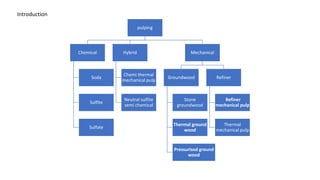
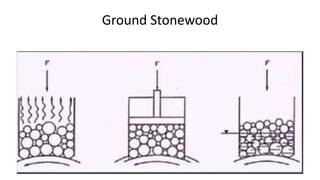
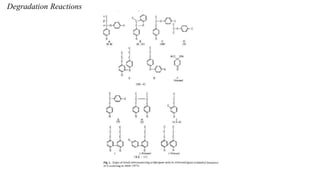
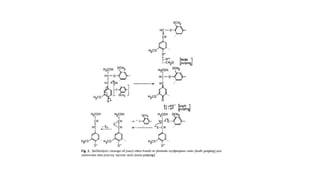
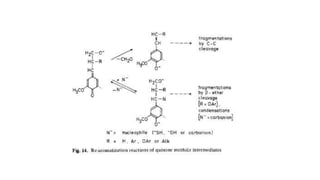
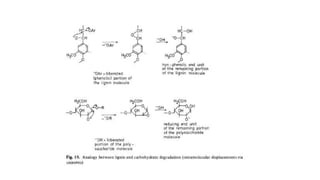
Kraft pulping is a chemical pulping process that uses sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide. There are two main types of reactions during kraft pulping - degradation reactions that break down lignin into smaller fragments that dissolve, and condensation reactions that join lignin fragments together and can cause precipitation. Degradation predominates early in kraft pulping while condensation reactions increase later. Carbohydrates like hemicellulose are also broken down during kraft pulping through reactions that change their structure.