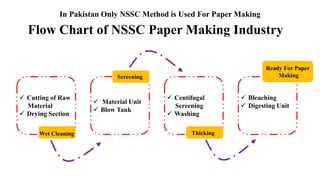
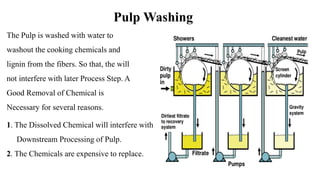
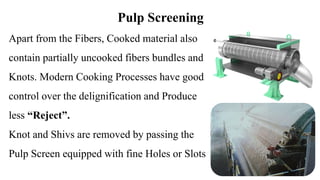
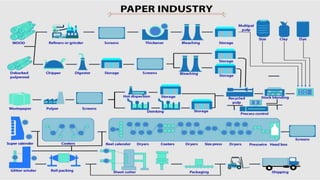
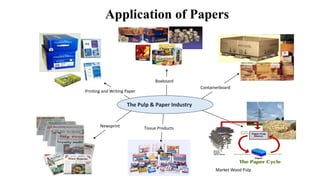
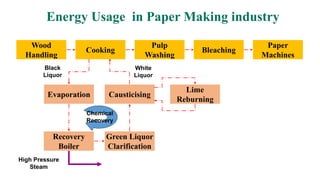
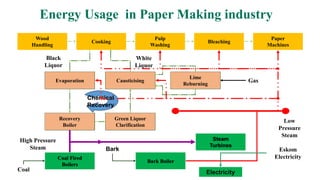
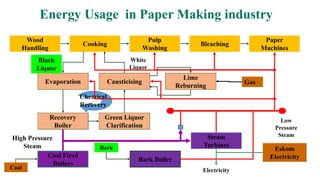
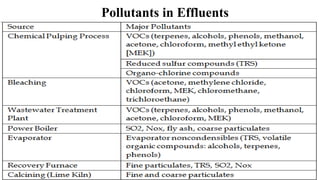
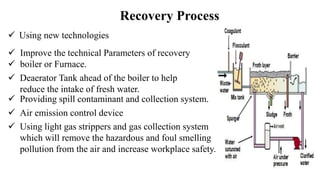
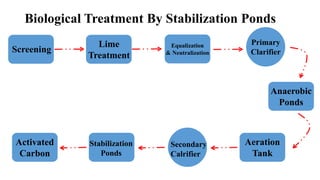
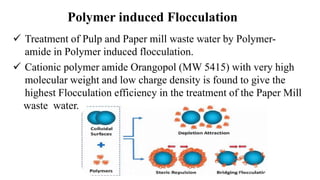
The document details the history and processes involved in paper making from its origins in China to modern practices. It highlights various manufacturing methods, raw materials, environmental impacts, and advancements in waste management and recycling efforts. The discussion also emphasizes the industry's initiatives to reduce its carbon footprint and promote sustainability.