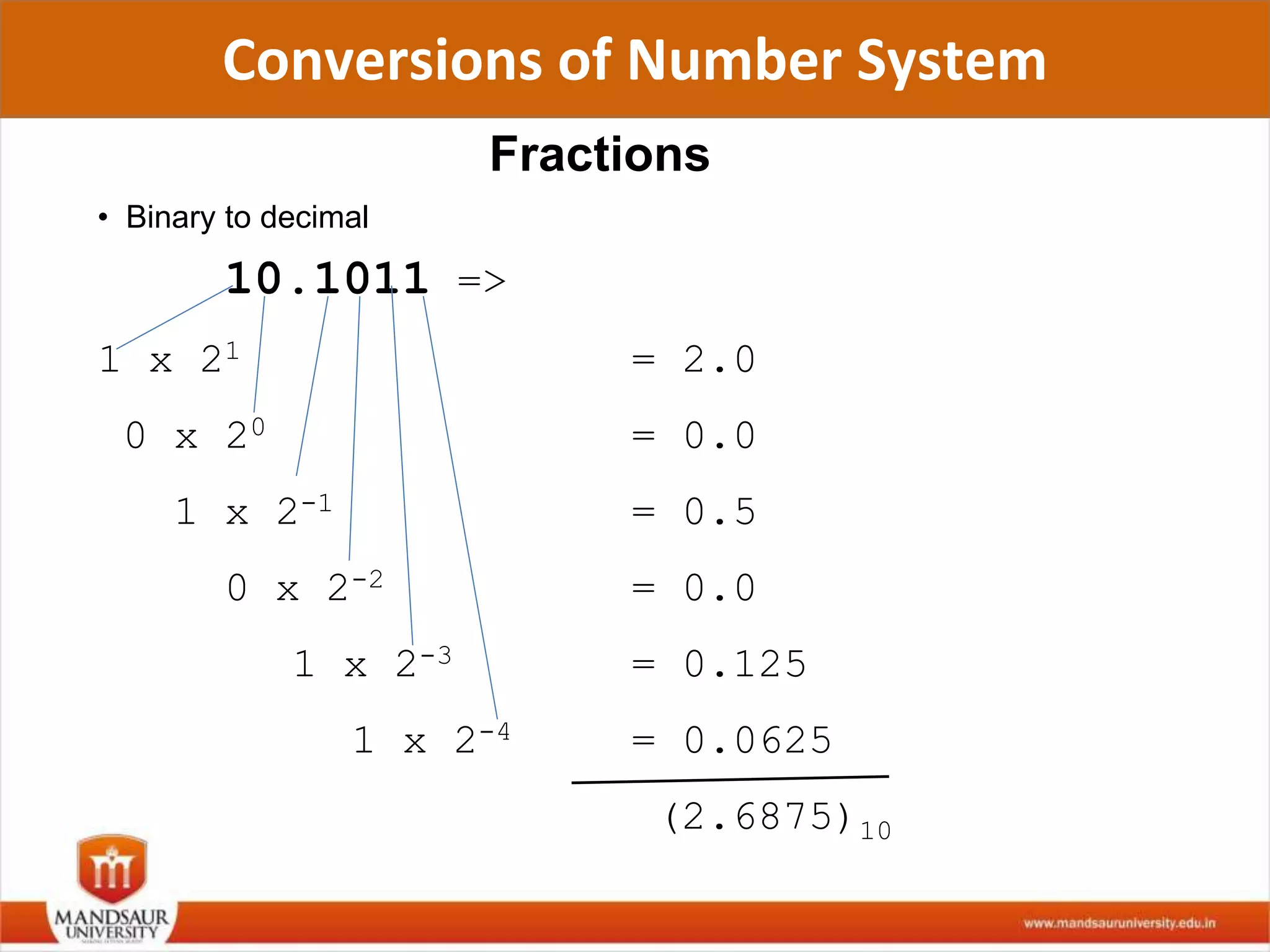
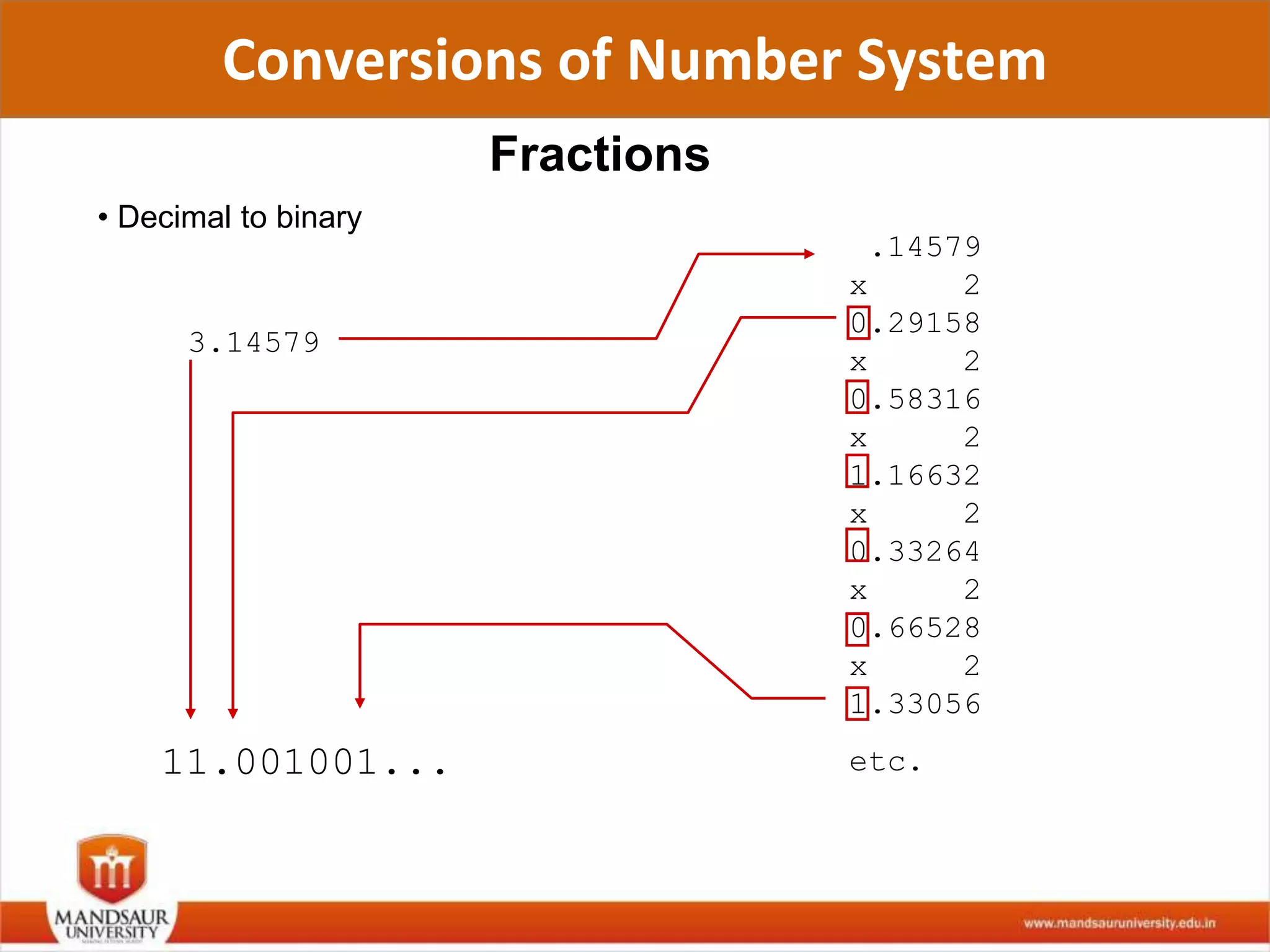
The document discusses different number systems used in computers such as binary, decimal, octal and hexadecimal. It provides examples and techniques for converting between these number systems. The key number systems covered are binary, which uses two digits (0 and 1), and is used in computers, decimal which uses 10 digits and is used in everyday life, octal which uses 8 digits, and hexadecimal which uses 16 digits and letters A-F. The document also discusses techniques for converting fractions between decimal and binary.