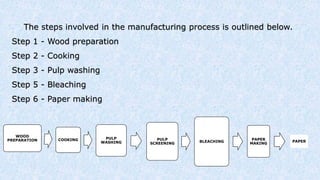
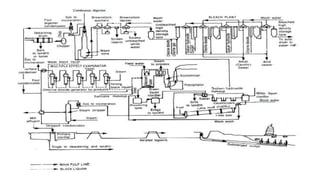
The document covers the historical development and processes involved in paper production, specifically focusing on the kraft process, which is the most efficient method used today. It details the steps from wood preparation to paper making, including pulping, bleaching, and chemical recovery, highlighting the importance of cellulose and lignin in producing quality paper. Additionally, it discusses the advantages and disadvantages of the kraft process, alongside the environmental considerations associated with chemical recovery.