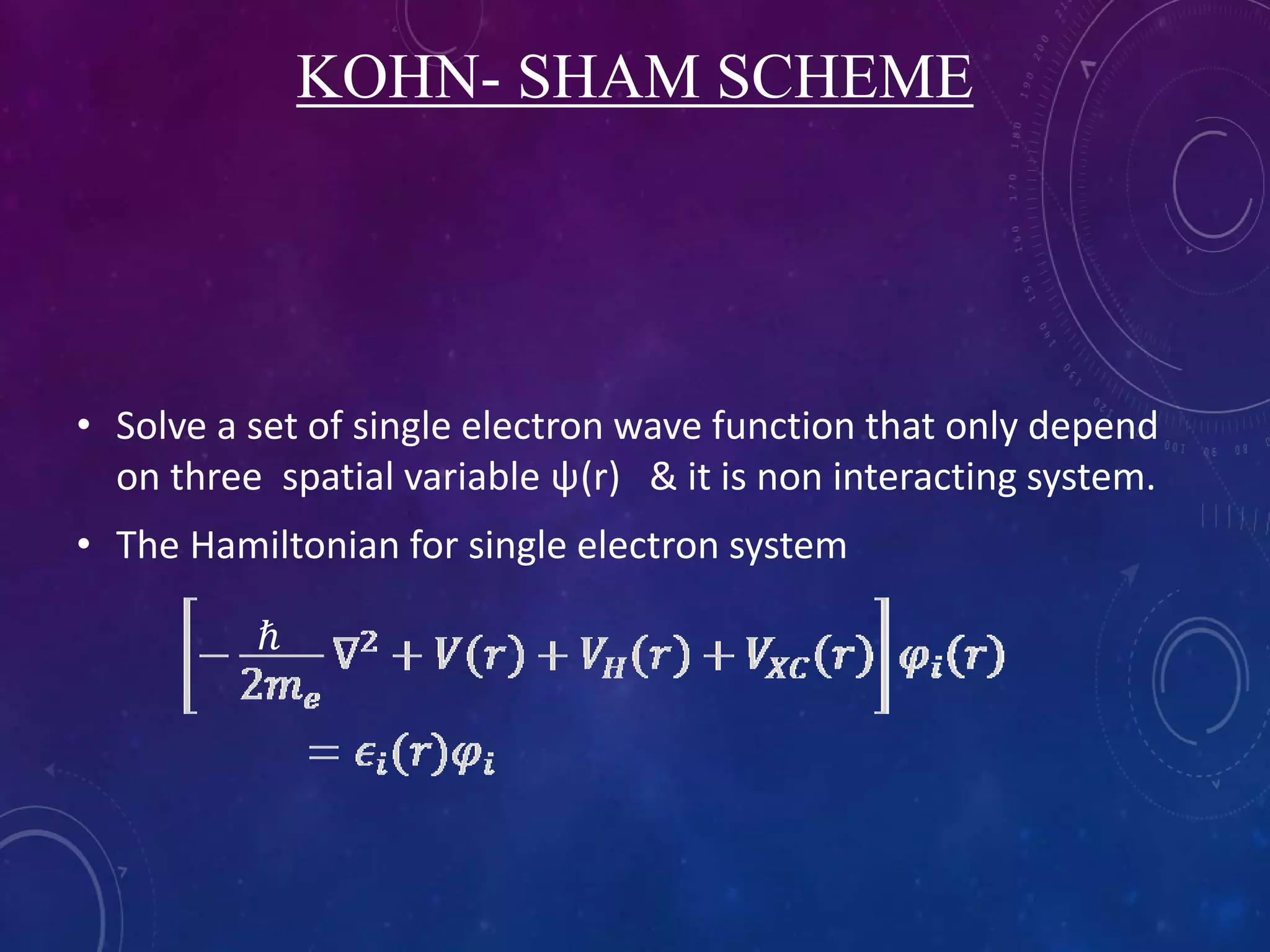
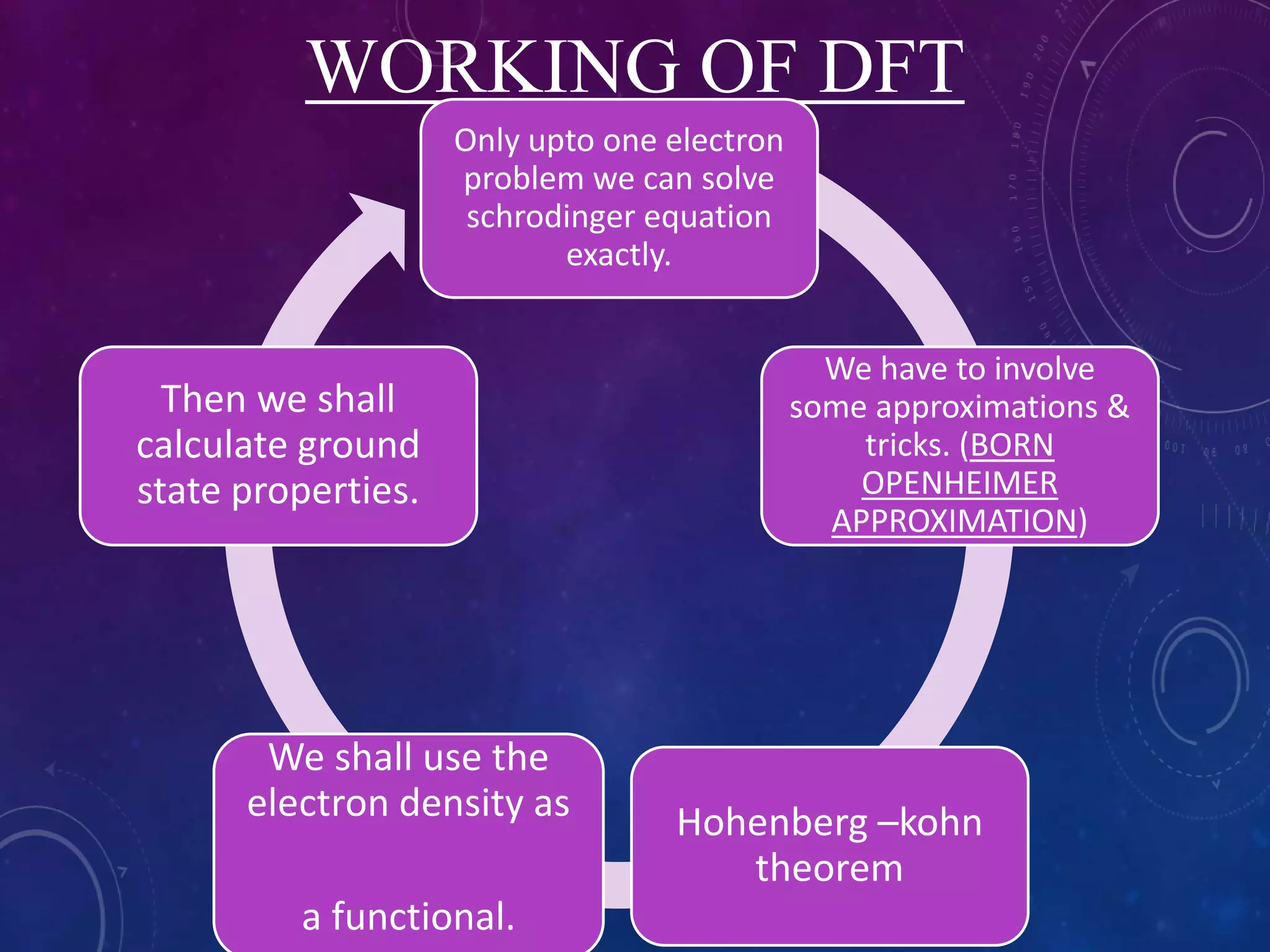
This document provides an overview of density functional theory (DFT). It discusses the history and development of DFT, including the Hohenberg-Kohn and Kohn-Sham theorems. The document outlines the fundamentals of DFT, including how it uses functionals of electron density rather than wavefunctions to simplify solving the many-body Schrodinger equation. It also describes the self-consistent approach in DFT calculations and provides examples of popular DFT software packages.





![DENSITY FUNCTIONAL THEORY
• DFT is a computational quantum mechanical modelling
method used in physics ,chemistry, & material science to
investigate the electronic structure ( ground state) of many
body systems .
• Using this theory the properties of many- electron system
can be determined by using FUNCTIONALS.
• in DFT instead of considering wave function we
considered density functional .
DFT : work in terms of density
E=E[n(r)]
𝜑2=n(r)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dftsandhya-180314035244/75/Density-functional-theory-6-2048.jpg)



![HOHENBERG – KOHN THEOREMS
Based on two fundamental theorems :
Theorem 1 : The external potential or the ground state energy
E is a unique functional of electron density .
functional is a function of a function.
Theorem 2 : The electron density that minimizes the energy
of the overall functional is the true ground state electron density
.
E=E[n(r)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dftsandhya-180314035244/75/Density-functional-theory-11-2048.jpg)