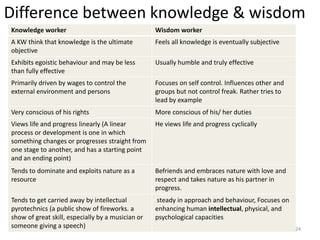
The document discusses the meaning of knowledge and wisdom. It defines knowledge as facts, information, and skills acquired through experience or education, while wisdom involves analyzing and applying knowledge to understand why things are a certain way. The document also discusses the differences between knowledge workers and wisdom workers, with knowledge workers focusing more on applying theoretical knowledge and wisdom workers focusing more on understanding why. Finally, the document discusses knowledge management and wisdom management, with knowledge management focusing on capturing and sharing explicit knowledge and wisdom management aiming to develop implicit understanding.