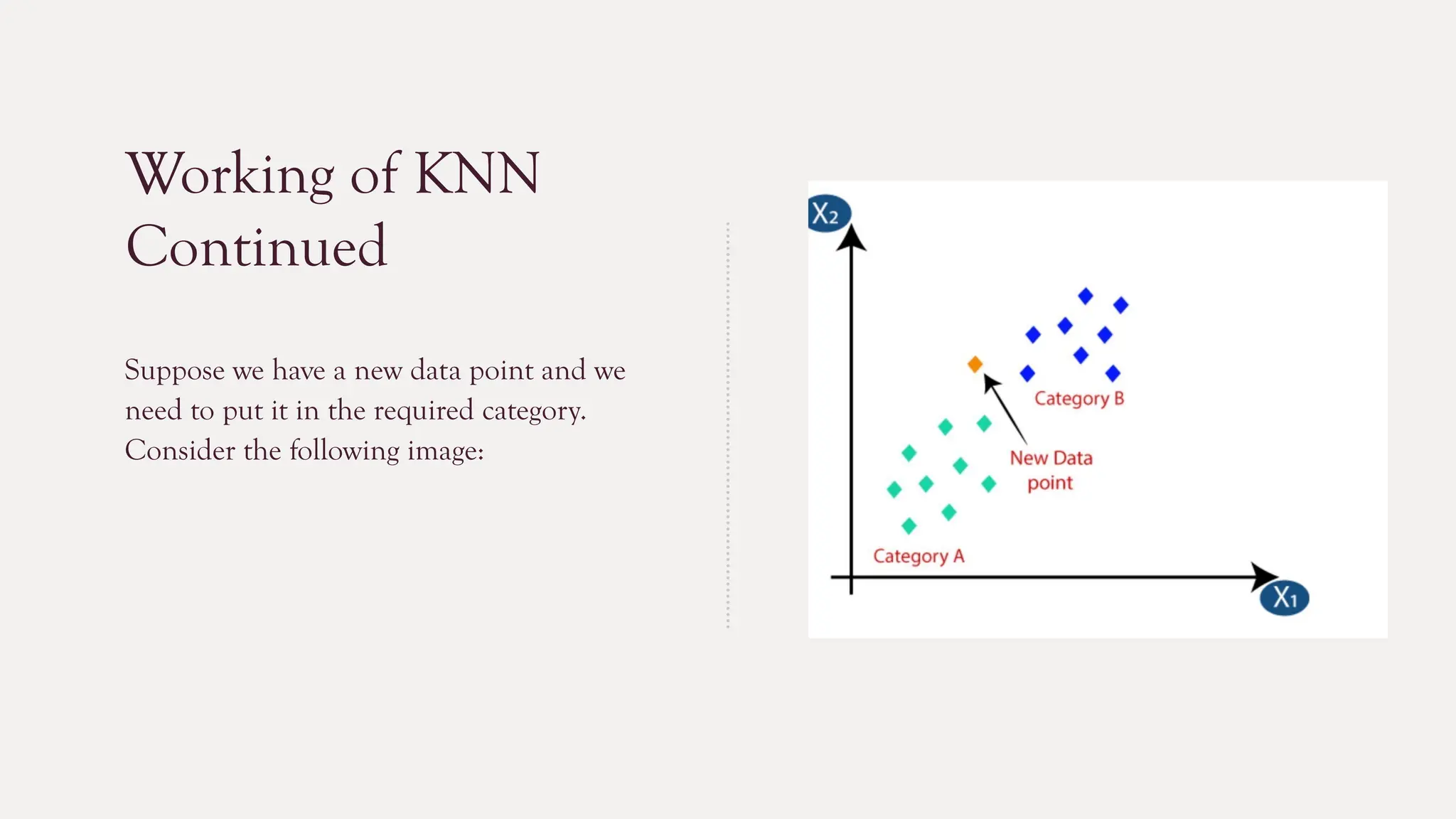
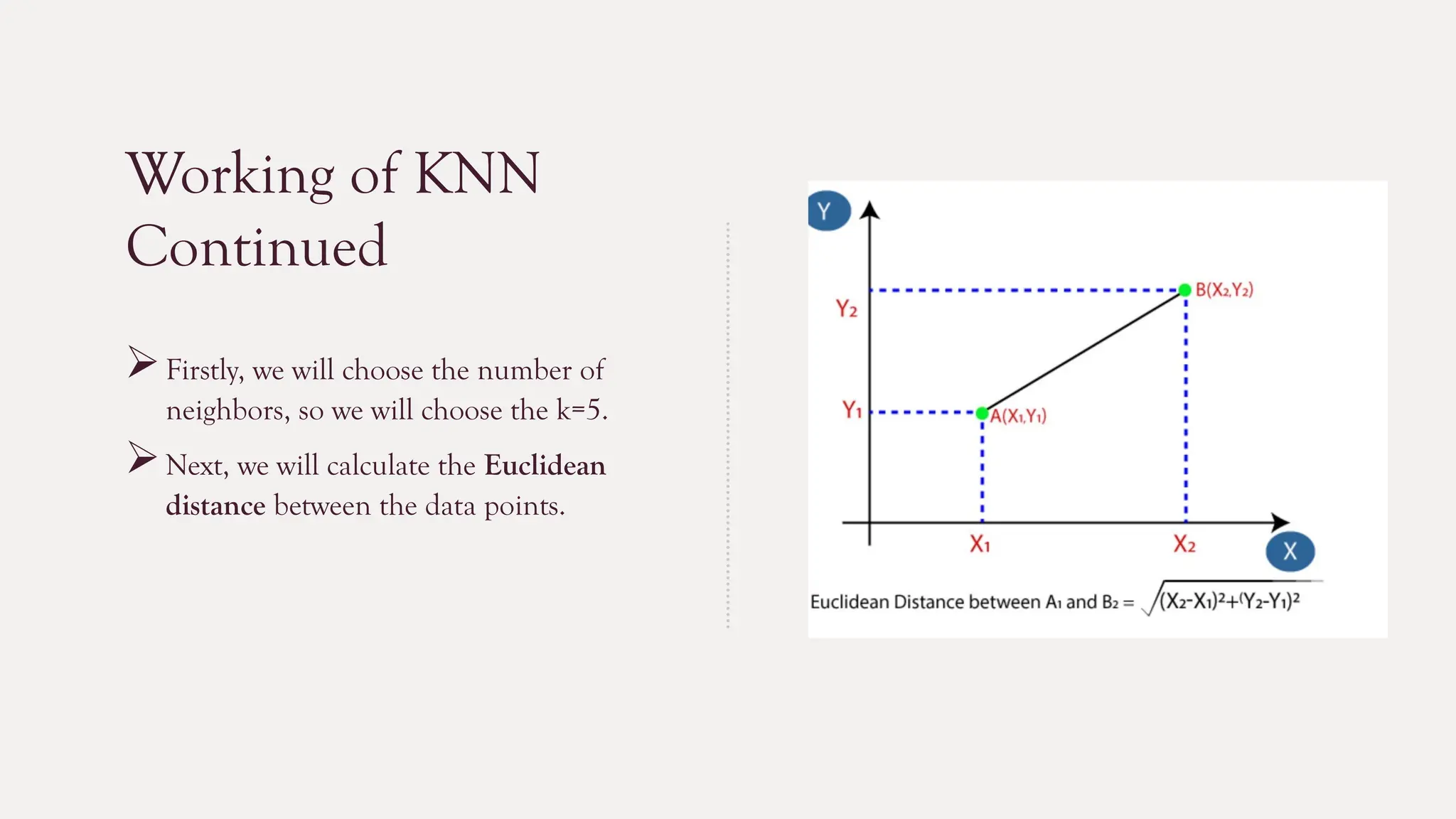
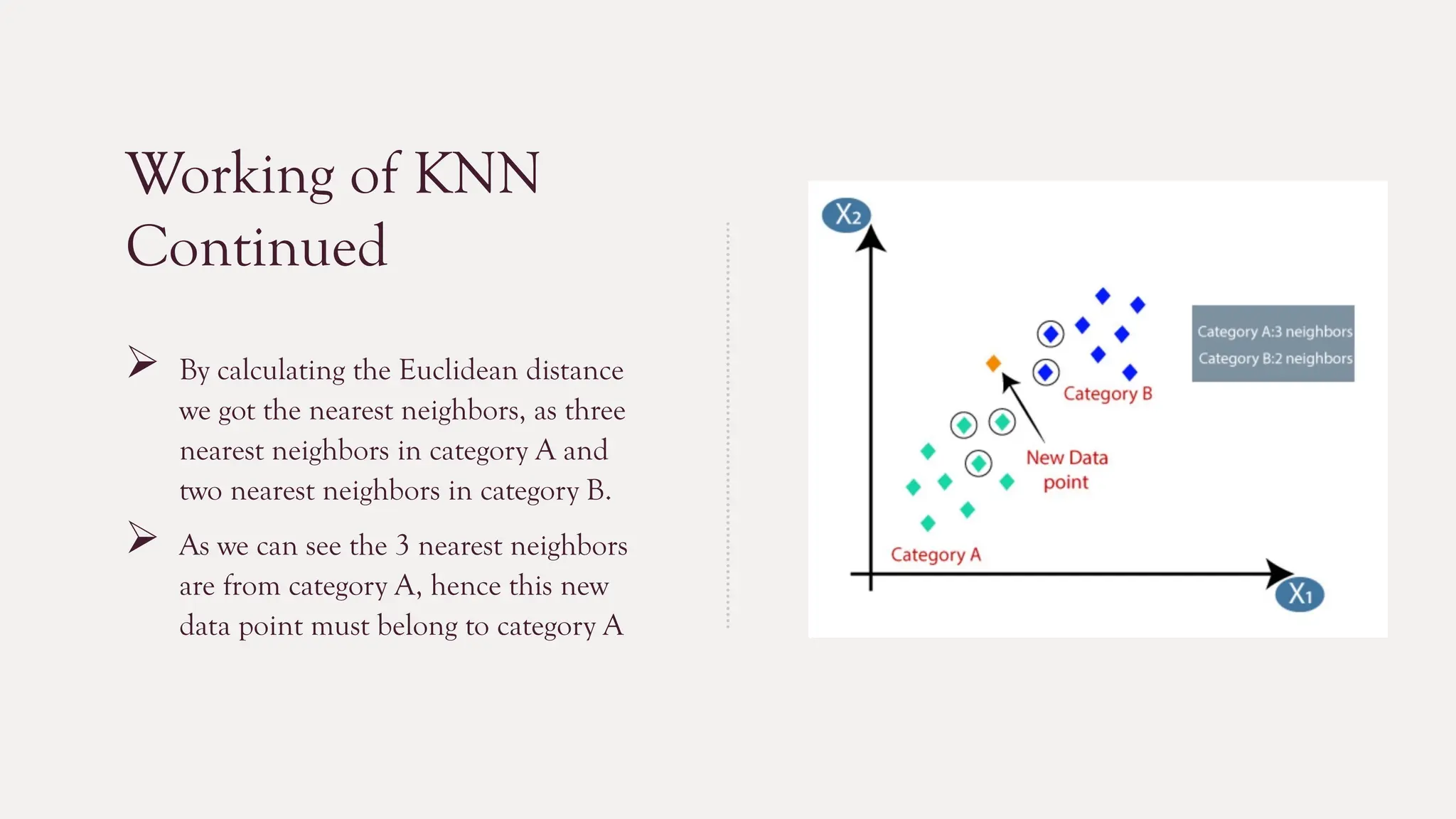
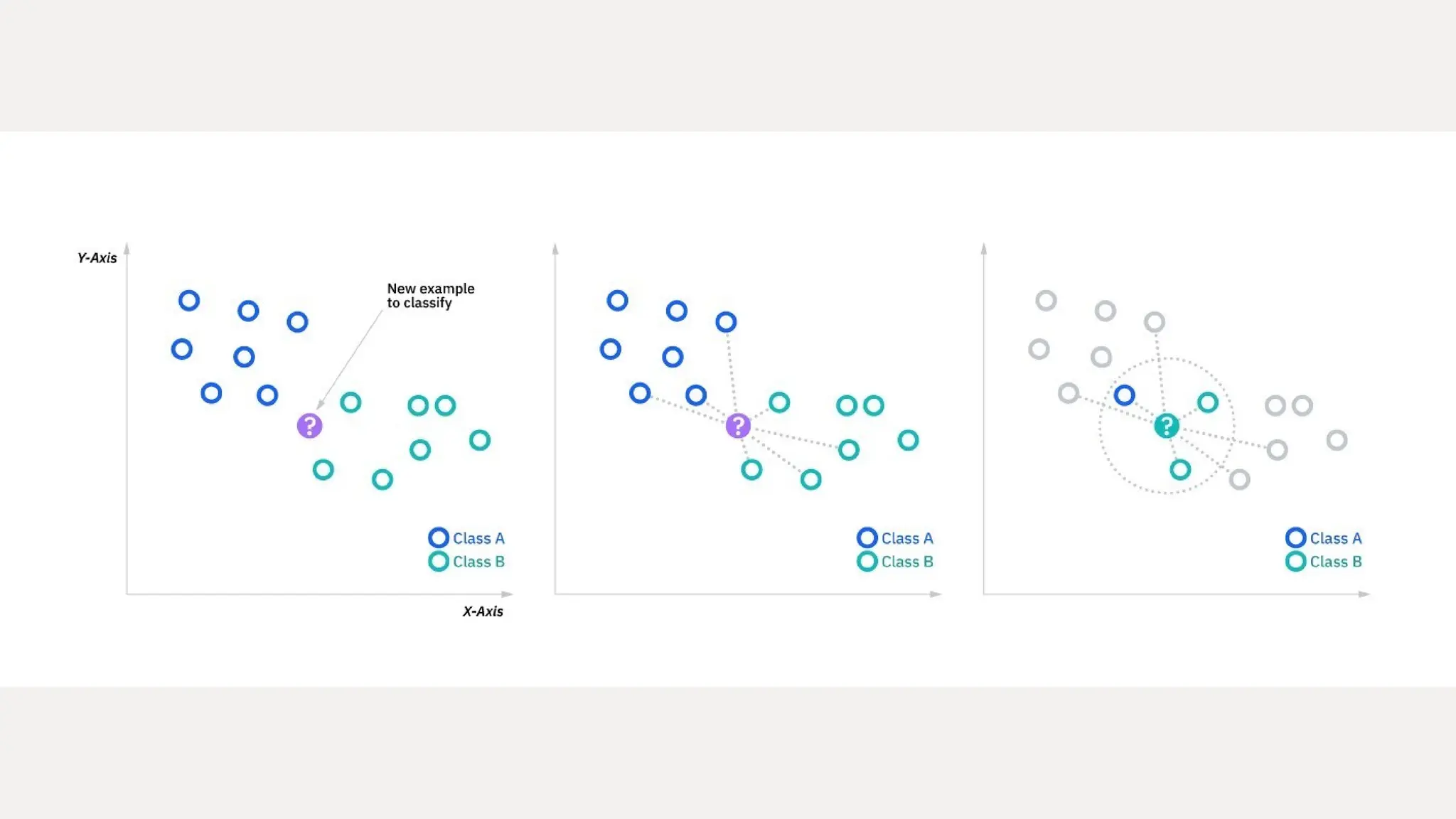
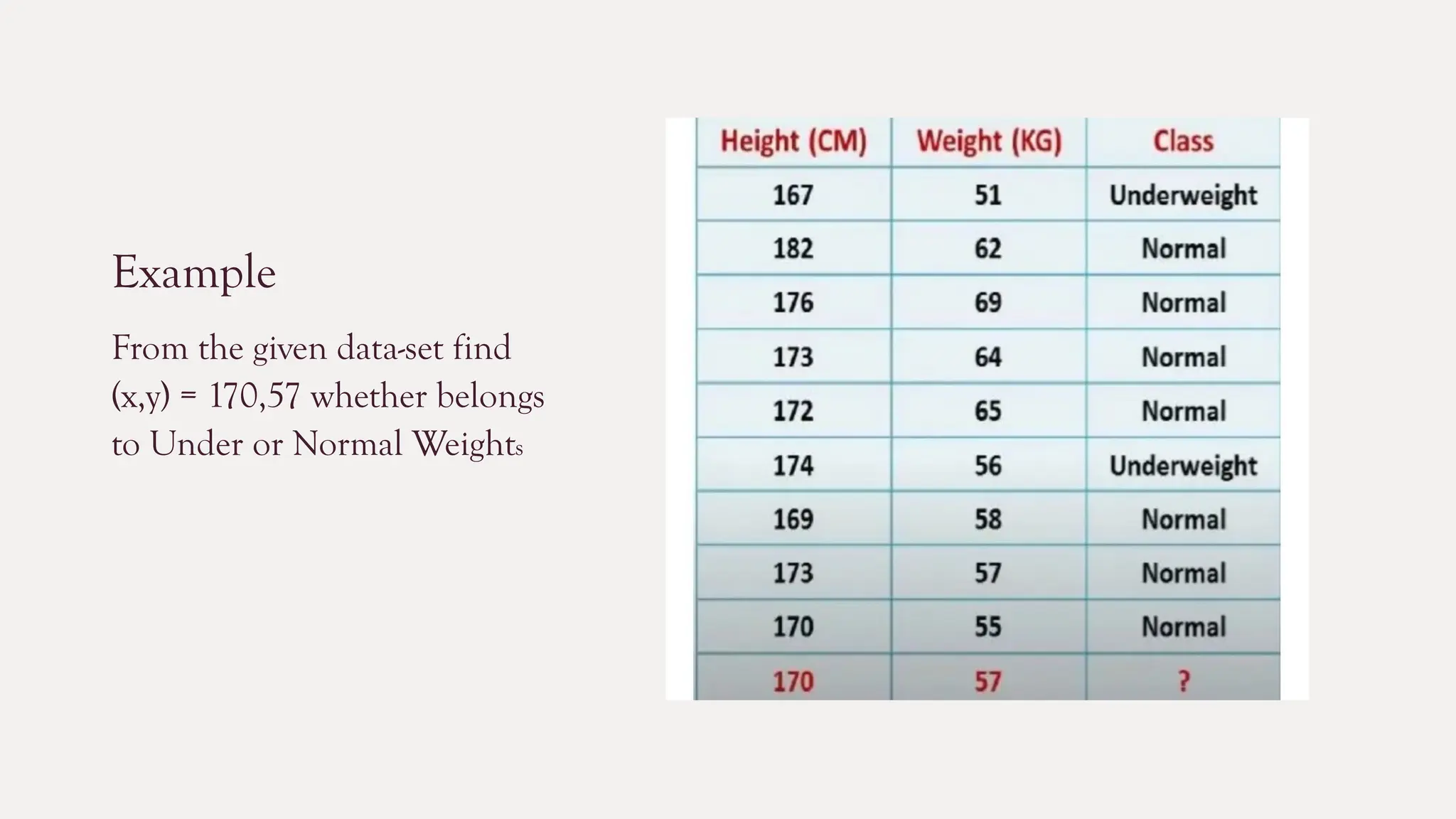
The k-nearest neighbors (k-NN) algorithm is a straightforward machine learning method primarily used for classification tasks, relying on similarity measures to classify data points based on their nearest neighbors. It is a lazy and non-parametric learning algorithm that does not require a training phase but instead uses all training instances during testing, making it efficient for certain tasks but computationally expensive with large datasets. While k-NN has advantages like simplicity and versatility, it also has drawbacks such as high memory requirements and sensitivity to high dimensionality.